Introduction
-
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Definition and Concept of Two-Factor Authentication
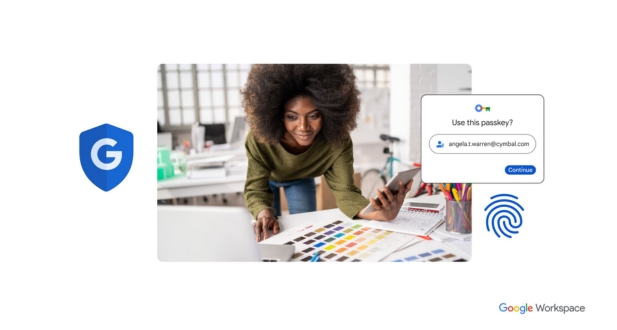
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is an advanced security measure designed to add an extra layer of protection beyond traditional username and password credentials. It involves the use of two distinct verification factors to ensure the identity of a user attempting to access a system or platform. These factors typically fall into three categories: something you know (password), something you have (security token or mobile device), and something you are (biometric data).
In the context of Google Workspace, 2FA provides an additional level of security by requiring users to go through a secondary authentication process beyond entering their password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as even if login credentials are compromised, an intruder would still need the second factor to gain access.
Importance of 2FA in Enhancing Security for Google Workspace
The digital landscape is increasingly fraught with sophisticated cyber threats and malicious activities. Passwords alone are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive information stored in platforms like Google Workspace. The importance of 2FA lies in its ability to fortify security by adding an extra layer of defense, making it significantly harder for unauthorized entities to breach accounts.
-
Significance in the Modern Digital Landscape
Evolving Cyber Threats and the Need for Additional Security Layers
The modern digital landscape is characterized by a surge in cyber threats, including phishing attacks, credential stuffing, and sophisticated malware. Cybercriminals are adept at exploiting vulnerabilities in traditional security measures, making it imperative for organizations to adopt more robust protection mechanisms.
Emphasizing the Role of 2FA in Protecting Sensitive Information
Google Workspace serves as a hub for collaborative work, housing sensitive business data, communication, and intellectual property. The significance of 2FA within Google Workspace is underscored by its role in safeguarding this wealth of information. By requiring an additional verification step beyond passwords, 2FA acts as a formidable barrier against unauthorized access, ensuring that only authenticated users can access critical business resources.
In summary, the introduction to Two-Factor Authentication provides a foundational understanding of its concept and highlights its crucial role in addressing the evolving cyber threats within the digital landscape. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into the benefits, implementation, user experience, and future trends of 2FA within Google Workspace.
Benefits of Google Workspace 2FA
Enhanced Security
Detailing the Additional Layer Provided by 2FA
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) significantly enhances security within Google Workspace by introducing an additional layer of protection beyond traditional passwords. While passwords serve as the first authentication factor, 2FA requires users to provide a second factor, which can be something they possess, such as a mobile device or security token.
Exploring Security Advantages Against Phishing and Unauthorized Access
- Phishing Protection:
2FA acts as a robust defense against phishing attacks. Even if users unwittingly provide their passwords in response to phishing attempts, malicious actors would still require the second factor to gain access. This greatly reduces the success rate of phishing attempts.
- Unauthorized Access Prevention:
By necessitating two distinct factors for authentication, 2FA ensures that even if login credentials are compromised, unauthorized access is thwarted. This is particularly crucial in securing sensitive data and communications within Google Workspace.
Mitigation of Common Security Risk
Addressing Common Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
- Password Reuse:
Password reuse across multiple accounts is a common security risk. If one set of credentials is compromised, attackers may attempt to use the same combination on other platforms. 2FA mitigates this risk by requiring an additional factor, limiting the impact of compromised passwords.
- Brute Force Attacks:
Brute force attacks involve systematically attempting various password combinations to gain unauthorized access. 2FA acts as a powerful deterrent, as even if attackers manage to crack the password, they would still need the second factor for successful authentication.
