Introduction: Ensuring Microsoft 365 Data Protection
In the dynamic landscape of modern business operations, the reliance on digital data is more pronounced than ever. Microsoft 365, a pivotal platform for collaboration and productivity, houses a wealth of critical information—from emails in Exchange Online to documents in SharePoint and OneDrive. Recognizing the paramount importance of this data, ensuring its protection through robust backup and recovery strategies is not just a best practice; it is a business imperative.
The Significance of Microsoft 365 Data Protection
In the Digital Age: As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud-based Microsoft 365 ecosystem, safeguarding sensitive information against potential threats becomes paramount. The sheer volume and diversity of data generated and stored within Microsoft 365 necessitate a comprehensive approach to data protection.
Business Continuity: Disruptions, whether due to accidental deletions, cyberattacks, or system failures, can have far-reaching consequences. An effective data backup and recovery strategy ensures that even in the face of unforeseen events, business operations can swiftly resume without compromising critical data.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with data protection regulations is a cornerstone of responsible business practices. Whether it be GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards, Microsoft 365 data protection measures play a crucial role in meeting and exceeding these regulatory requirements.
Understanding Microsoft 365 Data Architecture

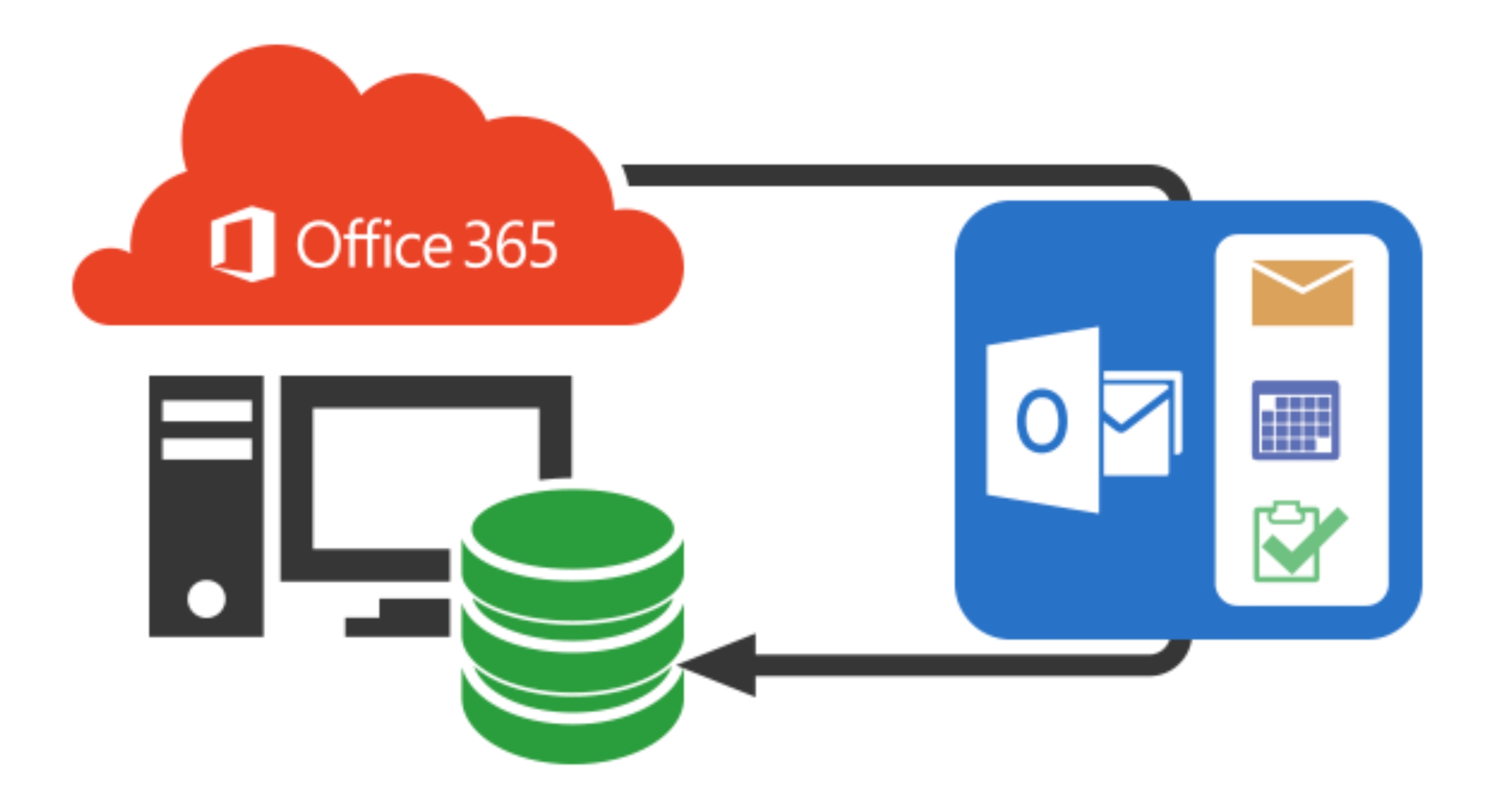
In the vast expanse of Microsoft 365, data architecture forms the foundational structure that dictates how information is stored, managed, and accessed across the platform. To comprehend the intricacies of data backup and recovery, it is essential to embark on a journey through the architecture that underpins the digital bedrock of Microsoft 365.
Overview of Data Storage in Microsoft 365
- Cloud-Based Paradigm: Microsoft 365 embraces a cloud-centric approach, where data is stored in secure, scalable cloud environments. This departure from traditional on-premises solutions not only fosters accessibility but also redefines the dynamics of data resilience and redundancy.
- Core Entities: Within this cloud-based ecosystem, three primary entities encapsulate the diverse array of digital assets:
- Exchange Online: The epicenter of email communication. Exchange Online stores emails, attachments, contacts, and calendars, forming the lifeblood of organizational communication.
