Understanding Salesforce CRM
Introduction to Salesforce CRM:
Salesforce CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is a cloud-based software platform that helps organizations manage their interactions and relationships with customers and potential customers. It provides a centralized hub for storing customer data, managing sales processes, and automating various tasks related to customer engagement. Salesforce CRM is known for its user-friendly interface, scalability, and customization options, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes and industries.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Customer Data Management: Salesforce CRM allows businesses to centralize customer information, including contact details, communication history, purchase history, and preferences, enabling a comprehensive view of each customer.
- Sales Process Automation: Automation features streamline repetitive tasks such as lead scoring, email follow-ups, and task assignments, freeing up sales representatives to focus on building relationships and closing deals.
- Customization and Scalability: Salesforce CRM offers a highly customizable platform that can be tailored to fit the specific needs and workflows of different businesses. Additionally, it is scalable, allowing organizations to adapt and grow without outgrowing their CRM system.
- Analytics and Reporting: The platform provides robust analytics and reporting tools that enable businesses to gain insights into their sales performance, track key metrics, and make data-driven decisions.
- Mobile Accessibility: Salesforce CRM can be accessed via mobile devices, allowing sales teams to stay productive and connected while on the go.
Importance of Forecasting and Pipeline Management:
- Forecasting: Forecasting in Salesforce CRM involves predicting future sales performance based on historical data, current trends, and other factors. Accurate forecasting helps businesses set realistic goals, allocate resources effectively, and make informed business decisions.
- Pipeline Management: Pipeline management refers to the process of tracking and managing sales opportunities as they progress through various stages of the sales cycle. Salesforce CRM provides tools for visualizing and managing the sales pipeline, including features such as drag-and-drop interfaces, customizable sales stages, and automated alerts. Effective pipeline management ensures that sales teams can prioritize leads, identify bottlenecks, and optimize their sales processes for maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Salesforce CRM offers a comprehensive solution for managing customer relationships, automating sales processes, and gaining insights into sales performance. By leveraging its key features and focusing on forecasting and pipeline management, businesses can drive growth, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Fundamentals of Forecasting
What is Sales Forecasting?
Sales forecasting is the process of predicting future sales levels or revenues for a business over a defined period. It involves analyzing historical sales data, market trends, economic indicators, and other relevant factors to estimate future sales performance. Sales forecasts serve as a crucial tool for businesses in budgeting, production planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and overall strategic decision-making.
Types of Sales Forecasting
There are various approaches to sales forecasting, each with its own methodologies and applications. Some common types of sales forecasting include:
Qualitative Forecasting: This method relies on expert judgment, market research, surveys, and other subjective factors to predict future sales. It’s often used when historical data is limited or when entering new markets with uncertain dynamics.
Quantitative Forecasting: Quantitative methods utilize mathematical models and historical sales data to generate forecasts. These methods include time series analysis, regression analysis, moving averages, exponential smoothing, and trend analysis. They are particularly useful when there is a substantial amount of historical data available.
Top-down vs. Bottom-up Forecasting: In top-down forecasting, overall sales projections are made first, and then these are allocated to specific products, regions, or divisions. Bottom-up forecasting, on the other hand, involves aggregating individual sales forecasts from various units or regions to derive the overall sales forecast.
Long-term vs. Short-term Forecasting: Long-term forecasts typically cover periods of one year or more and are crucial for strategic planning and investment decisions. Short-term forecasts, on the other hand, focus on immediate sales trends and are essential for tactical decision-making, such as production scheduling and inventory management.
Importance of Accurate Forecasting
Resource Allocation: It helps businesses allocate resources efficiently by ensuring that they have the right amount of inventory, staff, and production capacity to meet anticipated demand.
Financial Planning: Sales forecasts are essential for budgeting, cash flow management, and financial planning. They help businesses set revenue targets, assess profitability, and secure financing.
Performance Evaluation: By comparing actual sales figures with forecasted ones, businesses can evaluate their performance, identify deviations from the plan, and take corrective actions as needed.
Strategic Decision-making: Sales forecasts provide valuable insights into market trends, customer preferences, and competitive dynamics, enabling businesses to make informed strategic decisions about pricing, marketing, product development, and expansion.
Challenges in Forecasting
Despite its importance, sales forecasting poses several challenges:
Data Quality: Forecasting accuracy heavily relies on the quality and reliability of data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed forecasts.
Market Volatility: Rapid changes in market conditions, consumer behavior, and competitive landscape make it challenging to predict future sales accurately.
Uncertainty: External factors such as economic downturns, natural disasters, regulatory changes, and geopolitical events introduce uncertainty into the forecasting process.
Complexity: Businesses operate in increasingly complex environments with multiple sales channels, product lines, and geographic markets, making it difficult to capture all relevant factors in the forecasting models.
