Introduction:
QuickBooks is a widely used accounting software that has revolutionized how businesses manage their financial transactions. Designed for small and medium-sized enterprises, QuickBooks offers a comprehensive suite of tools for accounting, bookkeeping, and financial management. In this overview, we will delve into the key features and functionalities that make QuickBooks an indispensable tool for businesses of all sizes.
Overview of QuickBooks:
QuickBooks, developed by Intuit, is a cloud-based accounting software that simplifies the complex task of financial management for businesses. With user-friendly interfaces and intuitive features, QuickBooks allows users to effortlessly handle tasks such as invoicing, expense tracking, payroll processing, and more. The software is designed to streamline financial processes, saving time and reducing the likelihood of errors. QuickBooks comes in various versions, including Online, Desktop, and Self-Employed, catering to the diverse needs of different business models.
QuickBooks’ core functionalities include the ability to create and send professional invoices, track income and expenses, generate financial reports, and seamlessly integrate with other business applications. Additionally, it supports multi-user access, enabling collaboration among team members. The platform’s adaptability makes it suitable for a wide range of industries, from retail and service-oriented businesses to freelancers and consultants.
Importance of Financial Reporting:
Financial reporting is a critical aspect of business management, providing insights into the financial health and performance of an organization. QuickBooks plays a pivotal role in facilitating accurate and timely financial reporting, empowering businesses to make informed decisions. The software generates various financial reports, such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, offering a comprehensive view of the company’s financial position.
Accurate financial reporting enables businesses to assess profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions for future growth. QuickBooks’ reporting capabilities help users track key performance indicators, monitor trends, and comply with regulatory requirements. The importance of financial reporting extends beyond internal decision-making, as it also serves external stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and government agencies.
QuickBooks serves as a powerful ally for businesses seeking efficient financial management. Its user-friendly interface, diverse functionalities, and robust reporting capabilities make it an indispensable tool for organizations looking to streamline their accounting processes and gain valuable insights into their financial performance.
Getting Started with QuickBooks