- SharePoint: A collaborative workspace that serves as a repository for documents, lists, and libraries. SharePoint’s versatility makes it a hub for team collaboration and information dissemination.
- OneDrive: An individualized cloud storage space where users store and manage personal files. OneDrive ensures seamless access to files from any device, promoting flexibility in data utilization.
Importance of Data Backup in Microsoft 365
As organizations entrust their critical operations to the digital realm of Microsoft 365, acknowledging the inherent risks and prioritizing data backup becomes paramount. In this exploration, we dissect the significance of data backup by scrutinizing the risks of data loss within Microsoft 365 and unveiling the interconnected considerations of business continuity and regulatory compliance.
Risks of Data Loss in Microsoft 365
- Accidental Deletion: In the collaborative landscape of Microsoft 365, accidental deletion is an ever-present threat. Whether it’s an email from Exchange Online, a document from SharePoint, or a file from OneDrive, the ease of data removal can lead to irrevocable losses.
- Cybersecurity Threats: The modern era is fraught with cybersecurity challenges. Ransomware attacks, phishing attempts, and other malicious activities pose substantial threats to data integrity within Microsoft 365. Without robust backup measures, organizations risk falling victim to these digital menaces.
- System Failures: Despite the resilient architecture of Microsoft 365, unforeseen system failures can occur. Hardware malfunctions, software glitches, or disruptions in service can result in data loss if not countered with comprehensive backup strategies.
Business Continuity and Compliance Considerations
- Uninterrupted Operations: Data is the lifeblood of organizational operations. Without a robust backup system, the loss of critical data can lead to disruptions in business processes, affecting productivity, customer service, and overall organizational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data protection regulations is not just a legal necessity but a testament to ethical business practices. Many industries have stringent compliance requirements, and Microsoft 365 data backup is instrumental in meeting these standards, ensuring that sensitive information is safeguarded and retrievable when needed.
Microsoft 365 Native Data Protection Features

Within the expansive realm of Microsoft 365, a robust suite of native data protection features stands as a formidable guardian against the perils of data loss. In this section, we unravel the intricacies of these built-in defenses, focusing on the auto-save and versioning capabilities in SharePoint and OneDrive, as well as the deleted item retention feature in Exchange Online.
