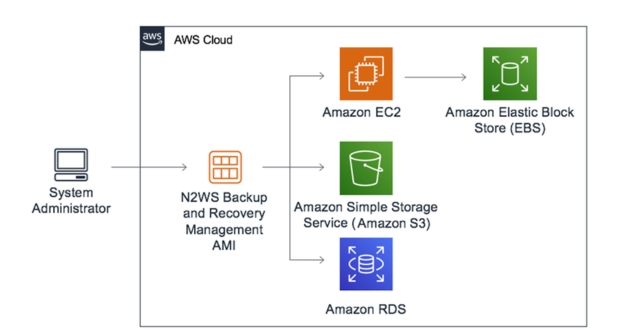
Introduction to AWS Cloud Storage:
Cloud storage has revolutionized the way businesses store, manage, and access data. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a comprehensive suite of cloud storage services that cater to various needs and requirements of businesses of all sizes. In this introduction, we’ll delve into the overview of AWS cloud storage services and explore the benefits of using AWS for backup purposes.
Overview of AWS Cloud Storage Services:
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3): Amazon S3 is one of the most popular and widely used object storage services offered by AWS. It provides scalable storage for data ranging from a few gigabytes to several petabytes. S3 offers high durability, availability, and security features, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases such as data lakes, backups, archiving, and content distribution.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS): Amazon EBS provides block-level storage volumes that are attached to EC2 instances. It is suitable for applications that require low-latency access to data and persistent storage, such as databases and enterprise applications. EBS volumes offer features like snapshots for backup and replication for data redundancy.
Amazon Glacier: Amazon Glacier is a low-cost storage service designed for long-term archival and backup of data. It offers three retrieval options – expedited, standard, and bulk – with varying retrieval times and costs. Glacier is ideal for storing data that is accessed infrequently but needs to be retained for compliance or regulatory purposes.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS): Amazon EFS provides scalable and highly available file storage that can be accessed concurrently by multiple EC2 instances and on-premises servers. It is suitable for use cases such as content management, media processing, and web serving, where shared file storage is required.
Benefits of Using AWS Cloud Storage for Backup Purposes:
- Scalability: AWS cloud storage services like S3 and Glacier offer virtually unlimited scalability, allowing businesses to store and backup large volumes of data without worrying about capacity constraints.
- Durability and Reliability: AWS storage services are designed to provide high durability and reliability, with built-in redundancy and data replication across multiple availability zones. This ensures that data is protected against hardware failures, natural disasters, and other unforeseen events.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model for its storage services, allowing businesses to pay only for the storage they use. This helps in reducing upfront capital expenses and optimizing costs for backup and archival storage.
- Security: AWS provides a wide range of security features and controls to protect data stored in the cloud. This includes encryption at rest and in transit, access controls, identity and access management (IAM), and compliance certifications.
- Simplified Management: AWS cloud storage services are integrated with other AWS services and management tools, making it easy to automate backup processes, manage storage resources, and monitor data usage and performance.
Importance of Backup Strategies
Risks of data loss and downtime:
- Data loss and downtime can have severe consequences for businesses, ranging from financial losses to damage to reputation and customer trust.
- Data loss can occur due to various reasons such as hardware failures, software corruption, cyberattacks, natural disasters, or human error.
- Downtime refers to periods when systems or services are unavailable, which can disrupt operations, impact productivity, and result in revenue loss.
- Having a robust backup strategy mitigates the risks associated with data loss and downtime by ensuring that critical data and systems can be restored quickly in the event of an incident.
Regulatory compliance requirements:
- Many industries are subject to regulatory compliance requirements regarding data protection, privacy, and retention.
- Regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) impose strict guidelines on how organizations handle and protect sensitive data.
- Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to legal penalties, fines, and reputational damage.
- Implementing appropriate backup strategies helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
Business continuity and disaster recovery planning:
- Business continuity refers to the ability of an organization to maintain essential functions during and after a disruption, ensuring minimal impact on operations.
