Introduction to AWS Managed Hosting Services
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, businesses are increasingly turning to managed hosting services to ensure the optimal performance, security, and scalability of their infrastructure. This section provides a comprehensive introduction to AWS Managed Hosting Services, shedding light on the concept of managed hosting, the specific offerings within the AWS ecosystem, and the critical role it plays in the broader realm of cloud computing.
Overview of Managed Hosting
Managed hosting is a service model where a third-party provider, in this case, AWS, takes on the responsibility of overseeing and managing the infrastructure, ensuring that it operates efficiently and remains secure. This approach allows businesses to offload the complexities of infrastructure management, including hardware provisioning, software updates, and security configurations, freeing up valuable resources and time for focusing on core business objectives.
Introduction to AWS Managed Hosting
AWS, as a leading cloud service provider, offers a suite of managed hosting services designed to cater to the diverse needs of businesses. These services go beyond traditional hosting solutions, providing a holistic and scalable infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) platform. AWS Managed Hosting encompasses a range of services, from virtual servers and databases to fully managed container orchestration, allowing businesses to tailor their hosting environment to match specific requirements.
Importance of Managed Hosting in Cloud Computing
In the realm of cloud computing, where agility and efficiency are paramount, the importance of managed hosting cannot be overstated. AWS Managed Hosting Services enable organizations to harness the full potential of the cloud without the burden of day-to-day infrastructure management. Key aspects of its significance include:
- Scalability and Flexibility
AWS Managed Hosting empowers businesses to scale their infrastructure dynamically in response to changing workloads. With the ability to swiftly provision resources as needed, organizations can seamlessly adapt to varying demands, ensuring optimal performance without the constraints of traditional hosting models.
- Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority in the cloud, and AWS Managed Hosting is designed with robust security measures. With features such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), encryption, and network security protocols, businesses can confidently meet compliance requirements and protect sensitive data in their hosted environments.
- Reliability and Performance
AWS’s global infrastructure provides a highly reliable and performant hosting environment. Leveraging a network of data centers worldwide, AWS Managed Hosting ensures low-latency access, high availability, and efficient content delivery, contributing to an enhanced user experience.
- Cost Optimization
By embracing managed hosting services on AWS, organizations can optimize costs by paying only for the resources they consume. With flexible pricing models and the elimination of upfront hardware investments, businesses can achieve cost-efficiency while enjoying the benefits of a fully managed hosting environment.
In essence, the introduction to AWS Managed Hosting Services sets the stage for a deeper exploration of its various components and functionalities. As businesses navigate the complexities of modern IT infrastructure, AWS Managed Hosting emerges as a strategic choice, offering a powerful combination of flexibility, security, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits of AWS Managed Hosting Services
AWS Managed Hosting Services bring a plethora of benefits to businesses seeking a robust, scalable, and secure hosting environment. In this section, we delve into the key advantages, outlining how AWS’s managed services contribute to scalability, security, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Dynamic Resource Provisioning
One of the standout benefits of AWS Managed Hosting is the unmatched scalability it offers. Organizations can dynamically scale their infrastructure based on demand, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently without the need for manual intervention. Whether facing sudden spikes in traffic or dealing with fluctuating workloads, businesses can seamlessly adjust their capacity to match specific requirements.
- Auto-Scaling Capabilities
AWS provides sophisticated auto-scaling features that enable businesses to set policies for automatic resource adjustments. This means that during periods of increased demand, additional resources are provisioned automatically, and during lulls, unnecessary resources are de-provisioned. This not only optimizes performance but also ensures cost efficiency by only paying for what is consumed.
- Tailored Solutions for Various Workloads
The flexibility of AWS Managed Hosting allows organizations to choose the most suitable hosting solutions for their specific workloads. Whether deploying traditional virtual servers with Amazon EC2, leveraging serverless computing with AWS Lambda, or managing containers with Amazon EKS, AWS accommodates a diverse range of use cases. This adaptability empowers businesses to tailor their hosting environment to match the unique needs of their applications.
Security and Compliance
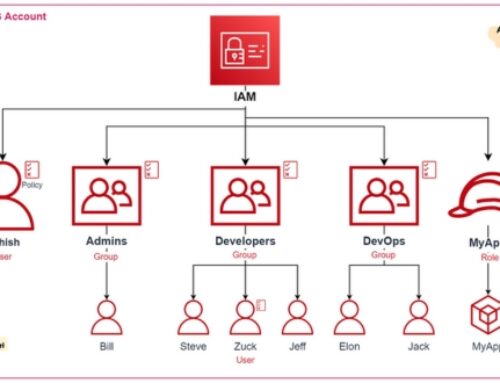
- Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Security is at the forefront of AWS Managed Hosting Services, with AWS IAM playing a central role. IAM enables organizations to manage user identities and access permissions with granular control. Businesses can define who has access to which resources, ensuring that only authorized personnel can interact with critical infrastructure components.
