Introduction
Microsoft 365, formerly known as Office 365, has become an integral part of the modern digital workplace. It comprises a suite of applications designed to enhance productivity, collaboration, and communication. Among the well-known applications like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, Microsoft Publisher and Microsoft Access stand out for their specialized functionalities. These applications, available exclusively on the PC platform, are designed to address distinct needs – desktop publishing and database management.
Microsoft Publisher: Empowering Users with Desktop Publishing Mastery
-
Overview of Microsoft Publisher
Microsoft Publisher is a desktop publishing application that has undergone significant evolution, transforming into a versatile tool for creating various types of publications. Its primary purpose is to empower users to produce professional-looking documents and marketing materials without requiring advanced graphic design skills.
- Evolution and Purpose:
Originally introduced as a part of the Microsoft Office suite, Publisher has evolved to offer a wide range of features catering to the needs of users who want to create visually appealing publications. It provides templates and tools that simplify the design process, making it accessible to individuals and businesses alike. Over the years, Microsoft Publisher has become an essential tool for creating flyers, brochures, newsletters, and other print or digital publications.
- Integration within Microsoft 365:
One of the key strengths of Microsoft Publisher lies in its seamless integration within the Microsoft 365 suite. Microsoft 365, a cloud-based productivity suite, includes applications like Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Publisher, among others. This integration facilitates a cohesive workflow, allowing users to collaborate and synchronize their work across different Office applications.
The integration is not only limited to file compatibility but extends to a shared interface and consistent user experience. Users can easily import content from other Office applications, such as text from Word or data from Excel, into Publisher. Likewise, Publisher allows for the export of content to other Office applications, ensuring a smooth transition between various elements of a project.
This interconnectedness enhances productivity and collaboration, as teams can work seamlessly on projects, share resources, and maintain consistency across their publications. It also streamlines the workflow for individuals who frequently switch between different Office applications, providing a unified environment for creating, editing, and sharing content.
Microsoft Publisher has evolved into a powerful desktop publishing tool within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, offering users the ability to create professional publications with ease and benefiting from a seamless integration with other Office applications. This integration not only simplifies the workflow but also promotes collaboration and ensures a consistent user experience across the Microsoft 365 suite.
-
User Interface and Navigation
Microsoft Publisher boasts a user-friendly Ribbon Interface, a hallmark of many Microsoft Office applications. The Ribbon is thoughtfully organized into tabs, each dedicated to specific tasks, fostering an intuitive user experience. This well-structured design ensures that users can easily locate and utilize the tools essential for diverse aspects of desktop publishing. Whether it’s formatting text, inserting images, or adjusting layout settings, the Ribbon Interface streamlines the navigation process for users, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Ribbon Interface: A Familiar Framework
The familiarity of the Ribbon Interface is a notable advantage for users familiar with other Microsoft Office applications. This consistency in design across the suite promotes a seamless transition for those accustomed to working with Word, Excel, or PowerPoint. As a result, individuals can leverage their existing knowledge of the Ribbon’s functionality, accelerating the learning curve for Microsoft Publisher.
- Templates and Design Tools: A Creative Toolkit
One of Microsoft Publisher’s strengths lies in its expansive collection of templates tailored to diverse publication types. Whether creating brochures, newsletters, or flyers, users can kickstart their projects with professionally designed templates, saving time and ensuring a polished look. Complementing this, the application provides a robust set of design tools. From a plethora of fonts and colors to versatile shapes and special effects, users can unleash their creativity and tailor publications to their specific preferences and branding requirements.
- Empowering Creativity: Design Customization
The availability of diverse design tools empowers users to personalize their publications with precision. The freedom to experiment with various fonts, colors, and shapes ensures that each project reflects the creator’s unique style. Furthermore, the inclusion of special effects allows users to add a touch of flair, making their publications visually engaging. Microsoft Publisher, therefore, not only streamlines the publication process but also serves as a creative playground for users to express their design prowess.
Microsoft Publisher’s user interface, characterized by the Ribbon Interface, coupled with its extensive collection of templates and versatile design tools, establishes it as a robust platform for desktop publishing. Whether users seek efficiency in navigation or a canvas to bring their creative visions to life, Publisher stands out as a comprehensive solution within the realm of design and layout software.
