Google Workspace formerly known as G Suite, is a comprehensive suite of cloud-based productivity and collaboration tools developed by Google. It is designed to help individuals and organizations streamline their work processes, enhance communication, and promote collaboration. Here’s a more detailed overview of Google Workspace:
- Gmail: Gmail is a widely used email platform that provides professional email addresses with your organization’s domain name. It offers a powerful search function, spam protection, and integration with other Google Workspace apps.
- Google Drive: Google Drive is a cloud storage and file-sharing service. It allows users to store and access files, documents, photos, and other data from any device with an internet connection. Google Drive also includes powerful sharing and collaboration features.
- Google Docs: Google Docs is a word-processing application that allows multiple users to collaborate on documents in real-time. It offers a wide range of formatting options, templates, and the ability to leave comments and suggest edits.
- Google Sheets: Google Sheets is a spreadsheet application for creating, editing, and sharing spreadsheets. It supports functions, charts, and the ability to work on spreadsheets simultaneously with others.
- Google Slides: Google Slides is a presentation software that makes it easy to create and collaborate on slide presentations. It offers various templates and features for adding images, videos, and animations to your slides.
- Google Calendar: Google Calendar is a scheduling and time management tool that helps users organize their events, meetings, and appointments. It can be easily shared with colleagues for team scheduling.
- Google Meet: Google Meet is a video conferencing and online meeting tool. It enables users to hold video and audio conferences, share screens, and collaborate with remote team members or clients.
- Google Forms: Google Forms is a survey and form-building application that allows users to create online forms for various purposes, such as surveys, questionnaires, and data collection.
- Google Sites: Google Sites is a website building tool that helps users create and share web pages, whether for intranet sites, project documentation, or public-facing websites.
- Google Chat: Google Chat is a messaging platform that facilitates real-time communication and collaboration within Google Workspace. It allows users to send direct messages, create group chats, and share files.
- Google Keep: Google Keep is a note-taking and organization tool. Users can create and organize notes, to-do lists, and reminders, and it syncs across all devices.
- Google Forms: Google Forms allows users to create surveys and forms, making it easy to gather information and feedback from others.
- Google Workspace Marketplace: The Google Workspace Marketplace offers a wide range of third-party applications and add-ons that can enhance the functionality and features of Google Workspace.
Google Workspace is highly scalable, meaning it can be tailored to the needs of small businesses, large enterprises, educational institutions, and non-profit organizations. It provides seamless collaboration, robust security features, and reliable cloud-based services, making it a popular choice for improving productivity and communication in a wide range of settings.
Licensing and Billing Overview
Licensing and Billing Overview in Google Workspace is a critical aspect of managing your organization’s access to and costs associated with the suite of services. Here’s a more detailed description of the components involved:
User Licenses: Google Workspace offers a variety of subscription plans to cater to different organizational needs, from small businesses to large enterprises and educational institutions. Each subscription plan comes with a specific set of services and a corresponding number of user licenses. These licenses are assigned to individual users or accounts within your organization. It’s crucial to choose the appropriate plan and license type for each user based on their role and requirements. For instance, some users may need advanced features available in higher-tier plans, while others can be assigned basic plans.
Billing: Google Workspace bills organizations regularly, typically on a monthly or annual cycle, depending on the chosen subscription plan. The billing process can be based on the number of user licenses or other factors like data storage, depending on your specific contract. Accurate billing management is essential to control costs and avoid unexpected overage charges. You need to ensure that you are only paying for the services and features you are actively using.
Add-Ons and Marketplace Apps: Google Workspace allows users to extend its functionality by integrating with various third-party applications and add-ons available through the Google Workspace Marketplace. Managing these add-ons and apps is part of the licensing and billing process. You’ll need to keep track of which users have access to which add-ons and ensure that these are properly licensed and billed.
Reporting and Analytics: Google Workspace provides robust reporting and analytics tools to help organizations monitor their usage, spending, and billing. These tools allow you to access and analyze data related to user activity, application usage, and costs. By using these reports and analytics, you can make informed decisions about optimizing your licensing and billing, identify areas where you may need to adjust licenses and track your spending more efficiently.
Security and Compliance: Maintaining licensing and billing compliance is essential for ensuring that your organization is using Google Workspace services in a secure and compliant manner. This involves managing user access, ensuring that data storage and transfer are in line with your organization’s policies and any legal or regulatory requirements, and maintaining an audit trail of licensing and billing changes for compliance and security purposes.
Effectively managing licensing and billing in Google Workspace involves strategically assigning user licenses, accurately tracking and controlling costs, managing add-ons and marketplace apps, utilizing reporting and analytics tools, and maintaining security and compliance to ensure that your organization’s use of Google Workspace is efficient, secure, and aligned with your budget and business needs.