- Encryption and Data Protection
AWS prioritizes data security through robust encryption mechanisms. Data in transit and at rest is encrypted, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access. AWS Key Management Service (KMS) allows organizations to manage cryptographic keys securely, providing an additional layer of control over data protection.
- Network Security and Isolation
AWS employs advanced network security measures to safeguard hosted environments. Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) enable businesses to create isolated network environments, controlling traffic flow and ensuring that resources are securely connected. Additionally, AWS offers features like Security Groups and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs) for fine-grained control over inbound and outbound traffic.
- Compliance Standards Adherence
AWS Managed Hosting facilitates adherence to various compliance standards and regulations. Whether complying with industry-specific requirements such as HIPAA or adhering to global standards like GDPR, AWS provides tools and features to help businesses maintain compliance. Regularly updated compliance documentation and certifications provide transparency and assurance.
Reliability and Performance
- Global Infrastructure
AWS’s extensive global infrastructure is a cornerstone of its reliability. With data centers strategically located worldwide, businesses can deploy applications in proximity to end-users, reducing latency and ensuring a seamless user experience. Multiple Availability Zones within regions further enhance reliability, providing redundancy and fault tolerance.
- High Availability Architectures
AWS Managed Hosting Services enable the implementation of high availability architectures. By distributing applications across multiple Availability Zones, organizations ensure that if one zone experiences an issue, traffic is automatically redirected to a healthy zone. This minimizes downtime and enhances the overall reliability of hosted applications.
- Efficient Content Delivery
AWS offers content delivery solutions like Amazon CloudFront, a global content delivery network (CDN). CloudFront caches content at edge locations, reducing latency and accelerating content delivery. This not only enhances the performance of web applications but also improves the user experience by delivering content from locations closer to end-users.
Cost Optimization
- Pay-as-You-Go Model
AWS Managed Hosting operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they consume. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, making it a cost-effective solution for organizations of all sizes. The flexibility to scale resources up or down ensures optimal cost management.
- Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
For organizations with predictable workloads, AWS provides options like Reserved Instances and Savings Plans. These offerings allow businesses to commit to a specific amount of usage in exchange for significant cost savings compared to on-demand pricing. This approach is particularly beneficial for long-term, stable workloads.
- Cost Explorer and Budgets
AWS’s Cost Explorer and Budgets tools empower businesses to monitor and analyze their spending. Cost Explorer provides insights into resource consumption, allowing organizations to identify areas for optimization. Budgets enable the setting of cost thresholds, providing proactive alerts when expenditures approach predefined limits.
- Resource Optimization and Right-Sizing
AWS Managed Hosting Services include tools for resource optimization and right-sizing. Businesses can leverage services like AWS Trusted Advisor, which offers recommendations for optimizing resources based on usage patterns. This ensures that organizations are not over-provisioning resources, leading to cost savings without compromising performance.
In conclusion, the benefits of AWS Managed Hosting Services extend across scalability, security, reliability, and cost optimization. As organizations increasingly embrace the cloud, AWS’s managed offerings provide a comprehensive solution to meet the evolving demands of modern applications, ensuring a secure, flexible, and high-performance hosting environment.
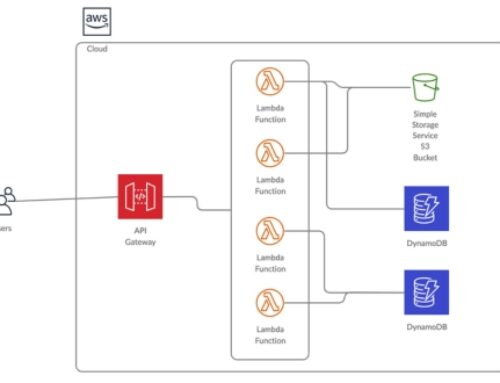
AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a fundamental component of AWS Managed Hosting Services, offering scalable compute capacity in the cloud. In this section, we explore the intricate details of EC2, from its foundational overview to various instance types, managed services, and best practices for optimal utilization.
Overview of EC2
- Foundational Concept of EC2:
Amazon EC2 provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud, allowing businesses to quickly scale their computing resources based on demand. This elastic nature of EC2 is essential for accommodating varying workloads efficiently.