-
Document Creation and Formatting
- Page Layout and Design: Microsoft Publisher provides users with robust tools for controlling the page layout and design of their documents. Whether creating brochures, newsletters, or other publications, users have the flexibility to customize factors such as margins, orientation, and page size. This level of control allows for the creation of visually appealing and professional-looking documents. One notable feature is the support for multi-page documents, empowering users to craft extensive publications with a cohesive and consistent design across multiple pages.
- Text and Typography Features: The application goes beyond basic text editing by offering a rich array of typography features. Users can exercise precise control over text elements, including font styles, sizes, colors, and paragraph alignment. This granular control over typography ensures that documents maintain a polished and cohesive appearance. Additionally, Microsoft Publisher provides advanced typography features such as drop caps, allowing for creative and eye-catching beginnings to paragraphs. Text effects and custom spacing further enhance the visual appeal of the text, enabling users to create documents that stand out with a professional and polished presentation. Whether it’s a business report or a promotional flyer, these text and typography features contribute to the overall aesthetic quality of the document.
-
Advanced Features
Mail Merge for Personalized Documents: Microsoft Publisher supports mail merge functionality, enabling users to create personalized documents by merging data from external sources, such as Excel spreadsheets or Access databases. This feature is particularly useful for producing customized newsletters or marketing materials.
Designing for Print and Digital Outputs: Users can optimize their publications for both print and digital distribution. Microsoft Publisher provides settings for print layout, including options for color management and print quality. Simultaneously, users can export their publications in digital formats suitable for online sharing or viewing.
Collaboration and Sharing Options: The application facilitates collaboration through features like real-time co-authoring, allowing multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously. Additionally, users can easily share their publications with others by saving them to Microsoft 365 cloud storage or exporting them in various formats for distribution.
Microsoft Publisher empowers users with a comprehensive set of tools for desktop publishing, making it accessible for a wide range of users to create professional-quality publications for both print and digital purposes.
Microsoft Access: Unleashing the Power of Database Management
Introduction to Microsoft Access:
- Role in Database Management:
Microsoft Access is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that provides an intuitive and user-friendly environment for creating, managing, and utilizing databases. It allows users to store, organize, and retrieve data efficiently.
Access plays a crucial role in managing data by providing tools to design and build databases without requiring extensive programming knowledge. It’s widely used in various industries and sectors for tasks ranging from small personal projects to complex business applications.
- Integration with Microsoft 365 Ecosystem:
Microsoft Access is part of the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, which means it seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft Office applications like Excel, Word, and Outlook. This integration enables users to import and export data easily, collaborate on projects, and use data from Access in conjunction with other Microsoft tools.
The compatibility with Microsoft 365 ensures a smooth workflow, making it convenient for users who are already familiar with other Microsoft products.
Database Design and Creation:
- Tables, Queries, Forms, and Reports:
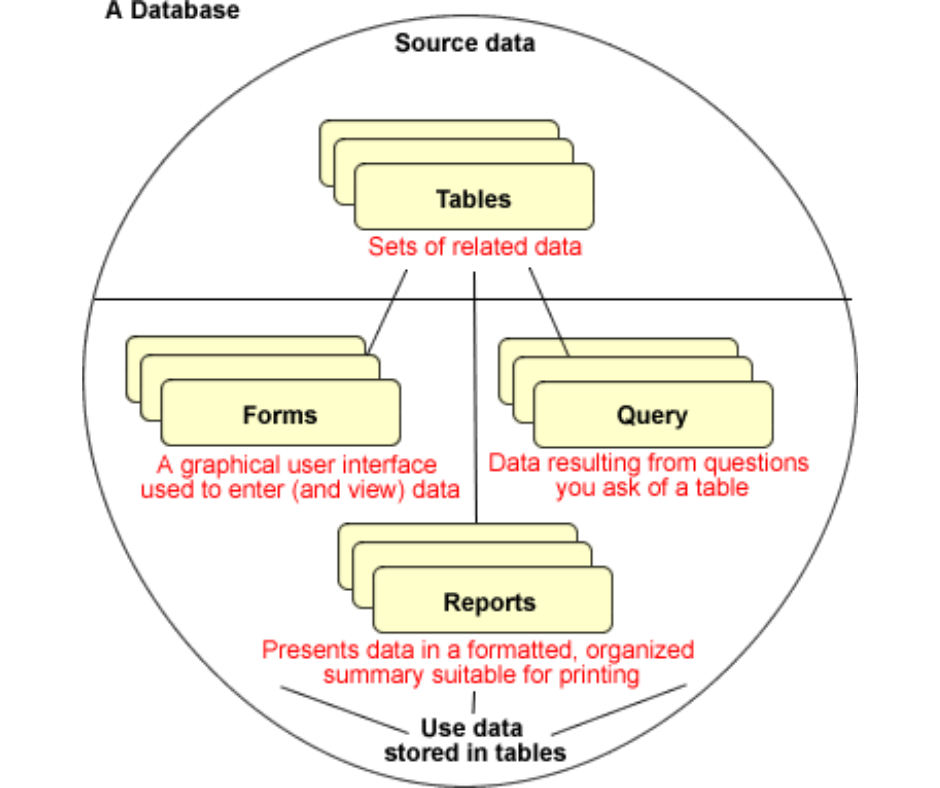
- Tables: In Access, data is stored in tables, which are similar to spreadsheets. Tables organize information into rows and columns, each representing a record and a field, respectively.
