Introduction: Mapping the Cybersecurity Landscape of Remote Work: Navigating Threats, Responsibilities, and Key Security Concepts
Identifying the Unique Threats and Vulnerabilities of Remote Work
The shift to remote work has reshaped the cybersecurity landscape, introducing a myriad of new threats and vulnerabilities that organizations must navigate. This section delves into the specific challenges posed by remote work environments, including the increased risk of phishing attacks, unsecured home networks, and potential data breaches.
The content emphasizes the need for organizations to conduct thorough risk assessments tailored to the remote work context. It explores the intricacies of securing diverse endpoints, ranging from personal devices to corporate laptops, and discusses the importance of user awareness and training in mitigating these unique threats.
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
In the era of cloud computing and remote collaboration, understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial for organizations leveraging platforms like Microsoft 365. This subsection elucidates the collaborative framework between Microsoft and organizations, shedding light on the respective roles and responsibilities in ensuring a secure digital environment.
The content emphasizes the distinction between Microsoft’s responsibility for the security of the cloud infrastructure and the organization’s responsibility for securing their data and user access. By comprehending this shared responsibility model, organizations can strategically align their cybersecurity efforts with Microsoft’s infrastructure safeguards.
Demystifying Key Security Concepts 
This part demystifies fundamental cybersecurity concepts critical for safeguarding remote work environments. It takes a deep dive into key security measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and the zero-trust security model.
The content elucidates how MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple factors. It explores the zero-trust model, emphasizing the shift from traditional perimeter-based security to a model that scrutinizes every user and device, regardless of their location.
By demystifying these concepts, organizations gain a clearer understanding of the tools and strategies at their disposal to enhance the cybersecurity posture of their remote work environments. This section serves as a foundational guide for organizations navigating the complex and evolving cybersecurity landscape associated with remote work.
Building a Secure Foundation for Remote Work: Strengthening Passwords, Embracing MFA, and Endpoint Protection
Implementing Strong Password Policies
A robust cybersecurity strategy begins with the foundation of strong password policies. This section delves into the importance of creating and implementing stringent password policies across the organization. It outlines the criteria for strong passwords, emphasizing the use of a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
The content guides organizations in establishing policies that discourage the reuse of passwords across multiple accounts and promote the use of unique, complex passwords. By instilling these practices, organizations can fortify their defenses against common cyber threats like password spraying and brute-force attacks.
Enforcing Regular Password Changes
Continuing the exploration of password security, this subsection advocates for the regular rotation of passwords. It provides insights into the frequency and methods for enforcing password changes, striking a balance between security and user convenience.
The content addresses the common misconception around frequent password changes and explains how this practice adds an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. Practical tips for communicating and implementing these changes effectively within a remote work setting are also discussed.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
The focus shifts to multi-factor authentication (MFA), a pivotal element in securing remote work environments. This part elucidates the significance of MFA in adding an extra layer of identity verification beyond passwords. It explores various MFA methods, including SMS codes, authenticator apps, and biometric authentication.
Organizations are guided on the seamless implementation of MFA across all accounts and devices, emphasizing its effectiveness in thwarting unauthorized access even in the event of compromised passwords. The content stresses the user-friendly aspects of modern MFA solutions to encourage widespread adoption.
Deploying Endpoint Protection Software
This section underscores the importance of safeguarding all devices, including personal ones, through the deployment of endpoint protection software. It explores the role of these solutions in detecting and mitigating a broad spectrum of cyber threats, from malware to phishing attempts.
By embracing endpoint protection, organizations extend their security measures beyond traditional corporate devices, acknowledging the prevalence of remote work. Practical tips for selecting, deploying, and managing endpoint protection software in diverse environments are discussed, ensuring a holistic approach to cybersecurity in the remote work landscape.
Access Control and Identity Management in Remote Work: Least-Privilege Access, Azure AD, and Conditional Policies
Granting Least-Privilege Access
This section delves into the crucial concept of least-privilege access, emphasizing the significance of providing users with the minimum permissions necessary for their roles. It explains the rationale behind adopting a least-privilege approach and its role in limiting the potential impact of security breaches.