Human Factors: Biases, subjective judgments, and cognitive limitations of forecasters can influence the accuracy of forecasts, especially in qualitative forecasting methods.
Salesforce CRM Forecasting
Overview of Salesforce Forecasting:
This section provides a foundational understanding of what Salesforce forecasting entails. It covers the importance of forecasting in sales management, including its role in decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning. It may also discuss the benefits of using Salesforce specifically for forecasting, such as its integration with sales data, customization options, and reporting capabilities.
Setting Up Forecasting in Salesforce:
This part delves into the practical aspects of configuring forecasting within the Salesforce platform. It includes step-by-step instructions on how to enable forecasting features, define forecast periods (e.g., monthly, quarterly), set up forecasting hierarchies (e.g., by sales team, territory), and assign forecasting permissions to users. Additionally, it may cover data synchronization and integration with other Salesforce modules or external systems for accurate forecasting.
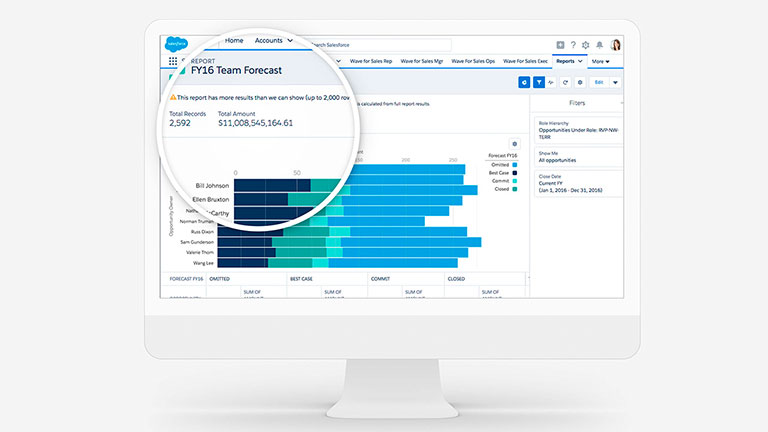
Forecast Categories and Customization:
Here, the focus is on the different types of forecasts that Salesforce supports and how they can be customized to align with the organization’s sales processes and terminology. This section may explain standard forecast categories such as commit, best case, and pipeline, as well as how to create custom forecast categories tailored to specific business needs. It may also touch upon configuring forecast adjustment settings, defining forecasting metrics, and creating custom reports and dashboards to visualize forecast data.
Forecasting Best Practices:
This section offers insights into recommended strategies and approaches for maximizing the effectiveness of Salesforce forecasting. It covers best practices for data hygiene and accuracy, such as regular updates, proper opportunity management, and clear communication among sales teams. It may also discuss techniques for forecasting accuracy improvement, such as leveraging historical data, incorporating qualitative inputs, and implementing sales forecasting models or algorithms. Additionally, it may address challenges and pitfalls to avoid, such as over-reliance on automated forecasting or neglecting qualitative factors.
Pipeline Management in Salesforce CRM
Understanding the Sales Pipeline:
The sales pipeline refers to the stages that a potential customer goes through, from initial contact to closing the deal. These stages typically include lead generation, qualification, proposal, negotiation, and ultimately, closing the sale. Understanding the sales pipeline involves having a clear grasp of each stage, the criteria for progression, and the typical duration of each stage. This understanding forms the foundation for effective pipeline management.
Importance of Pipeline Management:
Pipeline management is crucial for any sales organization as it provides insights into the health and effectiveness of the sales process. Effective pipeline management allows sales teams to identify bottlenecks, prioritize deals, forecast revenue accurately, and allocate resources efficiently. It also enables sales managers to coach and support their teams effectively, leading to improved sales performance and better customer relationships.