QuickBooks is a widely used accounting software that helps businesses manage their financial transactions efficiently. Before diving into its features, it’s essential to follow a systematic approach to set up and configure QuickBooks for your specific needs. This process involves several key steps, including setting up the software, defining your Chart of Accounts, and connecting your bank accounts.
Setting Up QuickBooks
The initial step in using QuickBooks is setting up the software on your computer. This involves installing the application and creating a new company file or opening an existing one. During the setup process, you’ll be prompted to input crucial information such as your company name, industry, and business type. Additionally, you’ll need to choose your fiscal year and accounting method. Accurate setup ensures that QuickBooks aligns with your business structure and requirements.
Chart of Accounts
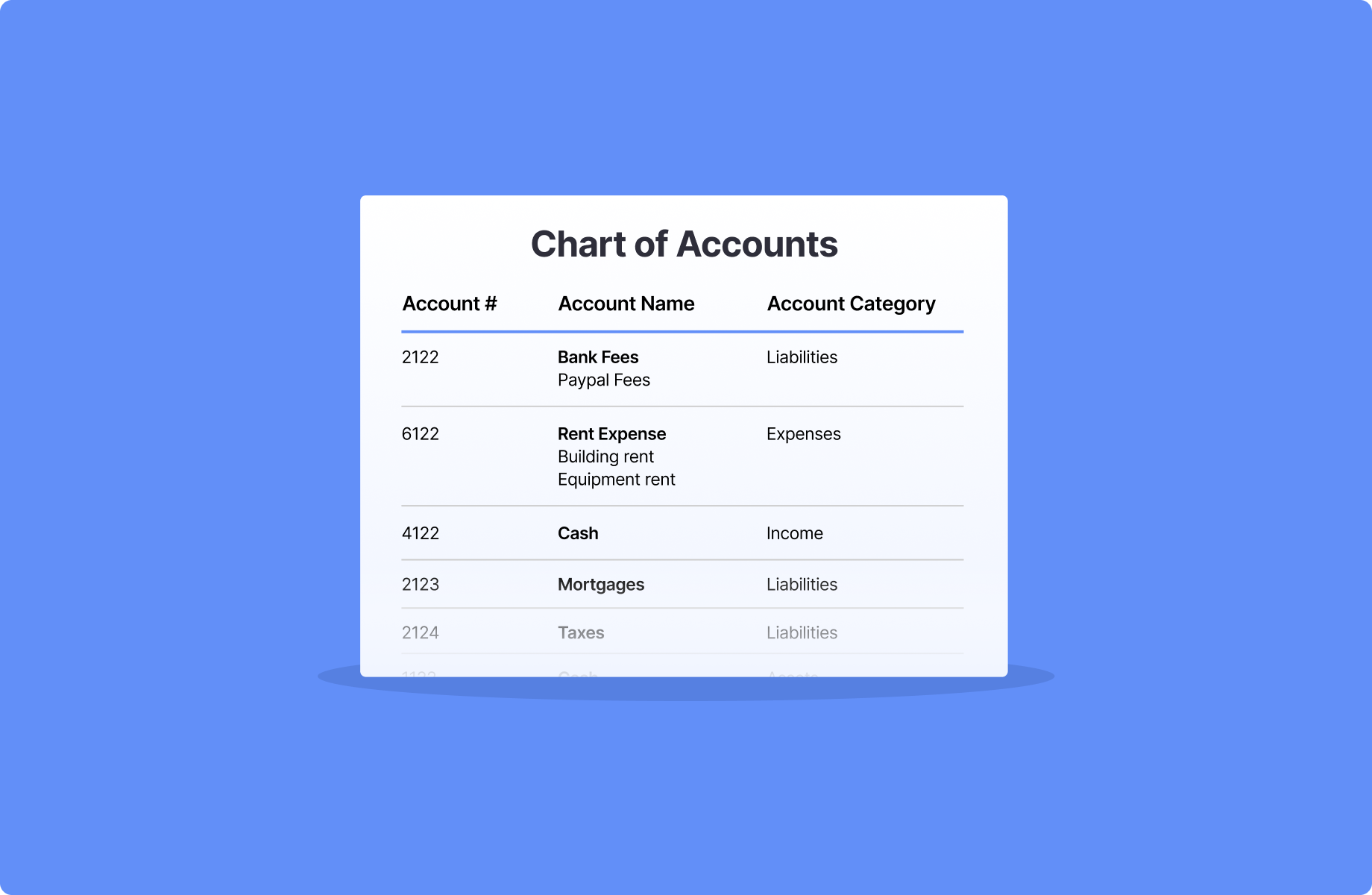
The Chart of Accounts is a fundamental component of QuickBooks and serves as the backbone of your financial records. It is essentially a comprehensive list of all the accounts used by your business, categorizing them into assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses. Configuring your Chart of Accounts correctly is crucial for accurate financial reporting. Take the time to customize it according to your business needs, adding or modifying accounts to reflect your unique financial structure.
Connecting Bank Accounts
One of the key advantages of using QuickBooks is its ability to connect directly to your bank accounts, streamlining the process of recording transactions. By linking your bank accounts to QuickBooks, you can automatically import and categorize your financial data, reducing manual data entry and minimizing errors. This feature enhances efficiency and accuracy in tracking income and expenses. Ensure you follow the necessary security protocols and provide the required authorization to establish a secure connection between QuickBooks and your bank accounts.
Getting started with QuickBooks involves a systematic approach, starting with the setup of the software, followed by the customization of the Chart of Accounts, and finally, connecting your bank accounts for seamless transaction tracking. Proper execution of these steps ensures that QuickBooks becomes a powerful tool for managing your business finances effectively.
Essential Financial Reports in QuickBooks
In the realm of financial management, QuickBooks plays a pivotal role in assisting businesses by generating essential financial reports. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial standing and are instrumental in making informed business decisions. This discussion delves into three crucial financial reports generated by QuickBooks: the Profit and Loss Statement, the Balance Sheet, and the Cash Flow Statement.
