Introduction to AWS Hybrid Cloud Integration
Definition and Significance of Hybrid Cloud:
Imagine a world where your IT infrastructure seamlessly blends on-premises resources with the power of the cloud. This is the essence of hybrid cloud, a flexible model that combines the best of both worlds:
- On-premises resources: Offer control, security, and compliance for sensitive data or applications with specific hardware requirements.Cloud resources: Provide scalability, agility, and access to cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning.
Why is hybrid cloud gaining traction? Modern IT landscapes are complex, with diverse workloads and compliance needs. Hybrid cloud offers:
- Flexibility: Deploy applications where they make the most sense, leveraging the strengths of both on-premises and cloud environments.
- Scalability: Seamlessly scale your resources up or down in the cloud as your needs evolve, without impacting on-premises infrastructure.
- Cost-effectiveness: Optimize costs by leveraging existing on-premises resources while utilizing cloud services for specific needs.
- Disaster recovery: Improve business continuity by replicating critical data and applications to the cloud for disaster recovery.
AWS as a Hybrid Cloud Solution Provider:
AWS is a leading provider of hybrid cloud solutions, offering a comprehensive suite of services and tools to seamlessly integrate your on-premises environment with the cloud:
- AWS Direct Connect: Establishes a dedicated, private network connection between your on-premises environment and AWS, ensuring secure and reliable data transfer.
- AWS Site-to-Site VPN: Creates a secure encrypted tunnel over the public internet for connecting your on-premises network to AWS.
- AWS Storage Gateway: Connects your on-premises storage to AWS cloud storage for backup, archiving, and hybrid storage solutions.
- AWS Outposts: Brings AWS infrastructure to your on-premises environment, allowing you to run AWS services locally with the same APIs, tools, and management experience as in the cloud.
- AWS Management Console: Provides a unified platform for managing both your on-premises and cloud resources, simplifying hybrid cloud operations.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Adoption:
By embracing hybrid cloud with AWS, you can unlock numerous benefits:
- Scalability: Easily scale your infrastructure up or down to meet fluctuating demands, ensuring optimal resource utilization and cost savings.
- Agility: Rapidly deploy new applications and services by leveraging the cloud’s agility and innovation.
- Flexibility: Choose the right environment for each workload, balancing security, compliance, and performance needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: Optimize costs by leveraging existing on-premises resources and utilizing cloud services strategically.
- Disaster recovery: Enhance business continuity by replicating critical data and applications to the cloud for disaster recovery.
- Access to innovation: Benefit from AWS’s continuous innovation and access to cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning.
Hybrid cloud is not just a technology trend; it’s a strategic approach to optimize your IT infrastructure and drive business agility. With AWS as your trusted partner, you can seamlessly integrate your on-premises resources with the cloud, unlocking scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness for your organization. Remember, the hybrid cloud journey is unique to each organization. Start by assessing your specific needs and workloads, and leverage AWS’s expertise and solutions to create a hybrid cloud environment that empowers your business success.
Key Components of AWS Hybrid Cloud
Building a successful hybrid cloud environment requires seamless integration between your existing on-premises infrastructure and AWS cloud resources. This section delves into the core components that enable this integration, providing you with a deeper understanding of their functionalities and benefits.
On-Premises Infrastructure Integration:
Connecting your on-premises infrastructure with AWS is crucial for hybrid cloud adoption. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Network connectivity: Establish secure and reliable network connections between your on-premises environment and AWS. Popular options include:
- Dedicated connections:
- AWS Direct Connect: Provides a dedicated, private network connection for high-bandwidth, low-latency data transfer. Ideal for large data transfers and mission-critical applications.
VPN connections:
- AWS Site-to-Site VPN: Creates a secure encrypted tunnel over the public internet, suitable for moderate data transfer needs and flexible deployment options.
- AWS Client VPN: Enables secure remote access to your on-premises resources from various devices.
- Data transfer: Utilize services like AWS DataSync or AWS Transfer Family to efficiently migrate and synchronize data between on-premises and cloud storage.
- Management tools: Leverage tools like AWS Management Console and AWS CloudTrail for centralized management and monitoring of both on-premises and cloud resources.
AWS Direct Connect:
For high-performance and secure connectivity, AWS Direct Connect shines. Here’s why you should consider it:
Benefits:
- Dedicated connection: Ensures consistent performance and low latency compared to public internet connections.
- Security: Provides a private network connection, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Scalability: Supports diverse bandwidth options to cater to your specific needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers significant cost savings for large and frequent data transfers compared to internet-based options.