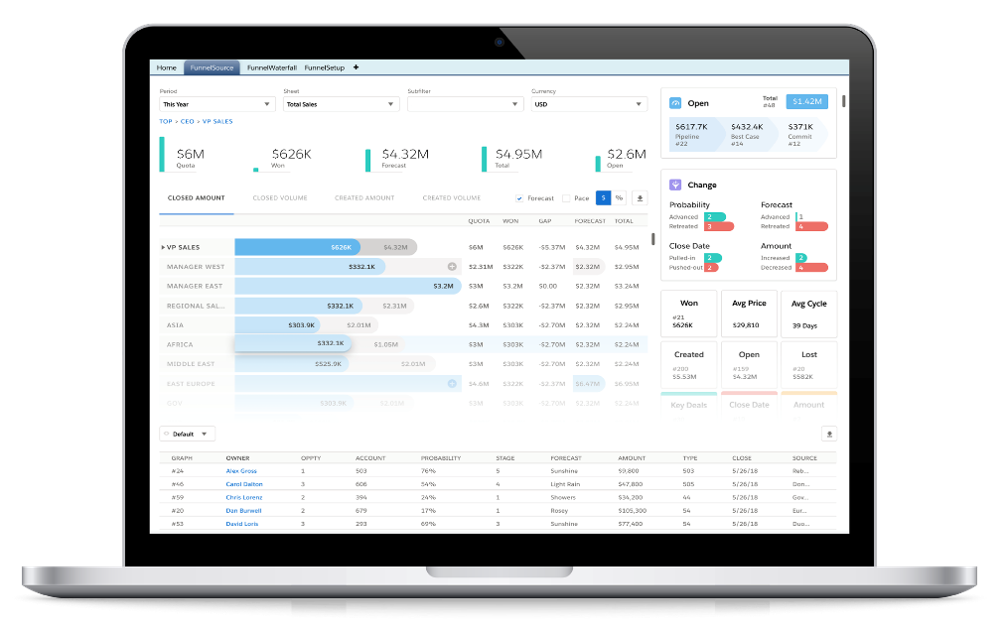
Salesforce Pipeline Management Tools and Features:
Salesforce CRM offers a robust set of tools and features for managing the sales pipeline effectively.
- Lead Management: Salesforce allows for the efficient capture, qualification, and assignment of leads to sales representatives.
- Opportunity Management: Sales opportunities can be tracked through various stages of the pipeline, with clear visibility into key details such as deal amount, close date, and probability of success.
- Forecasting: Salesforce provides forecasting tools that leverage historical data and pipeline information to generate accurate revenue forecasts.
- Reports and Dashboards: Customizable reports and dashboards provide real-time insights into pipeline performance, allowing users to track progress, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Workflow Automation: Automation features streamline repetitive tasks, ensuring that sales representatives can focus on high-value activities and opportunities.
- Integration: Salesforce integrates with various third-party applications and tools, enhancing its capabilities and providing a seamless user experience.
Optimizing Pipeline Visibility and Tracking:
Optimizing pipeline visibility and tracking involves ensuring that sales teams have access to the right information at the right time. This includes:
- Customizing Views: Tailoring pipeline views and reports to match the specific needs of different users or teams.
- Regular Updates: Encouraging sales representatives to update opportunity records regularly with the latest information, ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
- Pipeline Reviews: Conducting regular pipeline reviews and meetings to assess progress, identify potential issues, and strategize for future success.
- Training and Support: Providing ongoing training and support to sales teams to ensure they understand how to effectively utilize Salesforce for pipeline management.
Forecasting vs. Pipeline Management
Differentiating Forecasting and Pipeline Management:
Forecasting involves predicting future sales or business outcomes based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It provides estimates of potential revenue and helps in planning resources, setting targets, and making informed business decisions. Forecasting typically looks at the big picture and provides a high-level view of expected sales over a specific period, such as a quarter or a year.
Pipeline management, on the other hand, focuses on the current status and progress of individual sales opportunities or deals within the sales pipeline. It involves tracking and managing each stage of the sales process, from lead generation to deal closure. Pipeline management aims to ensure that opportunities move smoothly through the pipeline, identifying potential bottlenecks or risks, and taking action to accelerate deals or address issues as needed.
Interrelationship between Forecasting and Pipeline Management:
Although forecasting and pipeline management are distinct concepts, they are closely interrelated. The data and insights generated from pipeline management feed into the forecasting process. By analyzing the status and health of the sales pipeline, businesses can make more accurate predictions about future revenue and performance.
Conversely, forecasting provides context and guidance for pipeline management strategies. It helps sales teams prioritize leads and opportunities based on their potential impact on overall revenue targets. For example, if the forecast indicates a shortfall in revenue for a particular period, sales managers may need to focus on accelerating deals in the pipeline or generating new leads to meet targets.
Aligning Forecasting with Pipeline Management Strategies:
To optimize sales performance, it’s essential to align forecasting with pipeline management strategies effectively. This involves:
- Integrating data: Ensure that the data used for forecasting aligns with the information collected through pipeline management systems. Consistent and accurate data across both processes improves the reliability of forecasts.
- Continuous monitoring: Regularly review and update forecasts based on changes in the sales pipeline. Monitoring key metrics and indicators allows businesses to adjust forecasts dynamically as new information becomes available.
- Collaboration between teams: Foster collaboration between sales, marketing, and finance teams to align forecasting with pipeline management strategies. Shared goals and transparent communication help ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives.