The content guides organizations in devising and implementing least-privilege access policies tailored to remote work scenarios. It explores the challenges associated with striking a balance between productivity and security, providing actionable insights on achieving an optimal equilibrium.
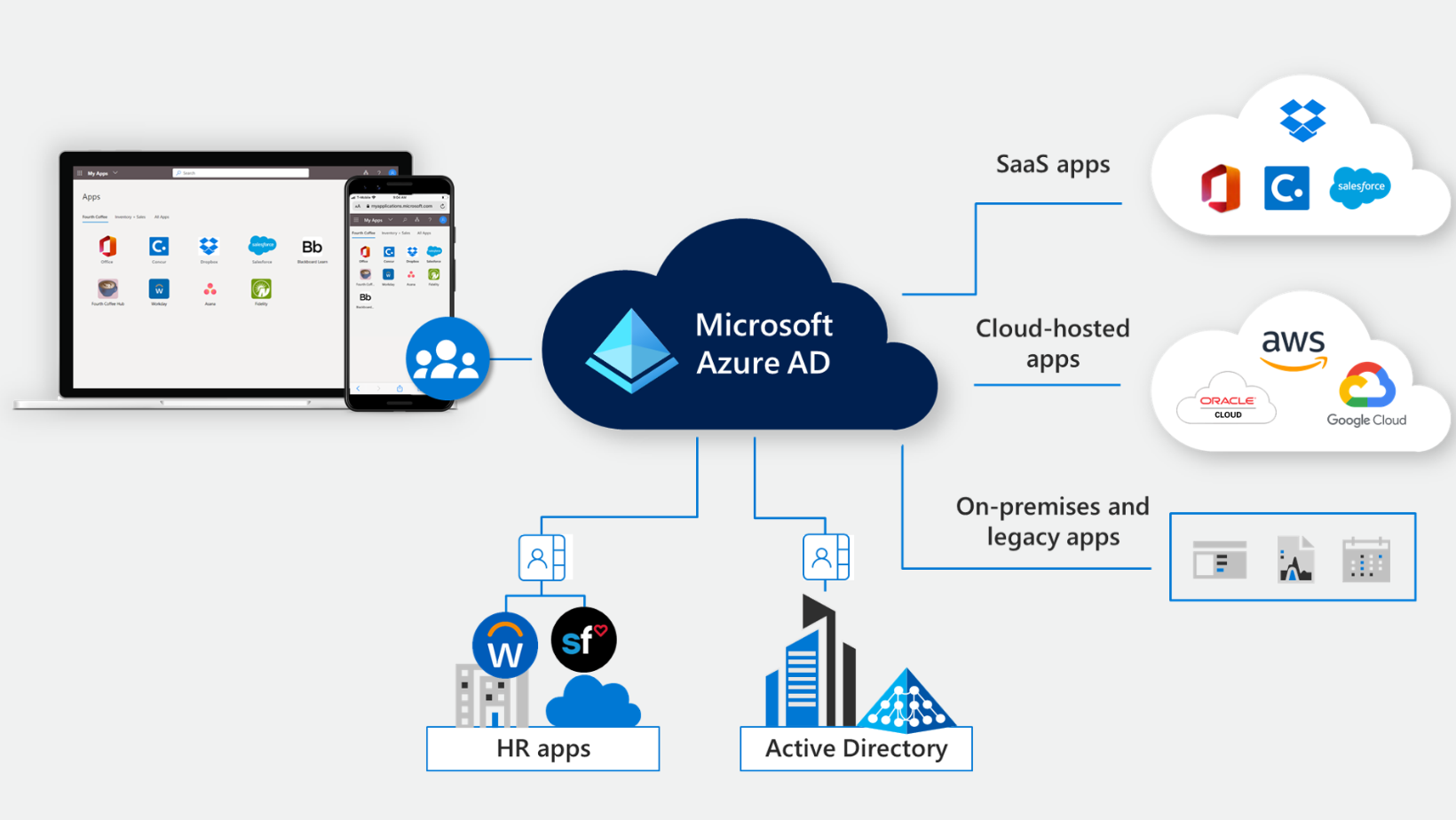
Leveraging Azure Active Directory (AD) for Centralized Identity Management 
The focus shifts to the pivotal role of Azure Active Directory (AD) in centralized identity management. This subsection highlights the capabilities of Azure AD in managing and securing user identities across diverse environments. It explores features such as single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user provisioning.