- Virtual Servers (Instances):
EC2 instances are virtual servers in the cloud, each equipped with its own CPU, memory, storage, and network interface. Users can choose instances with varying specifications to align with the specific requirements of their applications.
- AMI (Amazon Machine Image):
EC2 instances are launched from Amazon Machine Images (AMIs), which are pre-configured templates containing the necessary information to launch instances. AMIs encapsulate the operating system, application server, and applications, enabling swift deployment.
- Elastic Load Balancing:
EC2 instances can be deployed behind an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) to distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances. This enhances fault tolerance and ensures that the workload is evenly distributed, optimizing performance.
EC2 Instance Types
- General Purpose Instances (e.g., t4g, t3, t3a):
These instances provide a balance of compute, memory, and networking resources. They are suitable for diverse workloads, such as web servers, development environments, and small to medium databases.
- Compute Optimized Instances (e.g., c7g, c6g, c5, c5a):
Designed for compute-intensive tasks, these instances deliver high-performance processors. They are ideal for applications that require significant computational power, like high-performance computing (HPC) and scientific modeling.
- Memory Optimized Instances (e.g., r7g, r6g, r5, r5a, x1e, u-6tb1.metal):
Instances in this category are optimized for memory-intensive tasks. They are well-suited for applications that require substantial memory, such as in-memory databases, real-time big data analytics, and large-scale enterprise applications.
- Storage Optimized Instances (e.g., i3, i3en, h1, d2):
Designed for workloads that demand high, sequential read and write access to very large data sets on local storage, these instances are ideal for applications like data warehousing, distributed file systems, and log processing.
Managed Services for EC2
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling:
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling ensures that the desired number of EC2 instances are available to handle varying workloads. It automatically adjusts the number of instances based on parameters set by the user, optimizing resource utilization.
- Amazon EC2 Image Builder:
EC2 Image Builder simplifies the creation, maintenance, and deployment of customized, secure, and up-to-date Amazon Machine Images. It allows users to automate the image-building process, ensuring consistency and compliance.
- Amazon EC2 Systems Manager:
EC2 Systems Manager provides a unified user interface for viewing operational data from multiple AWS services. It simplifies resource and application management, offering features for automation, patch management, and configuration management.
- Amazon EC2 Spot Instances:
Spot Instances allow users to bid for unused EC2 capacity at potentially lower prices. While they can be interrupted by EC2 if the capacity is needed elsewhere, they are a cost-effective option for fault-tolerant and flexible workloads.
Use Cases and Best Practices
- Web Applications and Hosting:
EC2 is widely used for hosting web applications, offering the flexibility to choose the right instance type based on the application’s compute and memory requirements. Leveraging ELB ensures high availability and fault tolerance.
- Development and Testing Environments:
EC2 provides an efficient solution for creating development and testing environments. Users can launch instances with specific configurations, use them for testing purposes, and terminate them when no longer needed, optimizing costs.
- Data Processing and Analysis:
EC2 instances, especially those optimized for compute or memory, are suitable for data processing and analysis tasks. Whether running analytics, processing large datasets, or performing simulations, EC2 offers the necessary compute power.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC):
Compute-optimized EC2 instances are designed for high-performance computing workloads. Organizations engaged in scientific research, simulations, and complex computations can benefit from the superior processing power of these instances.
- Best Practices:
Right-Sizing Instances: Choose instance types based on the specific needs of the workload to avoid over-provisioning or under-provisioning.
- Implementing Security Groups: Use security groups to control inbound and outbound traffic to instances, enhancing network security.
- Monitoring and Logging: Leverage AWS CloudWatch for monitoring instance performance and set up logging to capture valuable information for analysis.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Utilize EC2 Systems Manager for automated patch management to ensure instances are running the latest software updates.
- Backup and Recovery Strategies: Implement regular backups and establish recovery strategies to safeguard data and ensure business continuity.
In conclusion, Amazon EC2 serves as the backbone of AWS Managed Hosting Services, offering a diverse range of instance types and managed services. Its versatility, scalability, and integration with other AWS services make it a foundational component for businesses looking to build scalable and reliable applications in the cloud. Understanding the nuances of EC2 instances and adopting best practices ensures optimized performance and cost-effective utilization of resources.