Admin Console: Your Central Hub
The Google Workspace Admin Console serves as the central management hub for administrators, providing a range of tools and features to efficiently oversee various aspects of the organization’s Google Workspace deployment. Here’s a closer look at the functionalities within the Admin Console:
User Account Management:
- Add, Delete, Modify Users: Administrators can easily add new users, remove obsolete accounts, and modify existing user profiles. This functionality streamlines the process of keeping the user directory up-to-date.
- License Assignment: Assign specific licenses to each user based on their role and requirements. This ensures that users have access to the appropriate set of Google Workspace features.
Billing and Payment Management:
- Payment Information: Input and manage payment information within the Admin Console, streamlining the billing process for Google Workspace services.
- Payment Plans: Set up and manage payment plans based on the organization’s needs. This includes defining billing cycles and choosing suitable payment methods.
Third-Party Application Control:
- Add-Ons and Marketplace Apps: Administrators have control over which third-party applications, add-ons, and marketplace apps are accessible to users. This feature ensures that only approved and secure applications are available within the organization.
Usage Reports:
Access to Usage Reports: Gain insights into how Google Workspace services are utilized within the organization through comprehensive usage reports. This information is valuable for making informed decisions about licensing, resource allocation, and optimizing the overall usage of Google Workspace.
Security Configuration:
Security Best Practices: Configure and manage security settings to ensure that the organization adheres to best practices. This includes settings related to user authentication, data protection, and other security features.
The Admin Console’s user-friendly interface makes these administrative tasks accessible to even those without extensive technical expertise. This centralized hub simplifies the complexities of managing a Google Workspace deployment, allowing administrators to focus on optimizing the organization’s use of these collaborative tools.
User Licensing and Provisioning
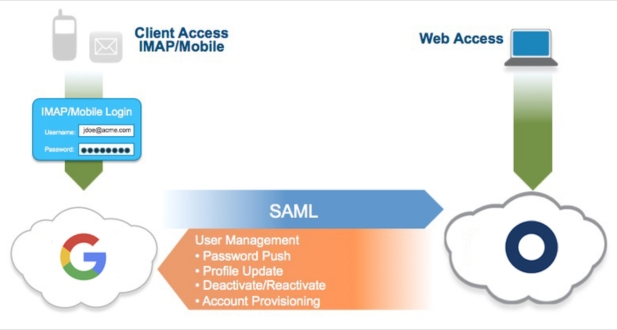
User licensing and provisioning are critical components of Google Workspace management, ensuring that users have appropriate access to services and applications. Here’s a more detailed explanation of user licensing and provisioning:
User Licensing:
Adding New Users: When onboarding new members to your organization, it’s essential to assign licenses through the Admin Console. This ensures that users have access to the Google Workspace services they need.
- Admin Console Management: The Admin Console is the central hub for managing user licenses. Admins can navigate through the console to assign licenses to individual users or groups based on the organization’s subscription plan.
Service Access Specification: When assigning licenses, administrators can specify the services that each user can access. This flexibility allows organizations to tailor access to match individual roles and responsibilities.
License Types:
- Range of Options: Google Workspace offers various license types, ranging from Basic to Enterprise. Each license type provides a specific set of services and features. Choosing the right license for each user is crucial for optimizing costs and ensuring that individuals have access to the tools necessary for their roles.
- Cost Optimization: By selecting the most appropriate license type for each user, organizations can manage costs effectively. This involves aligning the features offered by a license with the user’s job requirements.
License Assignment:
- Admin Console Functionality: The Admin Console streamlines license assignment processes. Admins can efficiently apply licenses to single users or multiple users simultaneously, simplifying the management of a growing organization.
- Dynamic Adjustments: As user roles and responsibilities evolve, administrators can easily adjust license assignments. This includes unassigning licenses for services that users no longer require, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Provisioning:
- User Account Creation: Provisioning involves creating and configuring user accounts within the Google Workspace environment. This process ensures that new users have the necessary access to services and applications required for their roles.
- Automated Provisioning: Google Workspace provides automated provisioning options, reducing the manual effort involved in setting up user accounts. Automated processes help streamline onboarding, making it faster and less prone to errors.
- Efficiency and Consistency: Automated provisioning promotes efficiency and consistency in user account creation. It helps maintain standardized access configurations, reducing the risk of oversights or inconsistencies in user permissions.
Effective user licensing and provisioning in Google Workspace involve thoughtful selection of license types, efficient assignment and adjustment processes through the Admin Console, and leveraging automated provisioning for streamlined user onboarding. This ensures that users have the right level of access to Google Workspace services, promoting productivity and cost-effectiveness within the organization.