- Iterative improvement: Use insights from both forecasting and pipeline management to refine sales strategies and processes continuously. By analyzing past performance and adjusting plans accordingly, businesses can enhance their ability to predict and manage sales effectively
Best Practices for Effective Forecasting and Pipeline Management
Establishing Clear Sales Processes:
Establishing clear sales processes involves defining the steps involved in the sales cycle, from lead generation to closing deals. This includes outlining the criteria for qualifying leads, setting up follow-up procedures, and defining roles and responsibilities within the sales team. Clear processes help streamline operations, reduce confusion, and ensure consistency in sales activities. It also enables better tracking and measurement of progress at each stage of the sales pipeline.
Utilizing Data Analytics and Insights:
Data analytics plays a crucial role in forecasting and pipeline management. By leveraging data analytics tools and techniques, sales teams can gather insights into customer behavior, market trends, and historical sales data. These insights help in identifying patterns, predicting future sales, and making informed decisions about resource allocation and strategy adjustments. Utilizing data analytics empowers sales teams to optimize their approach, identify opportunities for growth, and mitigate risks more effectively.
Regular Monitoring and Evaluation:
Regular monitoring and evaluation involve continuously tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) related to sales activities and pipeline metrics. This includes monitoring conversion rates, sales velocity, lead-to-opportunity ratio, and other relevant metrics. By closely monitoring these metrics, sales teams can identify bottlenecks, areas for improvement, and emerging trends in real-time. Regular evaluations allow for timely adjustments to strategies and tactics, ensuring that the sales pipeline remains healthy and aligned with organizational goals.
Collaboration between Sales and Marketing Teams:
Collaboration between sales and marketing teams is essential for effective forecasting and pipeline management. Close alignment between these two departments ensures that marketing efforts are targeted toward generating high-quality leads that are more likely to convert into sales. Sales teams can provide valuable feedback to marketing regarding lead quality and customer preferences, enabling marketing teams to refine their strategies accordingly. Likewise, marketing teams can support sales efforts by providing relevant content, and collateral, and leading nurturing campaigns. Collaboration fosters synergy between sales and marketing efforts, resulting in a more efficient and effective sales pipeline.
Advanced Techniques and Strategies
Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning:
Predictive analytics involves using historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes. In the context of sales, predictive analytics can be used to anticipate customer behavior, identify trends, and optimize sales strategies. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets to uncover patterns and correlations, enabling sales teams to make more informed decisions. For example, predictive analytics can help identify which leads are most likely to convert into customers, allowing sales reps to prioritize their efforts effectively.
Sales Performance Metrics and KPIs:
Sales performance metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of sales strategies and measuring the performance of sales teams. These metrics can include indicators such as sales revenue, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and sales pipeline velocity. By tracking these metrics regularly, organizations can identify areas for improvement, set benchmarks, and align sales activities with overarching business objectives.
Integration with Other Business Systems:
Integration with other business systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, marketing automation platforms, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, is crucial for streamlining sales processes and ensuring data consistency across the organization. Seamless integration allows for the efficient transfer of information between different departments, enabling sales teams to access relevant data, collaborate more effectively, and provide better customer experiences. For example, integrating CRM with marketing automation software can help track leads throughout the sales funnel and personalize marketing campaigns based on customer interactions.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation:
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle in sales management, emphasizing the importance of ongoing evaluation, learning, and adaptation. Sales teams must constantly assess their strategies, processes, and performance metrics to identify areas for enhancement and respond to changing market dynamics. This may involve conducting regular performance reviews, gathering feedback from customers and stakeholders, and staying abreast of industry trends and competitor activities. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can remain agile and competitive in today’s dynamic business environment.
Leveraging advanced techniques such as predictive analytics, optimizing sales performance metrics, integrating with other business systems, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are essential for achieving sustained success in sales management. These strategies enable organizations to make data-driven decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and stay ahead of the curve in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce CRM forecasting and pipeline management are indispensable components of a successful sales strategy. By understanding the fundamentals, leveraging advanced techniques, and embracing innovation, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and growth. With the right approach and tools in place, organizations can stay ahead of the curve in today’s competitive marketplace.
Benefits include improved accuracy in revenue predictions, better resource allocation, enhanced sales performance tracking, and increased visibility into the sales pipeline.
To set up Salesforce CRM Forecasting, you need to enable it in your Salesforce org, configure forecast settings, define forecast categories, assign forecast managers, and train users on how to use the forecasting tools.
Pipeline Management in Salesforce CRM involves tracking and managing sales opportunities as they progress through various stages of the sales cycle. It provides visibility into the sales pipeline and helps prioritize and nurture leads.
Salesforce CRM offers customizable dashboards, reports, and automation tools that enable users to track leads, opportunities, and sales activities. It also provides features like opportunity stages, sales processes, and workflow automation to streamline pipeline management.
Key metrics include the number of leads generated, conversion rates at each stage of the sales funnel, average deal size, sales cycle length, win/loss ratios, and pipeline velocity.