Organizations are provided with insights into the seamless integration of Azure AD with various applications and services commonly used in remote work setups. Practical tips on configuring Azure AD to enhance identity management, streamline access, and bolster security are discussed.
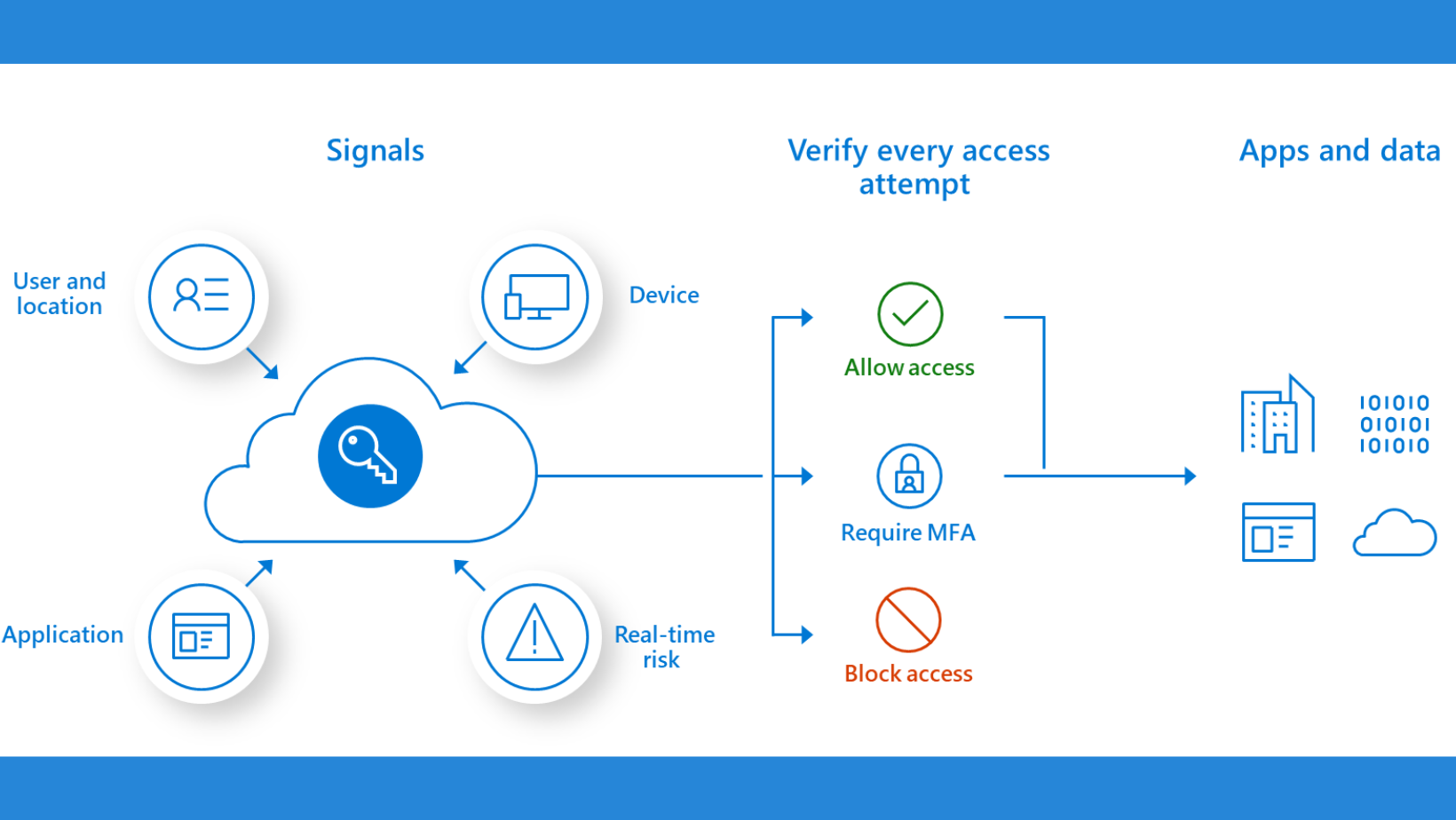
Implementing Conditional Access Policies
This part delves into the implementation of conditional access policies as a powerful tool for fine-tuning access controls based on specific conditions. It explores the flexibility and granularity offered by conditional access policies in enforcing access rules tailored to the organization’s security requirements.