- Disaster recovery involves the processes and procedures for restoring critical systems and data following a disruptive event.
- Backup strategies play a crucial role in business continuity and disaster recovery planning by providing a means to recover data and systems rapidly.
- Organizations need to develop comprehensive plans that outline procedures for data backup, restoration, failover, and failback to ensure resilience against various threats, including cyberattacks, natural disasters, or equipment failures.
- Testing and regular review of these plans are essential to ensure their effectiveness and responsiveness in real-world scenarios.
Types of AWS Cloud Storage Services
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service):
Amazon S3 is an object storage service that provides developers and IT teams with secure, durable, and scalable storage for various types of data.
It is designed to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases, including backup and restore, disaster recovery, content distribution, and data archiving.
With Amazon S3, you can store and retrieve data objects, such as files, images, videos, documents, and logs, using a simple web interface or API calls.
It offers high availability, durability, and scalability, making it ideal for storing mission-critical data and applications.
Amazon Glacier:
Amazon Glacier is a low-cost storage service designed for data archiving and long-term backup.
It offers extremely low storage costs compared to other AWS storage services, making it suitable for storing data that is rarely accessed but needs to be retained for compliance or regulatory purposes.
Amazon Glacier provides secure, durable, and reliable storage with options for data retrieval ranging from minutes to hours, depending on the retrieval speed chosen.
It is ideal for storing large volumes of data, such as backups, archives, and digital media assets, that do not require immediate access but need to be preserved for extended periods.
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store):
Amazon EBS is a block-level storage service designed for use with Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances.
It provides persistent block storage volumes that can be attached to EC2 instances as virtual hard drives, enabling them to store data persistently even after the instance is terminated.
Amazon EBS volumes offer low-latency performance and are suitable for applications that require high-speed data access, such as databases, transactional systems, and enterprise applications.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service):
Amazon RDS is a managed relational database service that simplifies the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases in the cloud.
It supports popular database engines such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB, allowing users to launch, operate, and scale relational databases with ease.
Amazon RDS automates common database administration tasks, such as hardware provisioning, database setup, patching, backup, recovery, and scaling, freeing users from the overhead of managing database infrastructure.
It offers built-in backup and restore features, including automated backups, manual snapshots, and point-in-time recovery, to help protect database data and ensure high availability and durability.
Factors Influencing Backup Strategy Selection
Data Volume and Frequency of Changes:
- Data volume refers to the amount of data that an organization needs to backup. Large volumes of data may require more sophisticated backup solutions to ensure efficient and timely backups.
- The frequency of changes refers to how often data within the organization is updated, modified, or created. For data that changes frequently, more frequent backups may be necessary to minimize the risk of data loss.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO):
- RTO refers to the maximum acceptable downtime that an organization can tolerate before operations need to be restored after a disruption or disaster.
- RPO refers to the maximum tolerable amount of data loss measured in time. It indicates the point in time to which data must be recovered in order to resume operations effectively.
- The backup strategy selected must align with the organization’s RTO and RPO objectives. For instance, if the RTO is minimal, the backup strategy should include solutions that enable quick restoration of data and systems.
Compliance and Security Requirements:
- Many industries are subject to regulatory compliance requirements that dictate how data should be handled, stored, and protected. Backup strategies must comply with these regulations to avoid penalties and legal consequences.
- Security requirements, such as encryption and access control, also influence backup strategy selection. Data must be protected both during transit and while stored to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
Budget Constraints:
- Budget constraints play a significant role in determining the backup strategy. Organizations must balance the cost of implementing and maintaining backup solutions with the level of protection they provide.
- Different backup solutions have varying costs associated with hardware, software, licensing, maintenance, and operational overhead. The chosen strategy should offer the best possible protection within the available budget.