Setup:
- Partner with a service provider: Collaborate with an AWS Direct Connect partner to establish a physical connection between your on-premises network and an AWS Direct Connect location.
- Configure your connection: Define your desired bandwidth and security settings within the AWS Management Console.
- Route your traffic: Configure routing protocols on your on-premises network to direct traffic destined for AWS through the Direct Connect connection.
Use Cases:
- Large data transfers: Ideal for migrating large datasets, replicating critical data for disaster recovery, or transferring big data workloads to the cloud.
- Mission-critical applications: Ensures reliable and predictable network performance for applications requiring low latency and high availability.
- Cloud-based storage access: Enables seamless access to cloud storage like Amazon S3 for on-premises applications with high data transfer needs.
Remember:
Direct Connect is a cost-effective solution for high-bandwidth scenarios but requires upfront investment and technical expertise for setup.
Evaluate your data transfer needs and budget before choosing Direct Connect.
AWS VPN (Virtual Private Network):
For a more flexible and cost-effective option, AWS VPNs offer secure communication over the public internet. Here’s what you need to know:
Types of VPNs:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Creates a secure tunnel between your on-premises network and a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) in AWS.
- Client VPN: Enables secure remote access to your on-premises resources from individual devices.
Benefits:
- Flexibility: Easy to set up and manage, ideal for smaller data transfers or remote access needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: No upfront investment required compared to Direct Connect.
- Scalability: Supports various bandwidth options to accommodate changing needs.
Setup:
- Configure your VPC: Create a VPC in AWS and configure security groups to allow specific traffic through the VPN tunnel.
- Establish the VPN connection: Use the AWS Management Console or CLI to configure the VPN connection settings and connect to your on-premises network.
Use Cases:
- Moderate data transfers: Suitable for migrating smaller datasets, replicating less critical data, or connecting to cloud resources from specific on-premises applications.
- Remote access: Enables secure remote access to on-premises resources for employees or IT staff working outside the office.
- Hybrid cloud deployments: Provides a secure connection for hybrid applications that span both on-premises and cloud environments.
Remember:
- VPNs rely on the public internet, so latency and performance might be slightly higher than dedicated connections.
- Evaluate your security requirements and data transfer needs when choosing between Site-to-Site VPN and Client VPN.
Integrating your on-premises infrastructure with AWS unlocks the potential of hybrid cloud. By understanding the key components like Direct Connect and VPNs, you can choose the right solution for your specific needs and build a secure, scalable, and cost-effective hybrid cloud environment that empowers your business to innovate and thrive. Remember, hybrid cloud is an ongoing journey, not a one-time destination. Continuously evaluate your needs, explore new technologies, and leverage AWS’s expertise to optimize your hybrid cloud strategy for long-term success.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture Design
Building a robust and effective hybrid cloud requires careful architectural planning. This section delves into three crucial aspects of hybrid cloud design: multi-cloud integration, workload distribution, and high availability/disaster recovery (HA/DR).
Multi-Cloud Integration:
Modern organizations often leverage multiple cloud providers for diverse needs. Hybrid cloud enables integrating these cloud environments with your on-premises infrastructure, creating a unified IT landscape. Here’s how:
Benefits:
- Flexibility: Access specialized services from different cloud providers while maintaining on-premises control.
- Vendor lock-in avoidance: Prevent being tied to a single vendor, ensuring access to the best solutions for each need.
- Cost optimization: Leverage the most competitive pricing offerings across different cloud services.
Integration Approaches:
- API integrations: Utilize public APIs provided by each cloud platform to exchange data and manage resources.
- Cloud management platforms (CMPs): Leverage tools like AWS CloudFormation or HashiCorp Terraform to manage infrastructure and resources across multiple clouds.
- Network connectivity: Establish secure connections between your on-premises environment and each cloud provider using Direct Connect or VPNs.
Security Considerations:
- Implement consistent security policies and access controls across all environments.
- Utilize identity and access management (IAM) solutions for centralized user authentication and authorization.
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit to ensure data privacy and compliance.
Use Cases:
- Utilize AI/ML services from one cloud provider while leveraging cost-effective storage from another.
- Run specific applications on a particular cloud based on unique resource requirements.
- Maintain on-premises control for sensitive data while leveraging cloud services for non-critical workloads.
Remember:
- Multi-cloud can add complexity, so start with a clear strategy and choose integration methods that align with your needs and expertise.
Scalable and Flexible Workload Distribution:
Effectively distributing workloads across your hybrid environment is crucial for optimal performance and resource utilization. Consider these strategies:
- Workload assessment: Analyze your applications and workloads, identifying their resource requirements, scalability needs, and latency sensitivity.