Billing and Payment
Billing and payment are essential aspects of managing Google Workspace licensing. Here’s what you need to know:
Billing Cycles:
Google Workspace provides flexibility in billing cycles, allowing organizations to choose between monthly and annual billing. The choice depends on the organization’s preferences and financial planning. Opting for an annual billing cycle may offer cost savings compared to monthly billing.
Payment Methods:
The Admin Console simplifies the payment process by allowing administrators to add various payment methods, including credit cards and bank accounts. This flexibility ensures convenience and accommodates the diverse needs of organizations. Admins can save multiple payment methods, streamlining the payment process for recurring charges.
Billing Administration:
The Admin Console serves as a centralized hub for billing administration. Admins can access comprehensive billing information, view invoices, and monitor charges in real-time. This transparency is crucial for financial management, enabling admins to keep a close eye on expenses and maintain control over the billing process.
Overages:
Effective management of data storage and user licenses is essential to prevent overage charges. Monitoring usage closely helps organizations stay within their allocated limits, avoiding unexpected costs associated with exceeding predefined thresholds. The Admin Console provides tools and reports that assist in tracking usage, helping admins make informed decisions to optimize resources and control expenses.
By understanding and utilizing these billing and payment features, organizations can efficiently manage their Google Workspace licensing, control costs, and make strategic decisions regarding billing cycles and resource allocation.
Managing Add-Ons and Marketplace Apps
Admin Approval:
Administrators play a crucial role in controlling the deployment of third-party applications by utilizing the Admin Console. Through this centralized platform, administrators can review and approve or disapprove applications before they are made available to users. This control mechanism is vital for maintaining the security and compliance standards of the organization. Admins can assess the functionality, permissions, and potential risks associated with each add-on or app, ensuring that only authorized and secure applications are integrated into the Google Workspace environment.
Monitoring Usage:
Regularly monitoring the usage of third-party apps is essential for understanding their impact on productivity and determining their value to the organization. Analytics and usage reports can provide insights into how frequently an app is used, by whom, and for what purposes. This information enables administrators to make informed decisions about whether to continue supporting specific apps or consider alternatives. Monitoring usage also helps in identifying trends and user preferences, allowing organizations to optimize their digital toolset based on real-world needs.
Security Considerations:
Security should be a top priority when managing add-ons and marketplace apps. Administrators must ensure that the apps meet the organization’s security and compliance standards. This involves verifying the permissions requested by the apps and assessing the security measures implemented by the developers. Any app with questionable permissions or inadequate security measures may pose a risk to the organization’s data and overall security posture. Regular security audits and reviews of marketplace apps are necessary to identify and address potential vulnerabilities promptly.
Cost-effectiveness:
In addition to security considerations, evaluating the cost-effectiveness of third-party apps is essential. Admins should assess whether the value provided by an app justifies its cost. This involves considering factors such as user satisfaction, productivity gains, and the overall impact on business processes. If an app is not delivering the expected value, administrators can make data-driven decisions about whether to continue with the subscription or explore alternative solutions.
Training and Support:
As new apps are introduced or existing ones are updated, providing adequate training and support for users is crucial. This ensures that employees are well-equipped to leverage the functionalities of the apps effectively, contributing to overall productivity and user satisfaction.
By actively managing add-ons and marketplace apps, organizations can harness the full potential of Google Workspace while maintaining a secure and optimized digital environment.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics play a crucial role in managing and optimizing the use of Google Workspace within an organization. Here’s a more detailed explanation of the key components:
Usage Reports:
Google Workspace offers a range of comprehensive usage reports that provide detailed insights into how the organization is utilizing its licenses. These reports cover various aspects, including user activity, email usage, storage consumption, and more. For example, you can track the number of emails sent and received, the amount of storage space used by each user, and other relevant metrics. This information is invaluable for understanding how different features are being utilized across the organization.
License Reports:
License reports are essential for monitoring and managing the allocation of licenses within your Google Workspace domain. These reports allow administrators to easily access and review information about license usage, ensuring that the organization is not over-allocating licenses. This helps prevent unnecessary costs associated with unused or underutilized licenses. By having a clear overview of license usage, organizations can make informed decisions about their licensing needs and avoid potential compliance issues.
Cost Optimization:
Regularly analyzing usage and license reports enables organizations to identify opportunities for cost optimization within Google Workspace. By understanding how licenses are being used, administrators can make informed decisions about reallocating licenses, modifying subscription plans, or taking advantage of more cost-effective licensing options. This proactive approach to cost optimization ensures that the organization is maximizing the value of its Google Workspace investment while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Reporting and analytics within Google Workspace provide the necessary tools to monitor usage, manage licenses effectively, and optimize costs. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make informed decisions, ensuring that they are not only meeting their collaboration needs but also doing so in a cost-effective manner.