Auto-Save and Versioning in SharePoint and OneDrive
- Auto-Save in OneDrive:
- Continuous Updates: OneDrive employs an auto-save mechanism, ensuring that changes to documents are automatically saved as users work, minimizing the risk of data loss due to unexpected interruptions.
- Real-time Collaboration: The auto-save feature fosters real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to edit documents concurrently with seamless synchronization.
- Versioning in SharePoint:
- Historical Document States: SharePoint’s versioning feature maintains a historical record of document changes. Each version is preserved, offering a chronological snapshot of the document’s evolution.
- Recovery Options: In case of accidental deletions or undesired edits, users can revert to a previous version, mitigating the impact of data loss incidents.
Deleted Item Retention in Exchange Online
- Retention Periods:
- Short-Term Retention: Deleted items, including emails and attachments, are retained in the Deleted Items folder for a specific period, allowing users to recover accidentally deleted content.
- Long-Term Retention: Beyond the initial retention period, Exchange Online provides extended, long-term retention options, safeguarding against permanent data loss.
- Litigation Hold:
- Legal Compliance: Exchange Online includes Litigation Hold, a feature designed for legal and compliance purposes. It ensures that deleted items are preserved, even if users attempt to permanently delete them.
Third-Party Backup Solutions

While Microsoft 365 offers robust native data protection features, augmenting these capabilities with third-party backup solutions provides an additional layer of security and flexibility. In this section, we delve into the landscape of third-party backup tools, exploring their key features, the benefits they bring to the table, and identifying popular providers in the Microsoft 365 backup solutions arena.
Overview of Third-Party Backup Tools
- Comprehensive Backup Coverage:
- Beyond Native Features: Third-party solutions extend backup coverage beyond the native capabilities of Microsoft 365, providing a holistic approach to data protection.
- Diverse Data Types: These tools often support a wide array of data types, including emails, documents, calendars, and more, ensuring comprehensive coverage for diverse organizational needs.
- Automated Backup Processes:
- Scheduled Backups: Many third-party solutions offer automated, scheduled backups, reducing manual intervention and ensuring regular, consistent protection.
- Incremental Backups: Incremental backup methodologies optimize storage space by only capturing changes made since the last backup, enhancing efficiency.
Benefits of Using Third-Party Solutions
- Enhanced Security:
- Encryption Protocols: Third-party backup providers often employ advanced encryption protocols, ensuring the secure transmission and storage of sensitive data.
- Access Controls: Granular access controls provide organizations with the ability to define who can access and manage backup data, enhancing security.
- Flexibility and Scalability:
- Tailored Configurations: Organizations can tailor backup configurations to align with specific data retention policies and compliance requirements.
- Scalability: These solutions scale seamlessly with organizational growth, accommodating increased data volumes and evolving backup needs.
Popular Third-Party Backup Providers
- Veeam:
- Comprehensive Suite: Veeam offers a comprehensive suite of backup and recovery solutions, catering to Microsoft 365’s various components.
- User-Friendly Interface: Known for its user-friendly interface, Veeam simplifies the backup process for administrators.
- Datto SaaS Protection:
- Automated Backup: Datto provides automated backup and recovery for Microsoft 365 applications, emphasizing ease of use and efficiency.
- Point-in-Time Restoration: Users can restore data to specific points in time, enabling precision in data recovery.
- Spanning:
- Cross-Platform Coverage: Spanning supports multiple cloud platforms, including Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Google Workspace, offering cross-platform coverage.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and alerts enhance proactive management of backup processes.
Best Practices for Data Backup in Microsoft 365
Implementing a robust data backup strategy within Microsoft 365 requires more than just choosing the right tools—it demands a thoughtful approach that aligns with organizational needs. In this section, we delve into best practices that encompass regular backup schedules, data classification and prioritization, and the critical testing of backup and recovery processes.
Regular Backup Schedules
- Frequency:
Establish regular backup schedules based on the criticality and volatility of data. High-frequency backups may be essential for real-time collaboration platforms, while less dynamic data can be backed up less frequently.
- Automated Scheduling:
Leverage automated scheduling features provided by backup solutions. Automation reduces the risk of human error and ensures consistency in adherence to backup timelines.
- Retention Policies:
Define retention policies that align with compliance requirements and organizational needs. Different types of data may necessitate varied retention periods.