- Right-sizing resources: Choose the appropriate deployment environment (on-premises, cloud, or both) based on workload characteristics.
- Hybrid containerization: Containerize applications for flexibility and portability, enabling seamless movement between environments.
- Auto-scaling: Implement automated scaling mechanisms to scale resources up or down based on demand, optimizing resource utilization.
Benefits:
- Cost optimization: Avoid overprovisioning by utilizing resources strategically across both environments.
- Improved performance: Match workloads to the most suitable environment for optimal performance and scalability.
- Disaster recovery: Distribute critical workloads across geographically diverse locations for better resilience.
Considerations:
- Network latency: Minimize latency between interconnected environments to avoid performance bottlenecks.
- Data management: Implement consistent data access and replication strategies for workloads spanning multiple environments.
- Monitoring and analytics: Monitor performance and resource utilization across your entire hybrid environment.
Use Cases:
- Run stateless microservices in the cloud for scalability, while keeping data-intensive applications on-premises.
- Deploy seasonal workloads in the cloud to handle temporary spikes in demand without impacting on-premises resources.
- Offload batch processing jobs to the cloud for cost-effective and scalable execution.
Remember:
- Workload distribution is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor your environment and adapt your strategy as your needs and workloads evolve.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery Planning:
Ensuring continuous operations and data recovery in case of failures is paramount for any IT infrastructure. In a hybrid cloud, consider these approaches:
- Redundancy: Deploy redundant resources (hardware, software, data) across multiple locations, both on-premises and in the cloud.
- Disaster recovery (DR) plan: Develop a comprehensive plan for responding to outages, including failover procedures and data recovery methods.
- Disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS): Leverage cloud-based DRaaS solutions for automated failover and recovery to the cloud.
- Backup and replication: Regularly back up critical data and replicate it to a secondary location, either on-premises or in the cloud.
Benefits:
- Minimized downtime: Ensure business continuity even during disruptions by quickly recovering from failures.
- Data protection: Safeguard critical data from loss or corruption through robust backup and recovery practices.
- Improved peace of mind: Operate with confidence knowing you have a plan to manage unexpected events.
Considerations:
- Recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs): Define acceptable limits for downtime and data loss to guide your DR strategy.
- Testing and validation: Regularly test your DR plan and recovery procedures to ensure their effectiveness.
Designing a robust hybrid cloud architecture requires careful consideration of multi-cloud integration, workload distribution, and high availability. By understanding these key aspects and implementing appropriate strategies, you can build a secure, scalable, and resilient hybrid cloud environment that empowers your business to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape. Remember, your hybrid cloud journey is unique, and continuous adaptation and improvement are key to long-term success
Data Management and Storage in a Hybrid Environment
In a hybrid cloud, seamless data management and storage are crucial for ensuring accessibility, consistency, and protection. This section explores key strategies and best practices for navigating data management in your hybrid cloud environment.
Hybrid Cloud Storage Solutions:
Leverage AWS storage services to bridge the gap between your on-premises infrastructure and the cloud, enabling:
- Centralized Storage: Consolidate data in a single, accessible location with services like Amazon S3 for object storage or Amazon EBS for block storage.
- Hybrid Storage Options: Combine on-premises storage with cloud storage through solutions like AWS Storage Gateway, enabling seamless data transfer and hybrid file/block storage options.
- Data Lakes and Analytics: Utilize services like Amazon S3 Glacier for cost-effective data archiving and Amazon Redshift for scalable data warehousing and analytics across your hybrid data landscape.
Benefits:
- Scalability: Scale storage capacity up or down effortlessly to meet fluctuating data demands.
- Disaster Recovery: Replicate data to the cloud for robust disaster recovery capabilities.
- Accessibility: Access data from anywhere with an internet connection, improving collaboration and flexibility.
Choose the right storage solution based on data type, access patterns, and cost requirements.
Implement proper security controls and access governance for all storage resources.
Data Replication and Synchronization:
Maintaining data consistency between on-premises and cloud storage is essential. Explore these options:
- AWS DataSync: Offers high-speed data transfers for large datasets, ideal for initial migrations or bulk data movement.
- AWS Storage Gateway: Enables continuous data replication between on-premises storage and cloud storage for near real-time updates.
- Third-party tools: Consider tools like Veeam or Rubrik for additional replication and orchestration capabilities.
Benefits:
- Ensures data consistency across environments for accurate analytics and decision-making.
- Minimizes data loss risk by maintaining redundant copies in both on-premises and cloud storage.