Contributing to a More Robust Security Posture
- Multi-Layered Defense:
Implementing 2FA establishes a multi-layered defense strategy. The combination of “something you know” (password) and “something you have” (second factor) creates a formidable barrier against a range of cyber threats, strengthening the overall security posture.
- User Accountability:
2FA reinforces user accountability by ensuring that users take an active role in securing their accounts. It encourages the adoption of secure practices and emphasizes the importance of safeguarding the second authentication factor.
Compliance Requirements
Aligning with Regulatory Compliance Standards
- Regulatory Landscape:
The regulatory landscape mandates stringent data protection measures. Implementing 2FA aligns with various regulatory compliance standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others, demonstrating a commitment to robust security practices.
- Data Protection and Privacy:
Google Workspace users handle sensitive data, and regulatory compliance is crucial for maintaining data protection and privacy. 2FA adds an extra layer of security, meeting compliance requirements and safeguarding sensitive information.
Exploring Compliance Benefits for Google Workspace Organizations
- Risk Mitigation:
2FA assists organizations in mitigating the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents. This risk mitigation aligns with compliance standards that prioritize the protection of sensitive information.
- Security Audits and Reporting:
Compliance often involves conducting security audits and providing detailed reporting. 2FA facilitates these processes by offering an additional layer of security that can be monitored and reported on within the Google Workspace environment.
In conclusion, the benefits of Google Workspace 2FA are multi-faceted, ranging from enhanced security and risk mitigation to alignment with regulatory compliance standards. The implementation of 2FA not only addresses common security risks but also contributes to a more resilient and secure digital environment within Google Workspace.
Implementing Google Workspace 2FA
-
Setting Up 2FA for Users
Step-by-Step Guide on Enabling 2FA for Google Workspace Users
User Access:
Users can initiate the 2FA setup process by accessing their Google Account settings. This is typically found in the Security section.
Enable 2FA:
Users navigate to the Two-Factor Authentication option and enable it. This prompts Google Workspace to guide them through the setup process.
Select Verification Method:
Users choose a verification method from the supported options, such as SMS, authenticator apps, or security keys.
Follow Setup Instructions:
Users follow the step-by-step instructions provided by Google Workspace to complete the setup. This may involve adding a phone number, configuring an authenticator app, or registering a security key.
Explanation of User Authentication Flow with 2FA
Login Attempt:
When a user attempts to log in to their Google Workspace account, they provide their standard username and password.
2FA Prompt:
Upon successful entry of credentials, the user is prompted to provide the second factor of authentication.
Verification Process:
Depending on the chosen method, the user verifies their identity. This could involve entering a code received via SMS, approving a notification on a mobile device, or using an authenticator app.
Access Granted:
If the second factor is successfully verified, the user gains access to their Google Workspace account.
-
Supported 2FA Methods
Overview of Supported 2FA Methods in Google Workspace
SMS Authentication:
Users receive a one-time code via SMS, which they enter during the login process.
Authenticator Apps:
Users can use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy to generate time-based codes for verification.
Security Keys:
Hardware security keys provide a physical token for authentication, offering an additional layer of security.
Guidance on Choosing the Most Suitable Method Based on Security Needs
SMS for Accessibility:
SMS is user-friendly and accessible but may be susceptible to SIM swapping attacks. It is suitable for users prioritizing accessibility.
Authenticator Apps for Enhanced Security:
Authenticator apps generate time-sensitive codes, enhancing security. They are suitable for users seeking a balance between security and convenience.
Security Keys for Maximum Security:
Security keys offer the highest level of security. They are ideal for users dealing with highly sensitive information and requiring maximum protection.
-
Admin Console Configuration
Instructions for Administrators on Configuring 2FA Settings
Accessing Admin Console:
Administrators log in to the Google Workspace Admin Console using their administrative credentials.
Navigating to Security Settings:
In the Admin Console, administrators navigate to the Security section and locate the Two-Factor Authentication settings.
Enabling 2FA:
Administrators enable 2FA for the organization and choose the default and allowable 2FA methods.
Customizing Policies:
Administrators customize policies based on organizational security needs. This may involve specifying which 2FA methods are acceptable and setting up rules for user groups.