-
Profit and Loss Statement:
The Profit and Loss Statement (P&L) is a fundamental financial report that provides a snapshot of a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period. It is a dynamic tool for analyzing the financial performance of a business. In dissecting the P&L, business owners and financial managers can gain insights into revenue sources, cost structures, and overall profitability. By closely examining revenue and expenses, stakeholders can identify areas for improvement, make strategic decisions, and gauge the financial health of the business.
Analyzing Revenue and Expenses:
Within the Profit and Loss Statement, a detailed analysis of revenue and expenses is imperative. Revenue breakdown helps businesses understand which products or services are the most lucrative, while expense analysis highlights areas where cost-cutting measures may be necessary. This granular examination enables businesses to optimize their operations and enhance overall financial performance.
Budgeting with P&L:
The P&L statement is a crucial tool for budgeting and forecasting. By understanding historical revenue and expense patterns, businesses can develop realistic budgets for the future. This aids in setting financial goals, allocating resources efficiently, and ensuring that the business operates within its means.
-
Balance Sheet:
The Balance Sheet is another critical financial report generated by QuickBooks. It provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, showcasing its assets, liabilities, and equity. Understanding the Balance Sheet is essential for assessing the overall financial health and solvency of a business.
Assets, Liabilities, and Equity:
Assets, liabilities, and equity are the three key components of the Balance Sheet. Assets encompass everything a company owns, while liabilities represent its obligations. Equity is the residual interest of the owners in the company after deducting liabilities from assets. A well-managed balance between these components is indicative of a stable and sustainable financial structure.
Monitoring Financial Health:
Monitoring the Balance Sheet regularly is crucial for assessing a company’s financial health. It helps stakeholders track changes in assets and liabilities, identify trends, and make strategic decisions to maintain a healthy financial position. This report is invaluable for investors, creditors, and management in evaluating the long-term sustainability of the business.
-
Cash Flow Statement:
The Cash Flow Statement is a vital report that outlines how changes in balance sheet accounts and income affect cash and cash equivalents. It provides insights into a company’s ability to generate cash and meet its short-term obligations.
Managing Cash Flow:
Effective cash flow management is essential for the day-to-day operations of a business. The Cash Flow Statement helps in tracking cash inflows and outflows, ensuring that there is sufficient liquidity to cover operating expenses, debt payments, and other financial obligations.
Forecasting Cash Position:
Forecasting the cash position is a proactive approach to financial management. By analyzing historical cash flow patterns, businesses can predict future cash needs and take preemptive measures to avoid cash shortages. This forward-looking perspective enables better financial planning and strategic decision-making.
Navigating QuickBooks Financial Reporting
Navigating QuickBooks Financial Reporting involves several key aspects that empower users to effectively manage and analyze financial data. In this overview, we’ll delve into three essential components: the Dashboard Overview, Customizing Reports, and Understanding Report Categories.
Dashboard Overview:
The Dashboard serves as the central hub within QuickBooks for financial reporting. It provides users with a comprehensive snapshot of their company’s financial health. Key performance indicators, financial summaries, and visual representations of data are displayed on the Dashboard. Users can quickly assess their current financial standing, including income, expenses, and overall profitability. The intuitive design of the Dashboard ensures that users can access critical information at a glance, facilitating informed decision-making.
Customizing Reports:
One of QuickBooks’ strengths lies in its flexibility to adapt to the unique needs of different businesses. Customizing reports is a crucial feature that allows users to tailor financial data presentations to meet specific requirements. QuickBooks offers a range of customization options, enabling users to choose relevant data fields, apply filters, and modify layouts. Whether it’s creating income statements, balance sheets, or cash flow reports, the ability to customize ensures that users can generate reports that align with their business objectives and reporting standards.
Understanding Report Categories:
QuickBooks organizes its reports into distinct categories, streamlining the process of accessing relevant financial information. Understanding these categories is pivotal for users to navigate through the extensive reporting options efficiently. Categories may include financial statements, sales reports, expense reports, and more. Each category encompasses a set of related reports, providing users with a structured approach to accessing the specific data they need. This segmentation enhances the user experience, making it easier to locate and analyze the desired financial information.