Backup and Recovery Best Practices:
Effective backup and recovery strategies are crucial for mitigating data loss risks:
- Regular backups: Implement automated backups for both on-premises and cloud data, considering different backup frequencies based on data criticality.
- Multiple backup targets: Utilize a combination of on-premises storage, cloud storage, and tape backups for added redundancy and disaster recovery options.
- Regular testing: Conduct backup and recovery tests periodically to ensure they function as expected during emergencies.
- Version control: Implement version control for critical data to revert to previous versions if necessary.
Benefits:
- Minimizes downtime and data loss in case of system failures or cyberattacks.
- Ensures business continuity and data availability during unplanned events.
By implementing these strategies and best practices, you can ensure efficient data management, seamless storage solutions, and robust data protection in your hybrid cloud environment. Remember, a well-defined data management plan is vital for maximizing the potential of your hybrid cloud and fostering data-driven decision making within your organization.
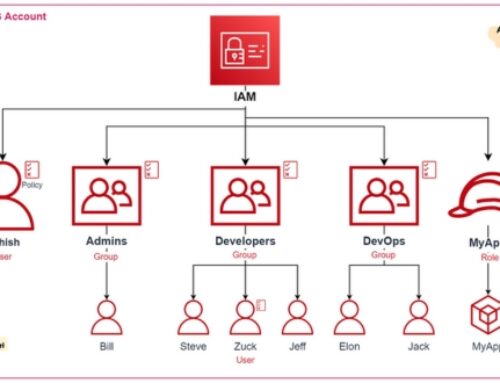
Identity and Access Management (IAM) for Hybrid Cloud
In a hybrid cloud environment, where resources span both on-premises and cloud platforms, managing user access and permissions securely and efficiently becomes paramount. This section dives into key IAM considerations for your hybrid cloud setup.
IAM Best Practices:
- Least privilege principle: Grant users only the minimum access required to perform their tasks, minimizing potential attack surfaces.
- Strong password policies: Enforce strong password complexity requirements and regular password rotations.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all user accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Regular user reviews: Regularly review and update user access permissions based on changing roles and responsibilities.
- Centralized logging and monitoring: Monitor user activity and access attempts across your hybrid environment to detect suspicious behavior.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration:
SSO streamlines user authentication by allowing users to log in once and access multiple resources with consistent credentials. This offers:
- Improved user experience: Eliminates the need for multiple logins, enhancing user convenience and productivity.
- Enhanced security: Reduces the risk of password fatigue and compromised credentials.
- Centralized access management: Simplifies user provisioning and deprovisioning across different environments.
Consider cloud-based SSO solutions like AWS Single Sign-On or Azure Active Directory to manage access across both on-premises and cloud resources.
Security Considerations in IAM:
- Identity provider selection: Choose an IAM solution that integrates seamlessly with your existing identity infrastructure and offers robust security features.
- Data encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Vulnerability management: Regularly patch and update your IAM systems to address potential security vulnerabilities.
- Compliance requirements: Ensure your IAM practices comply with relevant industry regulations and data privacy laws.
Remember:
- IAM is an ongoing process, not a one-time setup. Continuously evaluate your IAM strategy and adapt it to evolving security threats and business needs.
- Leverage tools and best practices from both AWS and on-premises identity management solutions to create a comprehensive and secure hybrid IAM environment.
By implementing these best practices and considerations, you can ensure secure and efficient identity and access management across your hybrid cloud, fostering a productive and secure environment for your users and data.
Networking Solutions for AWS Hybrid Cloud
Robust networking is the foundation of any successful hybrid cloud environment. Here are three key solutions to consider for seamless and secure connectivity:
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) Configuration:
- Designate private networks within AWS using VPCs, replicating your on-premises network structure for familiar management.
- Establish secure connections between VPCs and your on-premises network using Direct Connect, VPNs, or AWS Transit Gateway.
- Implement subnet segmentation for granular network security and traffic control within each VPC.
Hybrid DNS (Domain Name System) Management:
- Ensure consistent domain resolution across hybrid environments by integrating your on-premises DNS server with AWS Route 53.
- Leverage Route 53 features like private hosted zones and health checks for secure and reliable DNS resolution within your VPCs.
- Consider managed DNS solutions like AWS Route 53 Resolver for simplified DNS management and improved security.
Load Balancing Across Hybrid Infrastructure:
- Utilize Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) to distribute incoming traffic across multiple resources, ensuring high availability and scalability in your hybrid cloud.
- Configure ELBs within your VPCs to manage traffic for applications running on both AWS and on-premises resources.