Highlighting the Importance of Customizing Policies for Organizational Security
Tailoring Security Measures:
Customizing 2FA policies allows organizations to tailor security measures according to their specific requirements and risk tolerance.
Balancing Security and User Experience:
Organizations can strike a balance between security and user experience by choosing suitable 2FA methods and configurations.
Adapting to Organizational Changes:
Customizable policies enable organizations to adapt 2FA settings to changes in user roles, security threats, or technological advancements.
In summary, the implementation of Google Workspace 2FA involves a user-friendly setup for individuals, a variety of supported methods catering to different security needs, and configurable policies in the Admin Console for administrators. This comprehensive approach ensures a secure and adaptable 2FA implementation within Google Workspace.
User Experience with 2FA
-
Seamless Authentication Process
Discussing How 2FA Integrates into the User Authentication Process
Login Initiation:
The user initiates the login process by entering their standard username and password as usual.
2FA Prompt:
Following successful password entry, the user encounters a seamless 2FA prompt, indicating the need for an additional verification step.
Verification Options:
Users can choose from various verification methods, such as entering a code received via SMS, using an authenticator app, or utilizing a security key.
Efficient Authentication:
The 2FA process is designed to be efficient, adding an extra layer of security without causing significant delays in the user’s access to Google Workspace.
Emphasizing the User-Friendly Aspects of 2FA
Choice of Methods:
Users have the flexibility to choose a 2FA method that suits their preferences and comfort level, promoting a positive and user-centric experience.
Remembered Devices:
Google Workspace allows users to mark trusted devices, reducing the frequency of 2FA prompts for known and frequently used devices, enhancing convenience.
Intuitive Interfaces:
The interfaces for configuring and using 2FA are designed to be intuitive, ensuring that users can easily navigate the process without extensive technical knowledge.
-
Troubleshooting and Support
Providing Guidance on Common Issues Users May Encounter with 2FA
Lost Second Factor:
Users may encounter issues if they lose their second factor (e.g., mobile device or security key). Guidance on recovery options and steps to regain access should be provided.
Code Generation Issues:
For users using authenticator apps, occasional issues may arise in code generation. Troubleshooting steps, such as syncing time settings, should be outlined.
Highlighting Available Support Resources for Users and Administrators
User Support Portals:
Google Workspace provides user-friendly support portals with step-by-step guides, FAQs, and troubleshooting resources to assist users in resolving common 2FA issues.
Administrator Support Channels:
Administrators have access to dedicated support channels within the Admin Console, facilitating efficient issue resolution and communication with Google Workspace support teams.
Security Best Practices with 2FA
-
Password Management
Reinforcing the Importance of Strong, Unique Passwords in Conjunction with 2FA
Password Complexity Guidelines:
Reinforce the need for strong passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Avoiding Password Reuse:
Encourage users to avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts, emphasizing the unique security benefits that 2FA provides.
Providing Tips for Effective Password Management within Google Workspace
Password Manager Integration:
Encourage users to leverage password manager tools for secure storage and generation of complex passwords.
Regular Password Updates:
Remind users to update passwords regularly, especially in conjunction with 2FA implementation.
- Periodic Security Audits
Advocating for Regular Security Audits and Assessments in Tandem with 2FA
Scheduled Audits:
Emphasize the importance of scheduling regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of 2FA and overall account security.
Multi-Layered Assessments:
Advocate for a multi-layered assessment approach, including vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and user access reviews.
Discussing How Audits Contribute to Maintaining a Secure Google
Workspace Environment
Identifying Anomalies
Security audits assist in identifying anomalies or suspicious activities, enabling swift response to potential security breaches.
Continuous Improvement:
Regular audits contribute to the continuous improvement of security policies and practices, aligning them with evolving threats and industry best practices.
-
Communication and Training
Stressing the Significance of User Education and Awareness
Webinars and Training Sessions:
Conduct webinars and training sessions to educate users about the importance of 2FA, its benefits, and how to use it effectively.
Periodic Communication:
Implement a periodic communication strategy to remind users of security best practices, including 2FA usage and password management.