- Queries: Queries are used to extract specific information from the database. Users can define criteria to filter data and create custom views of the information stored in tables.
- Forms: Forms provide a user-friendly interface for entering and viewing data. They simplify data entry by presenting information in a structured and easily navigable format.
- Reports: Reports allow users to present data in a printable format. Users can design reports to summarize and format data for better analysis and presentation.
- Relationships and Normalization:
- Relationships: In relational databases like Access, relationships define how different tables are connected or linked to each other. Establishing relationships ensures data consistency and reduces redundancy by allowing information to be stored in separate tables but still connected logically.
- Normalization: Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. Access supports normalization techniques to structure data efficiently by eliminating data duplication and minimizing errors.
Microsoft Access empowers users to efficiently manage data through its intuitive interface, seamless integration with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, and robust features for designing and creating databases. Understanding database design principles, relationships, and normalization enhances the effectiveness of using Access for various applications.
Data Entry and Management:
- Forms for Efficient Data Input: This involves creating user-friendly forms to input data into Excel. Forms can help streamline the data entry process by providing a structured interface, reducing errors, and ensuring consistency. Excel allows you to create forms using various tools, making it easier for users to input data without directly interacting with the spreadsheet.
- Queries for Data Retrieval: Queries in Excel involve searching and extracting specific data based on defined criteria. By using queries, you can retrieve relevant information from large datasets quickly. This is particularly useful for large databases where manual searching would be time-consuming.

- Automation with Macros: Macros are sequences of instructions that automate tasks in Excel. They can be recorded or written using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Automation with macros can significantly enhance efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing the likelihood of errors, and saving time.
Integration with Other Microsoft 365 Apps:
- Exporting and Importing Data: Excel seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft 365 applications, allowing you to export and import data easily. For example, you can export Excel data to Word for creating reports or to PowerPoint for presentations. Similarly, you can import data from other Microsoft 365 apps into Excel for analysis.
- Collaboration with SharePoint and Excel: SharePoint is a collaborative platform, and when integrated with Excel, it allows multiple users to work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously. This collaboration is facilitated through SharePoint’s version control and Excel’s real-time co-authoring features. Users can edit and update data in real-time, making it a powerful tool for collaborative projects.
Publisher and Access Integration: Bridging the Gap between Design and Data
In the realm of data management and publication design, the integration of Microsoft Publisher and Access offers a powerful synergy. This integration serves as a bridge between the intricacies of database design in Access and the visually appealing presentation capabilities of Publisher. The seamless collaboration between these two tools opens up a spectrum of possibilities for creating dynamic and data-driven publications.
Embedding Access Data in Publisher Publications
One key aspect of this integration is the ability to embed Access data directly into Publisher publications. This functionality empowers users to create data-driven publications, where information from Access databases seamlessly flows into the designed layouts in Publisher. This not only streamlines the publication creation process but also ensures that the data remains up-to-date, providing a real-time connection between the Access database and the Publisher document.
Creating Data-Driven Publications
The concept of data-driven publications takes center stage, allowing users to design documents that automatically update as the underlying data evolves. This dynamic feature ensures that the information presented in the publication is always accurate, reflecting any changes made to the Access database. This not only saves time on manual updates but also enhances the reliability of the published content.
Dynamic Updates and Refresh Options
The integration goes a step further with dynamic updates and refresh options. Users can customize the frequency of data updates, ensuring that the published materials stay current without overwhelming the system. This flexibility in refresh options caters to different needs, from real-time data requirements to periodic updates, providing a tailored experience for diverse publishing scenarios.
Customizing Access Forms and Reports with Publisher
Moving beyond data integration, the collaboration between Access and Publisher extends to the customization of Access forms and reports within the Publisher environment. This synergy empowers users to enhance the output of their databases for both print and digital use, creating versatile materials that align with their specific needs.
Enhancing Database Output for Print and Digital Use
The customization capabilities within Publisher enable users to optimize the visual representation of Access forms and reports for various mediums. Whether the goal is to produce polished print materials or interactive digital documents, the integrated workflow ensures design consistency while accommodating the unique requirements of each platform.
Design Consistency Across Platforms
Maintaining design consistency across platforms becomes a significant advantage of this integration. Users can seamlessly transition between Access and Publisher, preserving the visual aesthetics and layout structures. This not only enhances the overall user experience but also streamlines the workflow, allowing for a cohesive and professional presentation of data across different mediums.
The integration of Microsoft Publisher and Access transcends the traditional boundaries between design and data. By embedding Access data in Publisher publications and customizing forms and reports, users can create dynamic, visually appealing materials with consistency across various platforms, ultimately bridging the gap between design and data harmoniously and efficiently.
Real-world applications and case studies:
Industry-Specific Use Cases:
- Publishing Solutions for Marketing and Advertising:
In this context, publishing solutions refer to tools and platforms that enable the creation, distribution, and management of marketing and advertising content. This could involve digital platforms, print materials, and multimedia content. Success in marketing often hinges on the ability to deliver compelling and timely content to target audiences. Case studies might showcase how companies have utilized publishing solutions to streamline their marketing processes, enhance content quality, and improve audience engagement.
- Database Management in Education and Research:
Database management is crucial in educational institutions and research settings for organizing and accessing vast amounts of information. Case studies in this category could illustrate how effective database management systems have been implemented to enhance educational processes, streamline administrative tasks, and facilitate research endeavors. This may include examples of improved data accessibility, collaboration among researchers, and the development of insights from structured data.
Success Stories: How Publisher and Access Transformed Businesses:
- Streamlining Communication with Professional Publications:
This success story may focus on how companies or professionals have transformed their communication strategies by leveraging publisher tools. This could involve the creation and distribution of professional publications, such as reports, journals, or white papers. Case studies might highlight improvements in communication efficiency, audience reach, and the overall impact on the organization’s reputation and authority in the industry.
- Empowering Decision-Making with Data-Driven Insights:
This success story would likely revolve around how businesses have utilized access to data-driven insights to make informed decisions. Access to relevant data can empower decision-makers by providing valuable information on market trends, consumer behavior, and operational efficiency. Case studies may showcase examples of businesses that have successfully integrated data analytics tools, leading to improved decision-making processes, strategic planning, and, ultimately, business growth.
These real-world applications and case studies highlight the practical use of publishing and database management solutions in specific industries. The success stories provide tangible examples of how businesses have benefited from these tools, whether by enhancing marketing efforts, improving educational and research processes, or making more informed decisions through data-driven insights.
Conclusion
Microsoft Publisher and Microsoft Access, exclusive to the PC platform, offer powerful tools for desktop publishing and database management. By exploring their features and functionalities, users can unlock new levels of creativity in design and efficiency in data management. As Microsoft continues to invest in innovation, the future promises even more exciting developments in these applications, further solidifying their role in the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
Yes, Microsoft Publisher is part of the Microsoft 365 suite, and you can access it online through the web version. This allows you to create and edit publications in a web browser without installing the desktop application.
Microsoft Access is a database management system that helps users create and manage databases. Key features include data entry forms, queries, reports, and the ability to build relational databases.
Yes, Microsoft 365 allows real-time collaboration on Publisher documents. Multiple users can edit the same document simultaneously, and changes are synced instantly.
Microsoft Publisher seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft 365 apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. You can easily import and export content between these applications.
Yes, Microsoft Publisher provides a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of publications. Users can choose a template as a starting point and customize it according to their needs.
Yes, Microsoft Access is often used by small businesses for database management. It’s a cost-effective solution for creating and maintaining databases without the complexity of larger database systems.
Yes, Microsoft Publisher supports digital publishing. You can create content for online use, such as web pages and digital newsletters, in addition to traditional print materials.
Microsoft Access includes powerful querying and reporting tools, allowing users to analyze data and generate reports. It’s especially useful for businesses that need to track and report on various aspects of their operations.
Yes, Microsoft provides extensive training resources for Publisher and Access within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. Users can access online tutorials, documentation, and community forums to learn and troubleshoot issues.