Effective navigation of QuickBooks Financial Reporting involves mastering the Dashboard Overview, utilizing the powerful Customizing Reports feature, and comprehending the organization of Report Categories. These elements collectively empower users to harness the full potential of QuickBooks for accurate financial analysis and strategic decision-making.
Tips for Efficient Financial Reporting
Data Accuracy and Consistency
Financial reporting hinges on the accuracy and consistency of the data presented. Reconciling accounts is a crucial step in ensuring the reliability of financial information. Regularly compare financial records with external statements, such as bank statements or vendor invoices, to identify and rectify discrepancies. This process not only helps in maintaining data accuracy but also aids in detecting potential errors or fraud.
Avoiding common mistakes is equally imperative. Ensure that data entry is meticulous and cross-verify calculations. Common errors, such as typos or incorrect formula applications, can distort financial reports. Implementing rigorous review processes can mitigate the risk of inaccuracies, enhancing the overall reliability of financial data.
Automation and Scheduled Reporting
Efficient financial reporting is often achieved through automation and scheduled reporting. Setting up scheduled reports ensures timely and consistent delivery of financial information. This regularity not only facilitates compliance but also enables stakeholders to anticipate and plan based on up-to-date financial insights.
Automation tools play a pivotal role in streamlining reporting processes. These tools can automate data collection, consolidation, and formatting tasks, reducing the chances of human error. Implementing such tools not only enhances efficiency but also frees up valuable time for finance professionals to focus on more strategic aspects of financial management.
Collaborative Reporting
Collaboration is key to effective financial reporting. Multi-user collaboration fosters a team approach, allowing different stakeholders to contribute their expertise and insights. This not only improves the accuracy of the reports but also ensures that diverse perspectives are considered in the decision-making process.
Shareable report links enhance collaboration by providing a convenient means of sharing real-time data with relevant parties. This feature enables stakeholders to access the latest financial reports without the need for constant manual updates. It promotes transparency and facilitates efficient communication within and outside the financial team, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the reporting process.
Integrating Third-Party Apps for Enhanced Reporting
In the realm of financial management and reporting, the integration of third-party applications has become pivotal for businesses seeking efficient and advanced reporting solutions. This practice allows organizations to extend the functionality of their existing software and streamline their financial processes. One notable ecosystem in this domain is the QuickBooks Apps Ecosystem, which offers a diverse range of applications designed to enhance reporting capabilities.
QuickBooks Apps Ecosystem Overview
The QuickBooks Apps Ecosystem is a rich collection of third-party applications that seamlessly integrate with QuickBooks, a popular accounting software. These apps are developed to address specific business needs, ranging from inventory management to advanced reporting tools. The ecosystem empowers businesses to tailor their financial systems to match their unique requirements, fostering a more personalized and effective approach to reporting.
Choosing the Right Apps for Reporting
Selecting the right apps from the QuickBooks ecosystem is a critical decision for businesses aiming to bolster their reporting capabilities. This involves a careful evaluation of the features and functionalities offered by each app, ensuring they align with the organization’s reporting goals. Factors such as data visualization, customization options, and compatibility with existing systems play a vital role in determining the suitability of an app for reporting purposes.
Connecting QuickBooks with Excel
In addition to leveraging third-party apps, businesses can enhance their reporting by integrating QuickBooks with Microsoft Excel, a widely used spreadsheet software. This integration opens up new avenues for data analysis, visualization, and reporting, providing users with a more robust toolkit for financial reporting.
Exporting Data to Excel
One key aspect of integrating QuickBooks with Excel is the seamless exportation of data from QuickBooks to Excel. This process facilitates a smooth transition of financial data, allowing users to manipulate and analyze the information within the Excel environment. By harnessing the power of Excel’s spreadsheet functionalities, businesses can create more dynamic and customizable financial reports.
Building Complex Models in Excel
Once data is exported to Excel, users can delve into building complex models to extract valuable insights. Excel’s advanced features enable the creation of intricate financial models, incorporating formulas, charts, and graphs to present data in a visually compelling manner. This step is crucial for businesses aiming to generate comprehensive and insightful reports that go beyond basic financial statements.