Offering Strategies for Effective Communication and Training on 2FA Adoption
Interactive Learning Materials
Develop interactive learning materials, such as videos, infographics, and interactive guides, to make the training process engaging and accessible.
Simulated Phishing Exercises:
Conduct simulated phishing exercises to train users on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts, aligning with the enhanced security provided by 2FA.
In conclusion, the user experience with Google Workspace 2FA is designed to be seamless and user-friendly, with support resources readily available for troubleshooting. Security best practices, including effective password management, periodic audits, and user education, further contribute to a robust and secure Google Workspace environment.
Challenges and Solutions
-
User Adoption Challenges
Addressing Potential Challenges such as User Resistance to 2FA
Resistance to Change:
Users may resist adopting 2FA due to the perception of added complexity. Address this by emphasizing the user-friendly aspects of 2FA and its role in enhancing overall security.
Perceived Inconvenience:
Some users may find 2FA inconvenient. Mitigate this by highlighting the efficiency and time-saving aspects of the streamlined authentication process.
Providing Strategies for Overcoming Resistance Through Education and Communication
User Education Campaigns:
Conduct comprehensive user education campaigns to communicate the importance of 2FA, its benefits, and the minimal impact on daily workflows.
Interactive Workshops:
Host interactive workshops or webinars to address user concerns, provide hands-on demonstrations, and answer questions about the 2FA implementation process.
Highlighting Success Stories:
Share success stories of early adopters within the organization who have experienced the positive impact of 2FA on security and convenience.
-
Technical Challenges
Discussing Technical Challenges in Implementing 2FA
Integration with Legacy Systems:
Organizations with legacy systems may face challenges integrating 2FA. Explore solutions such as custom API integrations or gradual system updates.
Mobile Device Compatibility:
Technical challenges may arise in ensuring that 2FA methods, particularly mobile-based ones, are compatible with a diverse range of devices. Provide guidance on supported devices and troubleshooting.
Offering Solutions and Workarounds for Common Technical Issues
Customization Options:
Implement customization options in the Admin Console to address integration challenges, allowing organizations to tailor 2FA configurations to their existing infrastructure.
Diverse Authentication Methods:
Ensure a variety of authentication methods are supported to address compatibility issues. For example, offer alternative methods for users without smartphones.
-
Case Studies
Including Real-World Examples of Organizations Successfully Overcoming Challenges During 2FA Implementation
Company X: Legacy System Integration:
Company X successfully integrated 2FA with its legacy systems by collaborating with its IT department and gradually updating the systems to support modern authentication standards.
Organization Y: User Adoption Strategies:
Organization Y implemented a comprehensive user adoption strategy, combining educational campaigns, workshops, and incentives. This resulted in a significant increase in 2FA adoption rates.
Enterprise Z: Technical Challenges Resolved:
Enterprise Z faced technical challenges related to mobile device compatibility. By providing a range of supported authentication methods and thorough troubleshooting guidance, they successfully addressed these issues.
In conclusion, addressing challenges in 2FA implementation requires a holistic approach, combining user education, technical solutions, and real-world examples. By implementing strategies that emphasize the benefits and mitigate concerns, organizations can successfully overcome challenges and create a secure and user-friendly Google Workspace environment.
Analytics and Monitoring for 2FA
-
Utilizing Analytics Tools
Discussing the Role of Analytics Tools in Monitoring 2FA Performance
Performance Metrics:
Analytics tools play a crucial role in monitoring the performance of 2FA by providing insights into authentication success rates, user login patterns, and potential anomalies.
Identifying Trends:
These tools help in identifying trends in 2FA usage, such as peak authentication times, preferred verification methods, and any irregularities that may indicate security concerns.
Introducing Google Workspace Reporting and Analytics Features Related to 2FA
Usage Reports:
Google Workspace offers usage reports specific to 2FA, allowing administrators to track the adoption rates, preferred authentication methods, and overall performance metrics.
Security Dashboard:
The Security Dashboard provides a centralized view of security-related activities, including 2FA usage, helping administrators quickly identify and respond to potential security incidents.