The content provides practical scenarios where conditional access policies can be applied, such as restricting access from certain geographical locations or requiring additional authentication steps for sensitive operations. It also addresses potential challenges and considerations in crafting and enforcing effective conditional access policies in the context of remote work.
Data Protection and Encryption in Remote Work: Safeguarding Sensitive Information
Classifying and Labeling Sensitive Data
This section emphasizes the critical importance of classifying and labeling sensitive data to establish a robust foundation for data protection. It explores the challenges organizations face in identifying and categorizing sensitive information when employees work remotely.
The content provides practical guidance on implementing data classification and labeling policies, leveraging Microsoft 365 tools to automatically classify and label data based on sensitivity levels. It discusses the role of user awareness and training in ensuring consistent and accurate data classification across remote work environments.
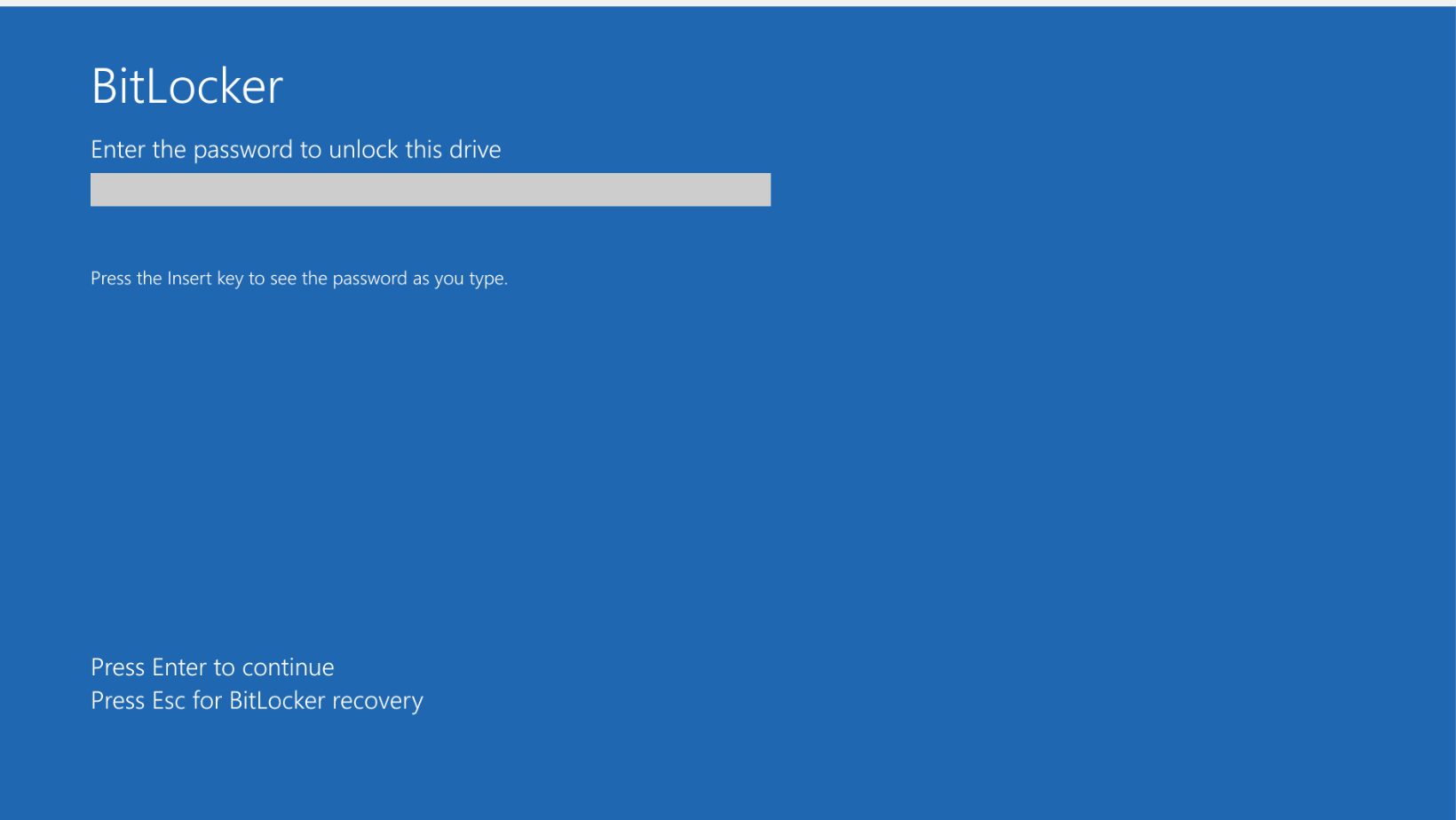
Enabling Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit 
The focus shifts to the pivotal role of encryption in securing data both at rest and in transit. This subsection delves into the significance of encrypting data to prevent unauthorized access, especially when transmitted over networks or stored on various devices.
Practical insights are offered on implementing encryption measures within Microsoft 365, covering features such as BitLocker for device encryption and Transport Layer Security (TLS) for securing data during transmission. The content also addresses the potential challenges and considerations in ensuring seamless encryption across diverse remote work scenarios.
Utilizing Cloud-Based Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools
This part explores the use of cloud-based Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools as a proactive approach to prevent unauthorized data leaks. It highlights the capabilities of Microsoft 365’s DLP features in identifying, monitoring, and protecting sensitive data across different applications and services.
Practical scenarios are discussed, illustrating how organizations can configure DLP policies to align with remote work dynamics. The content also covers the integration of DLP tools with other security measures to create a comprehensive data protection strategy for remote work environments.