Security and Compliance
Security Settings:
The Admin Console in Google Workspace offers a robust set of security settings. These settings include options for account authentication, password policies, two-factor authentication, and device management. Admins can configure these settings to enhance the overall security posture of the organization.
Data Retention and Archiving:
Google Workspace provides features for data retention and archiving to help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements. Admins can set retention policies to specify how long data should be retained before being automatically deleted or archived. This is particularly important for industries with strict data protection regulations.
Access Control:
Access control is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data. Google Workspace allows administrators to configure access controls, defining who has access to specific files, folders, or applications. By implementing least privilege principles, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Auditing and Compliance Reports:
Google Workspace includes auditing tools and compliance reports that provide insights into user activities and system events. These reports can be invaluable for tracking changes, monitoring user behavior, and ensuring that the organization is meeting its regulatory requirements. Regularly reviewing these reports allows administrators to identify potential security incidents or policy violations.
Google Workspace offers a comprehensive set of tools and features to help organizations maintain a high level of security and compliance. By leveraging these capabilities, administrators can create a secure environment, control access to sensitive information, and demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations. Regular monitoring, updates to security settings, and adherence to best practices contribute to a robust security posture within the Google Workspace environment.
Best Practices
To effectively manage billing and licensing for Google Workspace, consider these best practices:
Regularly Review and Audit Licenses:
Regular audits of your Google Workspace licenses are crucial to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently. This involves periodically reviewing the licenses assigned to users and making adjustments based on changes in personnel or organizational needs. By doing so, you can avoid over-assigning licenses (which can lead to unnecessary costs) or under-assigning licenses (which may hinder productivity).
Monitor Usage and Costs:
Keep a vigilant eye on usage reports and billing information. Monitoring usage patterns helps identify opportunities for optimization and potential cost savings. This involves understanding which features are heavily utilized and which may be underutilized. By being proactive in monitoring usage, you can align your licensing costs with actual organizational needs.
Train Administrators:
Well-trained administrators are essential for effective Google Workspace licensing and billing management. They should have a deep understanding of the licensing model, billing processes, and security considerations. This training not only helps prevent costly mistakes but also enhances the overall security posture of your organization by ensuring that administrators follow best practices.
Stay Informed:
Google Workspace regularly releases updates, new features, and improvements to licensing and billing management. Staying informed about these changes allows your organization to take advantage of new capabilities and ensures that you are using the most up-to-date and efficient licensing models. Regularly checking for updates also helps you stay compliant with any changes in terms of service or security protocols.
Plan for Growth:
As your organization grows, it’s important to be proactive in adjusting your licensing and billing accordingly. Google Workspace is designed to scale with your needs, so be prepared to adapt your plan as your organization evolves. This might involve reassessing user needs, adding new licenses, or considering different plans that align with the changing requirements of your expanding organization.
Conclusion
Billing and licensing management for Google Workspace is a critical component of efficient and cost-effective cloud-based collaboration and productivity. By understanding the licensing options, utilizing the Admin Console effectively, and following best practices, organizations can harness the full power of Google Workspace while maintaining control over costs and ensuring security and compliance. With the right approach, Google Workspace can be a valuable asset for organizations of all sizes, promoting productivity and collaboration in the modern digital workplace.
Google Workspace supports various payment options, including credit cards and bank transfers.
Yes, Google Workspace offers a 14-day free trial, allowing you to explore the features before committing to a subscription.
Licensing is user-based. Each user license allows access to Google Workspace apps on multiple devices.
Yes, you can switch plans or upgrade your subscription at any time. The changes will be reflected in your next billing cycle.
Yes, Google Workspace offers discounted pricing for qualified non-profit organizations and educational institutions.
If you exceed the user limit, you will be billed for the additional users. It’s important to stay within the allocated user quota to avoid extra charges.
Yes, you can cancel your subscription at any time. However, you will be billed for the current billing cycle.
Charges for partial months are prorated based on the number of days each user is active during that month.
No, Google Workspace does not offer refunds for mid-month cancellations. You will be billed for the entire month.
No, there is no minimum number of users required. You can subscribe to Google Workspace for any number of users.
Yes, you can use your own domain with Google Workspace. This allows you to have professional email addresses using your domain.
You can view and manage your billing information through the Google Workspace Admin Console.
No, customer support is included in your Google Workspace subscription, and there are no additional fees for support.
Yes, you can downgrade your subscription plan at any time. The changes will be applied in the next billing cycle.
Google Workspace has specific data usage and storage limits for each subscription plan. You can manage these limits in the Admin Console.
Yes, Google Workspace uses secure and encrypted connections to protect billing information. It’s important to follow best practices for account security.
Yes, you can purchase additional storage if you exceed the storage limits included in your subscription.
You can access and download detailed billing statements from the Billing section of the Google Workspace Admin Console.