-
Monitoring User Activity
Exploring Methods for Monitoring User Activity with 2FA
User Login Logs:
Detailed user login logs provide information about successful and unsuccessful login attempts, helping administrators identify potential security threats.
Device Authentication History:
Monitoring the history of device authentications ensures that only trusted devices are accessing Google Workspace, enhancing overall security.
Explaining How Monitoring Contributes to Security and Compliance Within Google Workspace
Security Incident Response:
Proactive monitoring enables swift response to security incidents, allowing administrators to take immediate action in the event of suspicious activities or unauthorized access attempts.
Compliance Audits:
Monitoring user activity with 2FA contributes to compliance efforts by providing a comprehensive audit trail, essential for demonstrating adherence to regulatory standards.
Future Trends and Innovations in Google Workspace 2FA
-
Emerging Technologies
Discussing Emerging Technologies Influencing the Future of 2FA
Biometric Authentication:
The integration of biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, is an emerging trend that enhances the security and user experience of 2FA.
Adaptive 2FA:
Adaptive 2FA involves dynamically adjusting the level of authentication based on risk factors, providing a more personalized and responsive security approach.
-
Google Workspace Updates and Roadmap for 2FA
Keeping Track of Google Workspace Updates Related to 2FA
Feature Enhancements:
Google Workspace regularly introduces feature enhancements and updates related to 2FA, addressing security vulnerabilities and improving overall functionality.
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Google’s roadmap for 2FA may involve integrating emerging technologies and aligning with industry best practices to stay ahead of evolving security threats.
In conclusion, effective implementation of Google Workspace Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) relies on a combination of user-friendly experiences, vigilant monitoring through analytics tools, and an adaptive approach to emerging technologies. By addressing challenges in user adoption and technical integration, organizations can establish a robust security framework. Looking ahead, staying attuned to Google Workspace updates and embracing emerging technologies like biometric authentication ensures organizations remain resilient against evolving cyber threats. Together, these efforts contribute to a secure, streamlined, and future-ready digital environment within Google Workspace.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the implementation of Google Workspace Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) stands as a pivotal step towards fortifying digital security and fostering a collaborative, trust-centric environment. Throughout this guide, we navigated the intricacies of setting up, securing, and optimizing 2FA within Google Workspace, addressing user experience, security challenges, and future trends.
By emphasizing user-friendly authentication processes, providing solutions to adoption challenges, and delving into the technical aspects, organizations can seamlessly integrate 2FA into their workflows. The significance of robust user education, continuous monitoring through analytics tools, and adaptation to emerging technologies were underscored as critical components of a comprehensive security strategy
Looking forward, the guide explored emerging trends such as biometric authentication and adaptive 2FA, signaling a dynamic landscape where security evolves alongside technological advancements. Google Workspace’s commitment to regular updates and feature enhancements reinforces its dedication to staying ahead of security threats.
In essence, the implementation of Google Workspace 2FA is not merely a technological upgrade but a strategic commitment to data protection, user empowerment, and resilience against evolving cyber threats. As organizations navigate the digital frontier, embracing 2FA is a forward-thinking measure that aligns with the imperative of securing collaborative workspaces in an ever-changing technological landscape.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) in Google Workspace adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before accessing their accounts. This typically involves something they know (password) and something they have (a verification code).
To enable 2FA in Google Workspace, go to your account settings, select the Two-Factor Authentication option, and follow the prompts to choose a verification method, such as SMS, authenticator apps, or security keys.
Google Workspace supports various 2FA methods, including SMS authentication, authenticator apps (e.g., Google Authenticator), and security keys.Users are able to select the method that meets their security requirements and personal preferences.
Monitoring user activity with 2FA allows administrators to track login attempts, identify potential security threats, and ensure that only authorized devices access Google Workspace. This contributes to a proactive security stance and compliance with regulatory standards.
Emerging technologies shaping the future of 2FA in Google Workspace include biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition) and adaptive 2FA, which dynamically adjusts authentication levels based on risk factors for a more personalized security approach.