Collaborative Security and Communication: Fostering a Secure Remote Work Environment
Promoting a Culture of Security Awareness
This section underscores the critical role of cultivating a culture of security awareness among remote employees. It delves into the challenges of maintaining a security-conscious mindset in a distributed work environment and provides insights into the significance of continuous training and education.
Practical strategies for promoting security awareness are discussed, including regular cybersecurity training sessions, simulated phishing exercises, and the use of engaging communication channels to disseminate security best practices. The content emphasizes the shared responsibility of employees in upholding security standards while working remotely.
Leveraging Microsoft Teams Security Features
This subsection focuses on harnessing the security features of Microsoft Teams to facilitate secure file sharing and collaboration. It explores the built-in security capabilities of Teams, such as access controls, secure channels, and information barriers, which contribute to a secure collaborative environment.
The content provides step-by-step guidance on configuring security settings within Microsoft Teams and highlights best practices for secure collaboration. It also addresses common security concerns related to file sharing in a remote work setting and offers practical solutions to mitigate risks.
Implementing Robust Email Security Protocols
The discussion shifts to the critical aspect of securing email communication in a remote work scenario. This part explores the challenges associated with phishing and malware attacks targeting remote employees and emphasizes the need for robust email security protocols.
Practical guidance is provided on implementing email security measures within Microsoft 365, including the use of advanced threat protection, email encryption, and multifactor authentication for enhanced email security. The content also discusses the importance of employee training in recognizing and mitigating email-based security threats.
The comprehensive approach outlined in this section aims to create a collaborative and communicative remote work environment that prioritizes security, ensuring that employees can effectively work together without compromising data integrity or falling victim to cyber threats.