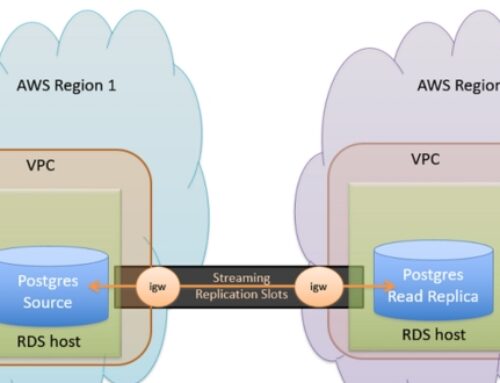
AWS RDS (Relational Database Service)
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is a fully managed database service provided by AWS, simplifying the deployment, operation, and scaling of relational databases. This section delves into the core components of RDS, emphasizing its managed database engines, automated backup features, and performance monitoring capabilities.
Overview of RDS
Amazon RDS is designed to handle the heavy lifting associated with database management, allowing users to focus on building applications rather than dealing with administrative tasks. RDS supports multiple popular database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB, providing flexibility to match the requirements of diverse applications.
Managed Database Engines
RDS offers a range of managed database engines, each tailored to specific use cases:
- MySQL and MariaDB: Ideal for web applications and content management systems.
- PostgreSQL: Suited for applications with complex queries and transactions.
- Oracle: Designed for enterprises with large-scale database requirements.
- SQL Server: Suitable for applications running on Microsoft technologies.
These managed engines relieve users of the operational complexities associated with traditional database management, ensuring high availability, security, and scalability.
Automated Backups and Failover
RDS automates critical aspects of database management, including:
- Automated Backups: RDS automatically performs regular backups of databases, allowing users to restore to any point within the retention period. This ensures data durability and provides a safety net against accidental data loss.
- Failover: In scenarios where the primary database instance becomes unavailable, RDS facilitates automatic failover to a standby instance. This enhances fault tolerance and minimizes downtime, crucial for maintaining continuous availability of applications.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
RDS provides robust tools for monitoring and optimizing database performance:
- Amazon CloudWatch Integration: RDS metrics are seamlessly integrated with Amazon CloudWatch, enabling users to monitor database performance, set alarms, and gain insights into resource utilization.
- Database Performance Insights: RDS offers a feature called Database Performance Insights, providing a detailed view of database activity. This aids in identifying bottlenecks and optimizing query performance.
- Automatic Performance Optimization: RDS continuously monitors database performance and automatically applies optimizations, such as parameter tuning and index recommendations, to maintain optimal efficiency.
In essence, Amazon RDS streamlines database management, offering a range of managed engines, automated backup and failover features, and tools for performance monitoring and optimization. This allows developers and businesses to focus on innovation, knowing that their relational databases are secure, highly available, and performing optimally in the AWS cloud.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk simplifies the deployment and management of applications, allowing developers to focus on writing code without getting bogged down by the complexities of infrastructure management.
Introduction to Elastic Beanstalk
Elastic Beanstalk provides an easy-to-use platform for deploying and scaling web applications, supporting multiple programming languages and frameworks.
Managed Application Deployment
With Elastic Beanstalk, deployment is streamlined. Developers upload their code, and the platform automatically handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning to load balancing.
Auto-Scaling and Load Balancing
Elastic Beanstalk ensures optimal application performance by automatically adjusting capacity based on demand. It integrates auto-scaling and load balancing to distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances, providing a seamless user experience.
Integration with Other AWS Services
Elastic Beanstalk seamlessly integrates with various AWS services, allowing developers to leverage functionalities like databases, storage, and messaging services effortlessly, creating a comprehensive and scalable application environment.
AWS Lightsail
AWS Lightsail is a simplified yet powerful service designed for users who need an easy way to deploy and manage applications in the cloud without delving into the complexities of infrastructure management.
Overview of Lightsail
Lightsail offers a user-friendly platform, providing a range of pre-configured, one-click launch applications and development stacks.
Simple Virtual Private Servers (VPS)
Lightsail delivers straightforward virtual private servers, allowing users to launch scalable compute instances with ease, catering to a variety of application workloads.
Managed Databases and Storage
Beyond compute instances, Lightsail includes managed databases and storage options, streamlining the setup and maintenance of databases and facilitating efficient data storage.
Use Cases and Pricing Comparison
Lightsail is ideal for small to medium-sized projects, personal websites, and development environments. It offers transparent pricing, making it easy for users to understand costs and compare options, ensuring affordability for a wide range of applications.
AWS Managed Hosting Security Best Practices
Ensuring the security of AWS Managed Hosting is paramount, and adopting best practices is crucial to safeguarding infrastructure and data.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implement granular access controls using AWS IAM. Assign least privilege permissions to users and resources, enhancing security by restricting access only to what is necessary.