- Consider AWS Network Load Balancer (NLB) for high-performance, low-latency load balancing across your hybrid infrastructure.
Remember:
- Choose the right networking solutions based on your specific needs, security requirements, and traffic volume.
- Leverage AWS tools and services to simplify hybrid networking management and optimize performance.
- Continuously monitor and adapt your network configuration as your hybrid cloud environment evolves.
By implementing these solutions, you can establish a robust and secure hybrid cloud network, ensuring efficient and reliable connectivity for your applications and services.
Monitoring and Optimization in AWS Hybrid Cloud
Maintaining optimal performance and cost-efficiency is crucial in any hybrid cloud environment. This section highlights two key aspects for success:
CloudWatch Integration for Hybrid Cloud Monitoring:
- Gain unified visibility into your entire hybrid infrastructure by integrating AWS CloudWatch with your on-premises monitoring tools.
- Collect metrics from both your on-premises resources and AWS services for centralized monitoring and analysis.
- Utilize CloudWatch dashboards and alerts to proactively identify and address performance issues across your hybrid environment.
Optimization Strategies for Cost Efficiency:
- Right-size your resources: Select the most cost-effective AWS instances and services based on your workload requirements.
- Utilize reserved instances and savings plans: Take advantage of reserved instances and savings plans to reduce costs for predictable workloads.
- Leverage auto-scaling: Enable auto-scaling for resources to automatically adjust based on demand, avoiding unnecessary costs during low usage periods.
- Monitor and optimize resource utilization: Analyze resource usage patterns and identify opportunities to optimize resource allocation and avoid overspending.
Remember:
- Monitoring and optimization are ongoing processes. Regularly review your metrics and implement adjustments to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Leverage AWS cost management tools and expertise to identify further optimization opportunities and maximize your return on investment.
By implementing these strategies, you can gain comprehensive insights into your hybrid cloud environment, proactively address performance issues, and optimize your resource utilization for cost efficiency, ensuring a healthy and sustainable hybrid cloud infrastructure for your organization.
Future Trends in AWS Hybrid Cloud Integration
The hybrid cloud landscape is constantly evolving, fueled by cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions. This section delves into two key areas to keep your eyes on:
Evolving Technologies:
- Multi-cloud orchestration: Simplifying management across multiple cloud providers with unified platforms and tools.
- Edge computing integration: Bringing cloud capabilities closer to edge devices for real-time processing and reduced latency.
- AI and ML-powered automation: Automating hybrid cloud tasks for increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Serverless computing advancements: Expanding serverless functionalities and hybrid deployment options for a wider range of workloads.
- Security advancements: Enhanced security solutions tailored for hybrid environments, addressing evolving cyber threats.
AWS Service Evolution:
- Expansion of hybrid-specific services: Expect more AWS services specifically designed for seamless hybrid cloud integration and management.
- Enhanced multi-cloud support: Continued improvements in tools and functionalities for managing workloads across multiple cloud providers.
- Focus on developer experience: Simplifying hybrid cloud development with developer-friendly tools and frameworks.
- Security-first approach: Integration of advanced security features into core AWS services, ensuring comprehensive protection for hybrid environments.
- Focus on data management: Continued development of robust data management solutions for hybrid cloud environments, addressing data privacy and compliance concerns.
By understanding these future trends and AWS’s service evolution, you can make informed decisions and optimize your hybrid cloud strategy for long-term success.
Conclusion: Achieving Synergy with AWS Hybrid Cloud Integration
The journey to hybrid cloud adoption starts with a vision, fueled by the need for flexibility, scalability, and the desire to unlock new opportunities. By leveraging AWS’s comprehensive suite of services and tools, you can seamlessly integrate your on-premises infrastructure with the cloud, creating a synergistic environment that empowers your organization to thrive.
This exploration has provided a glimpse into the key components of building a robust hybrid cloud with AWS, from multi-cloud integration and workload distribution to data management and security. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, and the optimal roadmap depends on your unique needs and aspirations.
As you embark on this journey, embrace the continuous evolution of hybrid cloud technologies. Experiment with emerging trends, stay informed about AWS’s service advancements, and leverage their expertise to optimize your strategy.
Remember, the true value of hybrid cloud lies in achieving synergy. It’s not just about connecting components; it’s about harmonizing your entire IT landscape to empower innovation, drive agility, and unlock the full potential of your data.
With AWS as your trusted partner, you can confidently navigate the hybrid cloud journey, turning synergies into tangible business success. By embracing this transformation, you’ll be well-positioned to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape, leaving the limitations of yesterday behind and embracing the boundless possibilities of tomorrow.