Monitoring and Incident Response: Safeguarding Your Remote Work Environment
Continuous Monitoring for Suspicious Activity (Approx. 350 words)
This section emphasizes the significance of ongoing monitoring to identify and address potential security threats in a remote work environment. It delves into the challenges associated with monitoring dispersed endpoints and provides practical strategies for implementing continuous monitoring within the Microsoft 365 environment.
Key elements discussed include leveraging security information and event management (SIEM) tools, employing user behavior analytics, and setting up alerts for unusual activities. The content also highlights the role of automation in enhancing the efficiency of monitoring processes.
Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
Building on the concept of proactive monitoring, this subsection explores the critical importance of having a robust incident response plan tailored to the remote work landscape. It outlines the key components of an effective incident response plan, including clear communication channels, designated response teams, and predefined steps for containment and remediation.
Practical insights are provided on creating and testing an incident response plan specific to Microsoft 365, ensuring that organizations are well-prepared to address security incidents promptly. The content emphasizes the need for alignment with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
The section concludes by highlighting the role of regular security audits and penetration testing in maintaining a resilient remote work environment. It explores the challenges of addressing vulnerabilities in a distributed setting and provides guidance on conducting thorough security audits and penetration tests within Microsoft 365.
The content discusses the benefits of engaging in ethical hacking practices to identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. It also underscores the continuous nature of security improvement, emphasizing that regular audits and testing are crucial elements of a proactive cybersecurity strategy.
By comprehensively addressing the monitoring and incident response aspects of remote work security, this section aims to equip organizations with the knowledge and tools needed to detect and mitigate security incidents effectively, ensuring the ongoing integrity of their Microsoft 365 environment.
Building a Secure Remote Work Culture: Fostering Trust and Accountability
Establishing Clear Policies and Procedures
This subsection emphasizes the importance of laying a solid foundation for a secure remote work culture through well-defined policies and procedures. It explores the key elements that should be included in remote work security policies, such as guidelines for device usage, secure communication practices, and adherence to compliance standards.
The content provides practical insights into crafting policies that balance security requirements with the flexibility needed for remote work. It also discusses the role of user awareness training in ensuring that employees understand and comply with established policies.
Promoting Open Communication
Highlighting the role of communication in building a secure remote work environment, this section explores strategies for promoting open dialogue about security concerns among employees. It delves into the challenges of remote communication and provides tips for creating channels where employees feel comfortable reporting potential security issues.
The content emphasizes the need for organizations to foster a culture that encourages employees to voice their concerns without fear of retribution. It also discusses the role of leadership in setting the tone for open communication regarding security matters.
Creating a Culture of Trust and Accountability
The final part of this section focuses on cultivating a culture of trust and accountability within the organization. It explores how building trust among remote teams is essential for maintaining a secure work environment. The content discusses strategies for instilling a sense of responsibility among employees for safeguarding sensitive information.
Practical examples and case studies are provided to illustrate successful initiatives taken by organizations to create a culture where employees prioritize data security. The content also explores the link between trust, accountability, and overall job satisfaction, emphasizing the positive impact of a secure work culture on employee well-being.
By comprehensively addressing the non-technical aspects of remote work security, this section aims to guide organizations in creating a holistic approach that combines clear policies, open communication, and a culture of trust and accountability.
Leveraging Microsoft 365’s Security Arsenal: Mastering Advanced Features
Exploring Microsoft’s Advanced Security Features
This section delves into the rich array of advanced security features offered by Microsoft 365. It provides an in-depth exploration of tools such as Defender for Cloud and Azure Sentinel, highlighting their capabilities in threat detection, incident response, and overall security management.
The content discusses how these features go beyond the basics, offering advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to proactively identify and respond to security threats. Case studies and real-world examples illustrate how organizations can leverage these tools to enhance their security posture.
Utilizing Third-Party Security Solutions
While Microsoft 365 provides a robust security infrastructure, this subsection acknowledges the value of complementing it with third-party security solutions. It explores the benefits of integrating additional security tools and services to address specific organizational needs and industry requirements.