Encryption and Data Protection
Leverage encryption mechanisms for data at rest and in transit. Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for managing cryptographic keys, adding an extra layer of protection to sensitive information.
Network Security and Firewall Configuration
Implement robust network security by utilizing Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), security groups, and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs). Define firewall rules to control inbound and outbound traffic, fortifying the overall network architecture.
Compliance and Auditing
Adhere to industry-specific compliance standards and conduct regular audits. Utilize AWS services and tools to track and monitor activities, ensuring continuous compliance and proactively identifying potential security risks.
AWS Managed Hosting vs. Traditional Hosting Solutions
Comparing AWS Managed Hosting to traditional hosting solutions reveals significant advantages in performance, cost, scalability, and management efficiency.
Performance Comparison
AWS Managed Hosting outperforms traditional solutions with its global infrastructure, offering low-latency access, high availability, and efficient content delivery. The dynamic scaling of resources ensures optimal performance under varying workloads.
Cost Analysis
While traditional hosting often involves upfront hardware investments and fixed costs, AWS’s pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to pay only for the resources consumed. This flexibility, along with options like Reserved Instances and Savings Plans, leads to potential cost savings for organizations using AWS.
Scalability and Flexibility
AWS excels in scalability, enabling businesses to dynamically adjust resources based on demand. Traditional hosting solutions may struggle to match this level of flexibility, often requiring manual intervention for scaling.
Management Overhead
AWS Managed Hosting minimizes management overhead by automating tasks such as backups, patching, and scaling. In contrast, traditional hosting solutions typically entail more manual management responsibilities, leading to increased complexity and potential operational challenges.
AWS Managed Hosting Case Studies
Exploring real-world case studies illuminates the success stories of organizations harnessing the power of AWS Managed Hosting, offering valuable insights and best practices.
Success Stories of Organizations Leveraging AWS Managed Hosting
Discover how diverse organizations have achieved success by leveraging AWS Managed Hosting. These case studies showcase the transformative impact of AWS services on businesses of varying sizes and industries.
Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Delve into concrete examples and use cases illustrating how AWS Managed Hosting has addressed unique challenges and empowered organizations to achieve their goals. These real-world scenarios showcase the versatility and applicability of AWS solutions.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices from Case Studies
Extract valuable lessons and best practices from the experiences of organizations highlighted in the case studies. Understand the strategies, approaches, and key takeaways that contribute to successful implementations and outcomes.
Future Trends in AWS Managed Hosting
Anticipating the future of AWS Managed Hosting unveils exciting prospects driven by emerging technologies and innovative advancements.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
Stay ahead of the curve by exploring emerging technologies such as serverless computing, artificial intelligence, and edge computing within the realm of AWS Managed Hosting. Witness how these technologies shape the future landscape of hosting solutions.
Predictions for the Evolution of Managed Hosting Services
As AWS continues to evolve, predictions for the future of managed hosting services point towards enhanced automation, deeper integration with cutting-edge technologies, and a continued focus on security and compliance. Stay informed about the trajectory of AWS Managed Hosting to align your infrastructure strategies with the upcoming trends and innovations in the cloud computing domain.
Conclusion
AWS Managed Hosting Services emerge as a cornerstone for businesses seeking a reliable, scalable, and secure cloud infrastructure. Through a comprehensive suite of offerings, AWS redefines the hosting landscape, empowering organizations to transcend traditional hosting limitations. The performance superiority of AWS, evident in global infrastructure and efficient content delivery, ensures an unparalleled user experience.
Striking a balance between scalability and cost-effectiveness, AWS Managed Hosting aligns with dynamic business needs, enabling optimal resource utilization through features like auto-scaling and flexible pricing models. Security, a paramount concern, is addressed through robust practices encompassing IAM, encryption, network security, and compliance adherence.
The platform’s versatility is highlighted by a range of managed services, from EC2 and RDS to Elastic Beanstalk and Lightsail, each tailored to diverse use cases. Real-world case studies underscore the tangible impact of AWS Managed Hosting, revealing success stories across industries.
As the technological landscape evolves, AWS Managed Hosting stands at the forefront of innovation, embracing emerging technologies and setting the stage for future trends. The platform’s trajectory points towards continuous advancements, making it a strategic choice for businesses aspiring to thrive in the ever-changing realm of cloud computing. In essence, AWS Managed Hosting Services not only redefine hosting but pave the way for a resilient, efficient, and future-ready cloud infrastructure.