Best Practices for AWS Cloud Storage Backup
Implementing a tiered backup approach:
Tiered backup involves categorizing data based on its importance and access frequency, then storing it in different tiers of storage accordingly. For instance, frequently accessed and critical data might be stored in high-performance storage like Amazon S3 Standard, while less frequently accessed data could be stored in a cheaper storage class like Amazon S3 Glacier or Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive. This approach helps optimize costs while ensuring that all data is appropriately backed up and accessible when needed.
Using lifecycle policies to manage data retention:
AWS provides lifecycle policies that allow you to automatically transition objects between different storage classes or delete them after a specified period. By setting up lifecycle policies, you can ensure that your backup data is retained for the required duration according to compliance or business requirements, and then automatically moved to more cost-effective storage classes or deleted when it’s no longer needed.
Encrypting data at rest and in transit:
Security is paramount when it comes to backup data. AWS offers various encryption options to ensure that your data is protected both at rest and in transit. You can use server-side encryption with Amazon S3-managed keys (SSE-S3), AWS Key Management Service (KMS) keys (SSE-KMS), or your own encryption keys managed by AWS Key Management Service (SSE-C). Additionally, you can enable SSL/TLS encryption for data transmitted between your applications and AWS services, ensuring end-to-end encryption.
Automating backup processes with AWS services like AWS Backup:
AWS Backup is a fully managed backup service that centralizes and automates the backup of your AWS resources, including Amazon EBS volumes, Amazon RDS databases, Amazon DynamoDB tables, and more. By using AWS Backup, you can create backup policies, manage backup schedules, and monitor backup activity from a single console, simplifying the backup process and ensuring consistent backups across your AWS environment.
Implementing Backup Strategies in AWS
Setting up backup policies and schedules:
- Define what data needs to be backed up: Determine which resources, databases, files, or directories require regular backups.
- Establish backup frequency: Decide how often backups should occur based on the criticality of data and the frequency of changes.
- Determine retention policies: Define how long backups should be retained. This could vary based on compliance requirements, business needs, and the nature of the data.
- Implement automated backup schedules: Utilize AWS services such as AWS Backup or AWS Data Lifecycle Manager to automate backup processes according to your defined policies and schedules.
Configuring versioning and cross-region replication:
- Enable versioning: In Amazon S3, enable versioning to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object stored in your bucket. This protects against accidental deletions or overwrites.
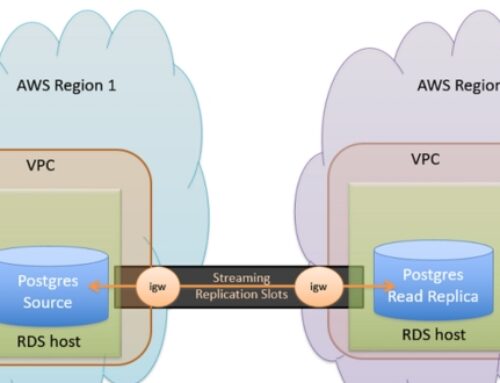
- Implement cross-region replication (CRR): Set up replication rules to automatically replicate objects across different AWS regions. This provides data redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring data availability even in the event of a regional outage.
Leveraging AWS Storage Gateway for hybrid cloud backup solutions:
- AWS Storage Gateway: This service enables hybrid cloud storage by seamlessly integrating on-premises environments with AWS cloud storage. You can deploy a gateway appliance on-premises, which connects to AWS storage services such as Amazon S3, Glacier, or EBS, allowing you to backup on-premises data to the cloud.
- Implementing backup with Storage Gateway: Configure the Storage Gateway appliance to create backups of on-premises data and store them in AWS storage services. This provides an efficient and scalable solution for backing up on-premises data to the cloud, with options for compression, encryption, and bandwidth management.
Monitoring and Testing Backup Strategies
Monitoring Backup Jobs and Storage Usage:
- Monitoring backup jobs involves actively tracking the status of ongoing backup operations to ensure they complete successfully within the defined backup windows. This includes verifying that backups are being performed according to the predetermined schedule and that they are capturing all required data.