Security and Privacy Considerations
In the realm of digital financial management, ensuring robust security measures is paramount. QuickBooks, as a widely used accounting software, addresses these concerns through various mechanisms.
Data Security in QuickBooks
User Permissions
User permissions play a pivotal role in QuickBooks’ data security framework. The software allows for finely tuned control over who can access sensitive financial information. By defining user roles and permissions, businesses can restrict access to specific modules, safeguarding against unauthorized viewing or modification of critical data. This granular control ensures that only authorized personnel have access to the necessary financial details, reducing the risk of data breaches or misuse.
Encryption and Secure Connections
QuickBooks employs encryption protocols and secure connections to fortify data in transit and at rest. Utilizing industry-standard encryption algorithms, the software encrypts sensitive financial data, making it significantly harder for malicious actors to intercept or tamper with information during transmission. Secure connections ensure that communication between the user’s device and QuickBooks servers occurs over protected channels, mitigating the risk of data interception or unauthorized access during the data transfer process.
Privacy Compliance
GDPR and QuickBooks
For businesses operating in the European Union or dealing with EU citizens’ data, compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is crucial. QuickBooks recognizes the significance of GDPR and has incorporated features to assist users in complying with its mandates. This includes tools for managing data subject rights, ensuring transparent data processing practices, and facilitating the creation of data processing agreements. By aligning with GDPR requirements, QuickBooks enhances user confidence in the software’s commitment to privacy and data protection.
HIPAA Compliance for Healthcare Businesses
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliance is imperative for businesses operating in the healthcare sector. QuickBooks recognizes the unique privacy and security needs of healthcare data and provides functionalities that support HIPAA compliance. This involves features such as access controls, audit trails, and secure storage options, ensuring that healthcare businesses can maintain the confidentiality and integrity of patient information while utilizing QuickBooks for their financial management needs.
QuickBooks places a strong emphasis on security and privacy considerations through user permission controls, robust encryption, and compliance features tailored to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. This multi-faceted approach aims to provide users with a secure and privacy-conscious environment for managing their financial data.
Future Trends in QuickBooks Financial Reporting
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial reporting, QuickBooks is poised to witness transformative changes driven by emerging technologies. Two prominent trends shaping the future of QuickBooks financial reporting are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cloud-Based Reporting.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are set to revolutionize QuickBooks financial reporting through the integration of predictive analytics. This entails utilizing advanced algorithms to analyze historical financial data and predict future trends. QuickBooks users can leverage predictive analytics to gain valuable insights into potential financial outcomes, enabling more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Automated Insights
The incorporation of AI and machine learning in QuickBooks will lead to the development of automated insights. These features will streamline the interpretation of complex financial data, providing users with actionable insights in real-time. QuickBooks users can expect automated insights to enhance efficiency and accuracy in financial reporting, reducing the manual effort required for data analysis.
Cloud-Based Reporting
Advantages of Cloud Reporting
Cloud-based reporting is another pivotal trend shaping the future of QuickBooks. Moving financial reporting to the cloud offers numerous advantages. Accessibility is greatly improved, allowing users to access their financial data from anywhere with an internet connection. Real-time collaboration becomes seamless, enabling multiple stakeholders to work on financial reports simultaneously. Moreover, the cloud provides a scalable infrastructure, accommodating the growing data needs of businesses without the constraints of traditional on-premise systems.
Risks and Mitigations
While the benefits of cloud-based reporting are substantial, it comes with its share of risks. Security concerns, data breaches, and potential downtime are valid worries for businesses relying on cloud services. However, as technology advances, so do security measures. Robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates are among the mitigations that cloud service providers implement to safeguard financial data. QuickBooks users should stay informed about security best practices and choose reputable cloud service providers to minimize these risks.
The future of QuickBooks financial reporting is marked by the integration of AI for predictive analytics and automated insights, as well as the widespread adoption of cloud-based reporting. These trends promise to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of financial reporting for businesses, positioning QuickBooks as a cutting-edge solution in the ever-evolving financial technology landscape.