Data Classification and Prioritization
- Understand Data Types:
Conduct a thorough assessment of data types within Microsoft 365. Understand the nature and sensitivity of each data category, from emails and documents to collaborative content.
- Categorize by Criticality:
Categorize data based on criticality to business operations. High-priority data, such as financial records or legal documents, should be accorded higher backup frequency and retention.
- Compliance Considerations:
Consider regulatory compliance requirements when classifying data. Certain data may have specific retention or protection mandates that influence backup practices.
Testing Backup and Recovery Processes
- Simulate Real-world Scenarios:
Regularly simulate real-world scenarios to test the efficacy of backup and recovery processes. This includes scenarios such as accidental deletions, system failures, or cyberattacks.
- Document and Analyze Results:
Document the results of each testing scenario and analyze the effectiveness of the backup and recovery processes. Identify areas for improvement and refinement.
- Incorporate User Feedback:
Solicit feedback from end-users who may be involved in data recovery processes. Incorporating their insights can enhance the usability and efficiency of the overall backup strategy.
Data Recovery Strategies in Microsoft 365
While data loss incidents are inevitable, Microsoft 365 empowers organizations with robust data recovery strategies. In this section, we delve into granular item recovery options within Exchange Online, SharePoint, and OneDrive, as well as explore comprehensive full account recovery measures.
Granular Item Recovery in Exchange Online, SharePoint, and OneDrive
- Exchange Online:
- Deleted Item Retention: Exchange Online retains deleted items in the Deleted Items folder for a specified period. Users can recover accidentally deleted emails, contacts, and other elements during this retention window.
- Recoverable Items Folder: For items deleted from the Deleted Items folder, the Recoverable Items folder provides an additional layer of recovery, allowing users to restore items even after the initial retention period.
- SharePoint:
- Version History: SharePoint’s version history feature enables granular recovery by maintaining a chronological record of document changes. Users can revert to previous versions, mitigating the impact of undesired edits or deletions.
- Recycle Bin: Deleted documents in SharePoint are initially moved to the Recycle Bin, providing a recovery window before permanent deletion.
- OneDrive:
- OneDrive Recycle Bin: Similar to SharePoint, OneDrive maintains a Recycle Bin where deleted files are temporarily stored. Users can recover files from this bin within a specific timeframe.
- Versioning: OneDrive supports versioning, allowing users to restore previous versions of documents, providing a safety net against unintended changes.
Full Account Recovery Options
- Account Restoration in Exchange Online:
- Deleted Mailbox Retention: In Exchange Online, deleted mailboxes are retained for a limited period. During this retention period, administrators can restore the entire mailbox, including emails, contacts, and calendar items.
- Inactive Mailboxes: Even after a mailbox is deleted, it can be retained as an inactive mailbox for compliance purposes.
- SharePoint and OneDrive:
- Site and User Deletion Recovery: SharePoint and OneDrive administrators have the capability to restore deleted sites and user accounts within a specified retention period.
Common Data Recovery Challenges and Solutions
Data recovery within Microsoft 365 is not without its challenges. Understanding and proactively addressing these challenges are essential elements of a comprehensive data management strategy. In this section, we explore common data recovery challenges, focusing on accidental data deletion and recovery, as well as the restoration of corrupted files.
Accidental Data Deletion and Recovery
Challenge: Accidental Deletion:
Human Error: Users may inadvertently delete critical emails, documents, or files, leading to potential data loss.
Retention Period Limitations: Relying solely on native retention periods may pose challenges, especially when users realize the deletion after the retention window has closed.
Solution: Granular Recovery Options:
Educate Users: Training users on the importance of cautious data management can mitigate accidental deletions.
Leverage Native Recovery Options: Utilize built-in recovery features such as the Recoverable Items folder in Exchange Online and the Recycle Bin in SharePoint and OneDrive for granular item recovery.
Restoring Corrupted Files
Challenge: Corrupted Files:
Document Edits Gone Awry: Unintended changes or edits to documents may result in file corruption.
External Factors: Viruses, malware, or software glitches can corrupt files stored in Microsoft 365.
Solution: Versioning and External Backup:
Leverage Versioning: Encourage users to make use of versioning in SharePoint and OneDrive. This allows for the restoration of previous versions in case of file corruption.
External Backup Solutions: Implement third-party backup solutions that offer versioning and additional protections against file corruption.
Monitoring and Auditing for Data Protection
In the dynamic landscape of Microsoft 365, robust data protection goes hand in hand with vigilant monitoring and auditing. In this section, we explore the native auditing features within Microsoft 365, emphasizing the importance of actively monitoring data activities to enhance overall data protection.
Microsoft 365 Auditing Features
- Audit Logs: Microsoft 365 offers comprehensive audit logs that capture a range of user and admin activities. This includes logins, document access, permission changes, and more.
- Security and Compliance Center: The Security and Compliance Center provides a centralized hub for managing and accessing audit logs, offering granular insights into data-related actions.
Importance of Monitoring Data Activities
- Proactive Threat Detection: Monitoring data activities enables organizations to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. Unusual patterns of access or suspicious activities can be identified promptly.
- Compliance Assurance: Meeting regulatory requirements necessitates ongoing monitoring. Regular audits ensure that data protection practices align with industry standards and legal obligations.
- User Accountability: Monitoring activities fosters a culture of user accountability. Knowing that actions are tracked encourages responsible behavior among users.
Conclusion: Navigating the Data Protection Landscape in Microsoft 365
As organizations continue to embrace the collaborative and dynamic environment of Microsoft 365, the imperative of safeguarding digital assets has never been more crucial. This comprehensive guide has navigated the intricate landscape of data protection within Microsoft 365, providing insights into key facets such as data backup, recovery strategies, and proactive monitoring.
Holistic Approach to Data Protection
From the foundational understanding of Microsoft 365 data architecture to the exploration of native and third-party backup solutions, organizations are equipped with a holistic understanding of safeguarding data. The importance of regular backup schedules, data classification, and thorough testing of recovery processes underscore the proactive measures necessary for robust data protection.
Navigating Recovery Challenges
Common challenges in data recovery, such as accidental deletions and file corruption, have been addressed with practical solutions. Granular recovery options within Exchange Online, SharePoint, and OneDrive, coupled with full account recovery measures, empower organizations to navigate the complexities of data loss incidents effectively.
Monitoring and Auditing Vigilance
The guide emphasizes the significance of monitoring and auditing in the proactive protection of data. Microsoft 365’s robust auditing features enable organizations to stay ahead of potential threats, maintain compliance, and foster a culture of user accountability.
Looking Forward: Empowering Microsoft 365 Users
As we conclude this journey through data protection in Microsoft 365, the aim is to empower organizations to proactively secure their digital assets. By leveraging the insights, best practices, and strategies outlined in this guide, users can confidently navigate the evolving landscape of data management within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
In an era where data is not just a commodity but a strategic asset, embracing a comprehensive data protection strategy is not just a necessity but a competitive advantage. May this guide serve as a beacon, guiding organizations toward a resilient and proactive approach to data protection within Microsoft 365.
The frequency of data backups depends on factors like the criticality and volatility of your data. For real-time collaboration platforms, consider more frequent backups. Establish automated schedules and retention policies based on your organizational needs.
Microsoft 365 offers native features like auto-save, versioning, and retention, but third-party backup solutions provide additional layers of security, flexibility, and comprehensive coverage. Third-party tools often include features like automated scheduling, advanced encryption, and support for various data types.
Microsoft 365 provides granular recovery options. For example, in Exchange Online, use the Recoverable Items folder for deleted emails. In SharePoint and OneDrive, items go to the Recycle Bin before permanent deletion. Educate users on native recovery features to minimize accidental data loss.
Best practices include establishing regular backup schedules, classifying and prioritizing data, and testing backup and recovery processes. Regularly simulate real-world scenarios, document results, and incorporate user feedback. These practices enhance the effectiveness of your data recovery strategy.
Microsoft 365 provides robust auditing features. Use audit logs and the Security and Compliance Center to monitor user and admin activities. Actively monitor data activities for proactive threat detection, compliance assurance, and fostering a culture of user accountability.