- Monitoring storage usage entails keeping track of the amount of data being backed up and stored over time. This helps in managing storage resources efficiently, identifying trends in data growth, and anticipating any potential capacity issues.
Performing Regular Data Recovery Tests:
- Regular data recovery tests involve simulating real-world scenarios where data needs to be restored from backups. This ensures that the backup processes are functioning correctly and that the data is recoverable in case of system failures, disasters, or other emergencies.
- These tests also help in identifying and addressing any weaknesses or gaps in the backup and recovery procedures before they become critical issues.
Using AWS CloudWatch and AWS Config for Monitoring and Compliance:
- AWS CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows users to collect and track metrics, monitor log files, set alarms, and automatically react to changes in AWS resources. It can be used to monitor the performance and health of backup systems and storage resources in AWS.
- AWS Config is a service that provides detailed information about the configuration of AWS resources over time. It helps in assessing, auditing, and evaluating the configurations of AWS resources for compliance with organizational policies and industry regulations.
- By leveraging AWS CloudWatch and AWS Config, organizations can gain visibility into their backup infrastructure, monitor its performance and compliance, and take proactive measures to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance.
Monitoring and testing backup strategies are essential for maintaining the reliability, availability, and security of data backups, whether they are stored on-premises or in the cloud. These practices help organizations mitigate risks associated with data loss and ensure that they can recover data efficiently when needed.
Cost Considerations and Optimization Techniques
Understanding pricing models for different AWS storage services:
- AWS offers various storage services with different pricing models, including Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service), Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store), Amazon EFS (Elastic File System), and Amazon Glacier.
- Each service has its own pricing structure based on factors such as storage capacity, data transfer, requests, and retrieval times.
- Understanding these pricing models is essential for making informed decisions about which storage service best fits your requirements while optimizing costs.
Implementing cost-saving measures like data deduplication and compression:
- Data deduplication involves identifying and eliminating duplicate copies of data within a storage system. By reducing redundant data, storage costs can be significantly lowered.
- Compression techniques can be used to reduce the size of data stored in AWS, leading to cost savings by requiring less storage space.
- Implementing these techniques can help optimize storage costs without sacrificing data integrity or accessibility.
Utilizing AWS Cost Explorer for cost analysis and optimization:
- AWS Cost Explorer is a tool provided by AWS that allows users to visualize, understand, and manage their AWS costs and usage.
- It provides detailed insights into spending patterns, cost drivers, and opportunities for optimization across various AWS services, including storage.
- By leveraging Cost Explorer, organizations can identify areas of overspending, implement cost-saving measures, and track the effectiveness of optimization efforts over time.
Effective cost management in AWS storage involves understanding pricing models, implementing cost-saving measures such as deduplication and compression, and utilizing tools like AWS Cost Explorer for ongoing cost analysis and optimization. By adopting these strategies, organizations can optimize their AWS storage costs while ensuring efficient resource utilization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective backup strategies are crucial for ensuring data integrity, regulatory compliance, and business continuity in AWS environments. By understanding the various AWS cloud storage services, factors influencing backup strategy selection, and best practices for implementation and optimization, organizations can mitigate risks and confidently embrace the cloud for their backup and recovery needs. As technology evolves, continuous monitoring, testing, and adaptation will remain essential to stay ahead of emerging threats and leverage new opportunities in AWS cloud storage backup.
AWS cloud storage backup offers durability, scalability, and reliability. It ensures data availability in case of disasters, hardware failures, or human errors.
AWS provides several services for backup, including Amazon S3, Amazon Glacier, AWS Backup, AWS Storage Gateway, and Amazon EBS snapshots.
Key considerations include data retention policies, recovery time objectives (RTOs), recovery point objectives (RPOs), cost-effectiveness, compliance requirements, and data encryption.
Amazon S3 is designed for frequent access to data with low-latency retrieval, while Amazon Glacier offers lower storage costs for infrequently accessed data with longer retrieval times.
You can ensure data security by implementing encryption at rest and in transit, managing access control through IAM policies, and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA).