Introduction:
In this section, the document or presentation likely sets the stage for what follows. It might provide context on the importance of the topics to be discussed and may briefly touch on the significance of Microsoft 365 and the evolving threat landscape in the context of modern technology and business.
Overview of Microsoft 365:
This section is likely to delve into the key features and components of Microsoft 365. Microsoft 365 is a comprehensive suite of productivity tools and cloud-based services that includes applications like Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and more, along with collaboration tools such as Teams and SharePoint. The overview may also touch on the integration of these tools to enhance productivity and streamline workflows for businesses and organizations.
The Evolving Threat Landscape:
This part is likely to address the dynamic and constantly changing nature of cybersecurity threats. The term “evolving threat landscape” suggests that the document will explore how cyber threats are continuously adapting and becoming more sophisticated. This could include discussions on various types of cyber threats such as malware, phishing attacks, ransomware, and other forms of cyberattacks. The document might also highlight the importance of staying vigilant and adopting robust security measures to protect digital assets and sensitive information.
This introduction appears to set the stage for a discussion on Microsoft 365 and its relevance in the context of the ever-changing and increasingly complex world of cybersecurity threats. It suggests that the document or presentation may provide insights into how Microsoft 365 addresses security challenges and helps organizations navigate the evolving threat landscape.
Identity and Access Management
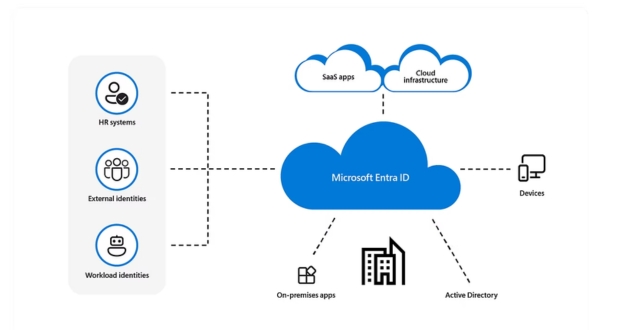
Azure Active Directory (AAD):
- Azure Active Directory is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service.
- It allows organizations to manage and secure their user identities and credentials.
- AAD supports single sign-on (SSO) to various applications, both on-premises and in the cloud.
- It is a crucial component for authenticating and authorizing users to access Azure resources and other integrated applications.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Multi-Factor Authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide more than one method of verification before granting access.
- Typically involves something the user knows (like a password) and something the user has (like a mobile device for receiving a verification code).
- Enhances security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
Conditional Access Policies:
- Conditional Access Policies allow organizations to enforce specific access controls based on certain conditions.
- Conditions can include user location, device health, or the sensitivity of the resource being accessed.
- Organizations can customize policies to meet their specific security requirements, ensuring a dynamic and context-aware access control.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- RBAC is a method of managing access to computer systems or network resources based on roles assigned to individuals or groups.
- In Azure, RBAC is used to control access to Azure resources, allowing organizations to manage permissions at a granular level.
- Users are assigned roles, and these roles determine what actions they can perform on specific resources.
- In summary, these components collectively contribute to a robust identity and access management strategy, helping organizations secure their digital assets and ensure that users have appropriate access levels based on their roles and contextual factors.
Data Protection and Encryption
Azure Information Protection (AIP):
Overview: Azure Information Protection is a cloud-based solution that helps organizations classify, label, and protect their sensitive information. It enables you to define and apply policies to automatically classify and protect data based on its sensitivity. AIP integrates with other Microsoft 365 services to provide persistent protection to files and emails, both within and outside the organization.
Key Features:
- Classification and Labeling: AIP allows you to classify data based on its sensitivity and apply labels to documents and emails.
- Rights Management: AIP provides rights management features, restricting access and permissions even after the data has left the organization’s network.
- Integration: Seamless integration with Microsoft 365 applications, ensuring protection across various collaboration platforms.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
Overview: Data Loss Prevention is a set of policies and technologies aimed at preventing the unauthorized sharing of sensitive information. In Microsoft 365, DLP policies can be configured to detect and protect sensitive data, such as credit card numbers or confidential documents, from being shared inappropriately.
Key Features:
- Policy Creation: Organizations can create custom DLP policies based on regulatory requirements or internal data protection needs.
- Content Detection: DLP uses content inspection to identify sensitive information in emails, documents, and other communication channels.
- Action Enforcement: When a DLP policy is violated, actions can be taken, such as notifying users, blocking access, or encrypting the data.
Encryption in Microsoft 365:
Overview: Encryption in Microsoft 365 involves protecting data by converting it into a secure format that can only be deciphered with the appropriate decryption key. This ensures that even if unauthorized users gain access to the data, they cannot interpret or use it without the correct encryption key.
Key Features:
- Email Encryption: Microsoft 365 supports encrypting emails to protect sensitive information during transmission.
- Azure Storage Encryption: Data stored in Azure services can be encrypted to provide an additional layer of security.
- End-to-End Encryption: Encryption can be applied to data at rest, in transit, and during processing, ensuring comprehensive protection.
Information Rights Management (IRM):
Overview: Information Rights Management is a technology that provides persistent protection to digital information, even when it is outside the organization’s boundaries. In Microsoft 365, IRM is often integrated with Azure Information Protection to control and protect access to sensitive data.
Key Features:
- Access Control: IRM restricts access to documents, emails, and other content based on user permissions and policies.
- Persistent Protection: Protection travels with the data, ensuring that it remains secure regardless of where it is stored or accessed.
- Usage Policies: Organizations can define policies governing how protected information can be used, preventing unauthorized actions such as copying or printing.
Threat Protection:
Threat protection refers to a comprehensive approach to safeguarding computer systems, networks, and data from potential security risks and cyber threats. It involves the deployment of various security measures and technologies to detect, prevent, and respond to malicious activities that could compromise the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint:
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a sophisticated endpoint security solution developed by Microsoft. It focuses on protecting devices such as computers, servers, and mobile devices from a wide range of cyber threats. The platform employs advanced threat detection algorithms, real-time monitoring, and automated response capabilities to identify and neutralize potential security risks. By providing insights into endpoint vulnerabilities, it enables organizations to enhance their overall security posture.
Microsoft Defender for Office 365:
Microsoft Defender for Office 365 is a security platform designed to protect the Microsoft 365 suite, including applications like Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and OneDrive for Business. The solution incorporates threat intelligence, behavioral analytics, and machine learning to identify and mitigate various email and collaboration-based threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, and data breaches. It serves as a crucial component in ensuring the security of communication and collaboration within organizations.
Advanced Threat Protection (ATP):
Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) is a category of security solutions that go beyond traditional measures to counteract sophisticated and evolving cyber threats. Microsoft’s ATP encompasses a range of products and services that provide enhanced security against advanced threats. These solutions often include features such as threat intelligence, sandboxing, and machine learning to analyze and respond to threats that may evade conventional security measures.
Zero Trust Security Model:
The Zero Trust Security Model is a security framework that challenges the traditional approach of trusting entities within a network by default. Instead, it advocates for continuous verification of the identity and security status of all users, devices, and applications, regardless of their location or network connection. Microsoft has embraced the Zero Trust Security Model in its solutions, emphasizing the importance of least privilege access, continuous monitoring, and strict access controls to minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. This approach is particularly relevant in today’s dynamic and interconnected digital landscape, where traditional perimeter-based defenses may no longer be sufficient.
Cloud App Security:
Cloud App Security is a comprehensive approach to securing cloud-based applications and data. It involves deploying tools and measures to safeguard sensitive information stored and processed in the cloud. This security framework addresses the unique challenges associated with cloud computing, where data is often dispersed across various platforms and services. The goal is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data while leveraging the benefits of cloud technology.
Discovering Shadow IT:
One crucial aspect of Cloud App Security is the identification and management of Shadow IT. This refers to the use of unauthorized applications or services by employees within an organization. Discovering Shadow IT involves monitoring and analyzing network traffic, user behavior, and data access patterns to identify instances where employees are using unapproved applications. By gaining visibility into Shadow IT, organizations can assess potential security risks and enforce policies to mitigate them effectively.
Real-time Data Protection:
Real-time data protection is a fundamental component of Cloud App Security. It involves the implementation of mechanisms that continuously monitor and safeguard data as it moves within and outside the organization’s network. This includes encryption, access controls, and activity monitoring to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. By providing real-time protection, organizations can respond swiftly to potential security incidents and minimize the impact of data breaches.
Conditional Access App Control:
Conditional Access App Control is a security feature that allows organizations to enforce specific conditions or policies based on user access to cloud applications. This involves setting rules and restrictions that dictate how users can interact with sensitive data and applications based on factors such as device type, location, and user behavior. By implementing conditional access controls, organizations can enhance security by ensuring that only authorized users with compliant devices can access critical resources.
Threat Detection and Analytics:
Threat detection and analytics play a vital role in Cloud App Security by identifying and mitigating potential security threats. This involves utilizing advanced analytics tools to analyze patterns and anomalies in user behavior, network traffic, and application usage. By leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence, organizations can detect unusual activities that may indicate a security threat, enabling proactive responses to prevent or minimize potential damage. Continuous monitoring and analysis of threats contribute to a dynamic and adaptive security posture in the cloud environment.
Security and Compliance Center

Security Score:
Description: Security Score is a tool within the Security and Compliance Center that provides an overall security rating for your Microsoft 365 organization. It evaluates your security settings and activities across various services and provides recommendations to enhance your security posture.
Functionality:
- Measures the effectiveness of security configurations.
- Offers actionable insights and improvement suggestions.
- Helps organizations prioritize security tasks.
Compliance Manager:
Description: Compliance Manager is a solution designed to help organizations manage their compliance with various regulatory standards and requirements. It provides a dashboard to view and manage compliance data, helping organizations assess their adherence to regulations and standards.
Functionality:
- Assesses and tracks compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, etc.
- Generates compliance reports and documentation.
- Offers risk assessment tools and improvement recommendations.
Audit Logging:
Description: Audit Logging is a feature that allows organizations to track user and administrator activities within Microsoft 365. It provides detailed logs of actions taken by users, giving administrators insights into who did what and when.
Functionality:
- Captures events related to user sign-ins, file access, permission changes, etc.
- Supports forensic analysis and investigation.
- Helps organizations meet compliance requirements by maintaining an audit trail.
Insider Risk Management:
Description: Insider Risk Management is a set of tools and features that help organizations identify and mitigate risks associated with insider threats. It enables proactive monitoring of user activities to detect potential risks posed by employees within the organization.
Functionality:
- Monitors user behavior and activities to identify anomalies.
- Flags potential insider threats based on predefined policies.
- Integrates with other security tools for a comprehensive risk management approach.
The Security and Compliance Center in Microsoft’s ecosystem provides a centralized hub for managing and enhancing the security and compliance aspects of an organization’s digital environment. The tools mentioned contribute to assessing, improving, and maintaining a robust security posture while ensuring compliance with various regulatory standards.
Collaboration Security Overview:
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital collaboration, ensuring the security of sensitive data and communications is paramount. Organizations leverage a variety of tools and platforms to facilitate collaboration among employees, and each of these tools requires robust security measures. In this context, collaboration security encompasses the protective measures put in place to safeguard information, communications, and user access within collaborative platforms. Let’s delve into the specific components of collaboration security:
SharePoint and OneDrive Security:
SharePoint and OneDrive are integral components of Microsoft’s collaboration suite, providing users with cloud-based storage and sharing capabilities. Security in SharePoint and OneDrive revolves around controlling access to files and data, ensuring data integrity, and preventing unauthorized sharing. Organizations employ features such as encryption, access controls, and auditing to monitor and manage file access. Version control and backup mechanisms further enhance data protection, allowing for recovery in the event of accidental deletions or unauthorized changes.
Teams Security:
Microsoft Teams serves as a hub for teamwork, facilitating chat, video conferencing, file sharing, and more. Teams security focuses on securing communication channels, protecting shared files, and ensuring that collaboration occurs in a secure environment. Encryption, user authentication, and compliance features play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information. Additionally, Teams security integrates with other Microsoft 365 security components, providing a comprehensive approach to data protection and threat mitigation.
Exchange Online Security:
As a critical element of Microsoft 365, Exchange Online handles email communication for organizations. Exchange Online security is designed to protect against email threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, and spam. Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) features, including link checking and attachment scanning, add layers of defense against malicious content. Additionally, encryption and data loss prevention (DLP) policies help organizations maintain control over sensitive information shared through email.
Yammer Security:
Yammer facilitates enterprise social networking, allowing employees to collaborate and share information within an organization. Yammer security focuses on identity and access management, ensuring that only authorized users can access and contribute to conversations. Encryption and compliance features assist in protecting the confidentiality and integrity of discussions. Integration with other Microsoft 365 security tools further enhances overall security posture.
Collaboration security is a multifaceted approach that addresses the unique challenges posed by various collaboration platforms. By implementing robust security measures across SharePoint, OneDrive, Teams, Exchange Online, and Yammer, organizations can foster a secure and productive collaborative environment for their teams.
Best Practices for Microsoft 365 Security
Periodic Security Assessments:
Ensuring the robustness of your Microsoft 365 security requires regular and thorough assessments. Periodic security assessments involve evaluating the effectiveness of existing security measures, identifying vulnerabilities, and devising strategies to address potential risks. This practice involves conducting comprehensive reviews of user access controls, data encryption protocols, and system configurations. By routinely assessing your Microsoft 365 security infrastructure, you can stay ahead of emerging threats and adapt your defenses accordingly.
User Training and Awareness:
One of the fundamental aspects of maintaining a secure Microsoft 365 environment is cultivating a culture of security awareness among users. Regular training programs are essential to educate users about phishing threats, password hygiene, and other security best practices. Users should be equipped with the knowledge to recognize and report suspicious activities, fostering a collaborative approach to cybersecurity. An informed user base becomes a critical line of defense against social engineering attacks and inadvertent security breaches.
Regularly Update Policies and Configurations:
The dynamic nature of cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach to policy management and system configurations. Regularly updating security policies ensures that they remain aligned with evolving compliance standards and industry best practices. Additionally, keeping system configurations up-to-date helps in mitigating vulnerabilities and enhancing overall security. This practice involves staying informed about the latest security developments and promptly implementing necessary changes to maintain the integrity of your Microsoft 365 environment.
Third-Party Integration for Enhanced Security:
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, leveraging third-party solutions can significantly enhance Microsoft 365 security. Integrating specialized security tools and services provides an additional layer of protection against advanced threats. This includes implementing threat intelligence platforms, advanced malware detection solutions, and identity management systems. Third-party integrations can offer insights beyond the capabilities of native Microsoft 365 security features, creating a more resilient defense mechanism against a diverse range of cyber threats.
Adopting these best practices contributes to a comprehensive and proactive approach to Microsoft 365 security. Periodic assessments, user training, policy updates, and third-party integrations collectively strengthen the security posture, helping organizations navigate the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Emerging Trends in Microsoft 365 Security
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, Microsoft 365 Security is at the forefront of embracing cutting-edge technologies to fortify its defenses. One of the pivotal trends is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Microsoft has infused these technologies into its security solutions to enhance threat detection, automate responses, and adapt to evolving threats dynamically. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI and ML algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies, providing a more proactive and robust defense against cyber threats.
Another significant aspect of Microsoft 365 Security’s evolution is in Identity and Access Management (IAM). Azure Active Directory (AAD) is a central component, facilitating secure and seamless user authentication and authorization processes. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple means, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Conditional Access Policies and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) further refine access management, ensuring that users have the right level of access based on their roles and contextual factors.
Continuous Authentication represents a paradigm shift in security strategies. Traditionally, authentication was a one-time event at login. However, in the era of continuous authentication, user activities and behaviors are constantly monitored to detect anomalies. This approach provides a more dynamic and real-time response to potential security threats, allowing for immediate action when unusual patterns are detected.
The integration of Microsoft 365 Security with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) is a strategic move to streamline and enhance incident response capabilities. SOAR platforms automate repetitive security tasks, enabling faster response times and freeing up human resources for more complex analysis and decision-making. This integration ensures a coordinated and efficient response to security incidents, reducing the overall risk and impact of cyber threats.
Microsoft 365 Security is embracing these emerging trends to stay ahead of cyber adversaries. The combination of AI and ML, advancements in Identity and Access Management, continuous authentication, and integration with SOAR reflects a holistic and forward-thinking approach to safeguarding digital assets and ensuring a resilient security posture in the dynamic and ever-evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion
As organizations continue to navigate the dynamic landscape of digital transformation, securing data and communication is non-negotiable. Microsoft 365, with its extensive suite of tools, offers a comprehensive solution to safeguard against a myriad of threats. By implementing the best practices and staying abreast of emerging trends, businesses can not only mitigate risks but also foster a secure and productive digital environment. This guide serves as a roadmap for organizations seeking to fortify their digital fortresses within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, ensuring a resilient defense against the ever-evolving threat landscape.