The content provides guidance on selecting and integrating third-party solutions seamlessly into the Microsoft 365 environment. It emphasizes the importance of a cohesive security ecosystem that combines both Microsoft’s offerings and external solutions for comprehensive protection.
Optimizing Microsoft 365 for Security and Efficiency
Building on the idea of a dual-purpose Microsoft 365 environment, this part of the section focuses on optimizing the use of Microsoft 365 not only for security but also for operational efficiency. It explores how organizations can strike a balance between security measures and ensuring a seamless and productive user experience.
Practical tips and best practices are provided to help organizations maximize the benefits of Microsoft 365’s security features without compromising user productivity. The content also emphasizes the role of ongoing monitoring and adjustment to optimize security measures based on evolving organizational needs.
By thoroughly exploring Microsoft’s advanced security features, discussing the integration of third-party solutions, and providing insights on optimization, this section aims to equip organizations with a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage Microsoft 365’s security arsenal for both robust security and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Nurturing a Secure Remote Work Environment
Reemphasizing Proactive Security Measures
This section begins by reiterating the critical importance of adopting proactive security measures to establish and maintain a secure remote work environment. It stresses the dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats and the need for organizations to stay ahead by being vigilant and proactive in their security strategies.
The content emphasizes that security is not a one-time endeavor but a continuous process that demands ongoing attention and adaptation. It encourages organizations to foster a security culture that values constant improvement and readiness against emerging threats.
Highlighting the Benefits of Robust Security
Building on the premise that robust security measures contribute significantly to organizational well-being, this part of the conclusion delves into the tangible benefits. It explores how a secure remote work environment safeguards sensitive data, enhances trust among stakeholders, and ultimately boosts employee productivity.
Real-world examples and case studies illustrate instances where organizations have experienced the positive outcomes of prioritizing cybersecurity. Whether it’s preventing data breaches, ensuring compliance, or fostering a secure collaboration platform, the content underscores the multifaceted advantages of a robust security posture.
Guidance on the Next Steps
The conclusion wraps up by providing practical guidance on the next steps organizations should take in their ongoing remote work security journey. It highlights the importance of staying informed about the latest security trends, adopting new technologies, and regularly reassessing and enhancing security protocols.
The content directs readers to relevant resources, including security forums, industry publications, and Microsoft’s official updates, to aid them in staying well-informed. It stresses the collaborative nature of cybersecurity, encouraging organizations to engage with the broader security community for shared insights and best practices.
In conclusion, this section aims to leave readers with a comprehensive understanding of the ongoing nature of cybersecurity efforts, the benefits of robust security, and practical guidance for their continued journey towards maintaining a secure remote work environment.
The primary security challenges involve securing endpoints, ensuring secure communication channels, and mitigating the risks associated with employees working from various locations. To address these challenges, organizations should implement strong endpoint protection, enforce secure communication protocols, and educate employees about safe remote work practices.
Striking a balance between robust security measures and a seamless user experience is crucial. This can be achieved by leveraging user-friendly security solutions, providing comprehensive training to employees on security best practices, and adopting technologies that seamlessly integrate with daily workflows without compromising security.
Employee training is a cornerstone of a secure remote work environment. It empowers employees to recognize and respond to potential security threats, promotes a culture of security awareness, and establishes a sense of responsibility among team members to actively contribute to the organization’s overall security posture.
Effective monitoring and incident response involve the use of advanced security tools, continuous monitoring of network activities, and a well-defined incident response plan. Organizations should conduct regular security audits, implement automated threat detection mechanisms, and ensure that employees are well-trained to report and respond to security incidents promptly.
Microsoft 365 offers a robust set of security features that can be optimized for remote work. This includes configuring access controls, utilizing multi-factor authentication, leveraging collaboration tools securely, and staying updated on the latest security features released by Microsoft. Regularly assessing and adjusting security configurations based on evolving needs is key to maximizing the benefits of Microsoft 365’s security arsenal.