Introduction:
Salesforce CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is a comprehensive cloud-based platform that helps organizations manage and streamline their interactions with customers, prospects, and partners. It provides a centralized hub for storing and managing customer data, tracking sales leads, managing marketing campaigns, and facilitating customer support.
Brief overview of Salesforce CRM:
Salesforce CRM is known for its flexibility, scalability, and user-friendly interface. It offers a range of tools and features that empower businesses to effectively manage their relationships with customers and improve overall operational efficiency. The platform is highly customizable, allowing organizations to tailor it to their specific needs and industry requirements.
Importance of user interface in CRM systems:
The user interface (UI) of a CRM system plays a crucial role in its effectiveness and adoption within an organization. A well-designed and intuitive UI enhances user experience, making it easier for employees to navigate the system, input and retrieve data, and perform various tasks. An intuitive UI reduces the learning curve for new users, increases productivity, and encourages widespread adoption of the CRM system across different departments.
Purpose of enhancing the Salesforce CRM user interface:
- Improved User Experience: An enhanced UI provides a more visually appealing and user-friendly environment, making it easier for users to interact with the CRM platform. This leads to increased user satisfaction and productivity.
- Increased Adoption: A well-designed UI encourages more users to embrace the CRM system, leading to higher adoption rates within the organization. When employees find the interface easy to use and navigate, they are more likely to actively engage with the platform.
- Efficiency and Productivity: A streamlined and intuitive UI can significantly reduce the time and effort required for users to perform tasks. This, in turn, boosts overall efficiency and productivity as employees can focus on their core responsibilities rather than struggling with a complex interface.
- Data Accuracy: A user-friendly interface often results in more accurate data entry and retrieval. When users can easily input and access information, the likelihood of errors decreases, leading to a more reliable database and better decision-making.
- Competitive Advantage: In today’s competitive business environment, having a CRM system with an enhanced user interface can be a differentiator. It positions the organization as forward-thinking and invested in providing its employees with tools that support their work effectively.
Enhancing the Salesforce CRM user interface is essential for creating a positive user experience, increasing system adoption, improving efficiency, ensuring data accuracy, and gaining a competitive edge in the market. It aligns the CRM system more closely with the needs and expectations of the users, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Evolution of Salesforce UI
Historical Context of Salesforce UI:
Origins: Salesforce was founded in 1999 as a cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform. Initially, its user interface (UI) was basic and focused primarily on functionality rather than aesthetics.
Early Challenges: In the early years, users faced challenges with the UI, which was not as intuitive as contemporary standards. The platform’s growth and feature expansions necessitated a more user-friendly interface.
Milestones in UI Development:
Salesforce Classic: The initial UI, known as Salesforce Classic, served its purpose but was characterized by a relatively dated and cluttered design. It became evident that a more modern and streamlined UI was necessary to meet evolving user expectations.
Introduction of Lightning Experience: In 2015, Salesforce introduced the Lightning Experience, a significant shift in UI design. This update aimed to enhance user experience, offering a more visually appealing and efficient interface. The Lightning Experience brought about improved navigation, responsive design, and a greater focus on user productivity.
Ongoing Innovations: Salesforce continues to evolve its UI with regular updates. These may include enhancements in design, the introduction of new features, and optimizations for different devices. The company often seeks to align the UI with industry trends and user preferences.
User Feedback and the Need for Improvement:
Listening to Users: Salesforce places a strong emphasis on user feedback. Through forums, surveys, and direct interactions, the company gathers insights into user experiences and pain points.
Identifying Pain Points: Feedback from users often highlights areas of the UI that need improvement. This could range from issues with navigation to suggestions for additional features.
Iterative Design: Salesforce adopts an iterative design approach, using user feedback to guide updates and refinements to the UI. Regular releases and patches address identified issues and introduce improvements, ensuring that the platform stays responsive to user needs.
Adapting to Industry Trends:
Mobile Responsiveness: With the increasing prevalence of mobile devices, Salesforce has placed a strong emphasis on making its UI mobile responsive. This ensures that users can access and manage their CRM data seamlessly across various devices.
Integration of AI and Analytics: The evolution of Salesforce UI also involves integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics features. This not only enhances the user experience but also empowers users with insights and automation.
Key Components of Salesforce CRM UI
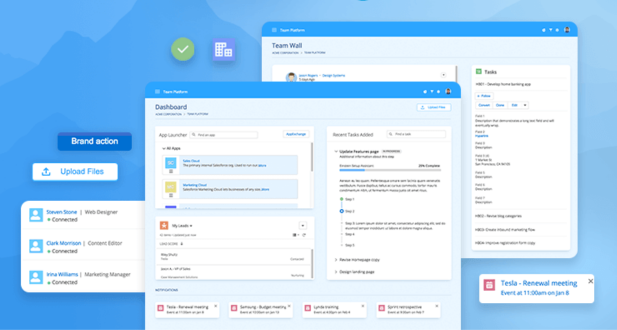
Dashboard:
Definition: A dashboard in Salesforce is a visual representation of key metrics and data points that provide a real-time overview of an organization’s performance.
Functionality: Users can customize dashboards to display various charts, graphs, and reports, allowing for quick and easy monitoring of important business metrics. Dashboards can be tailored to specific roles and provide insights that help in decision-making.
Home Page:
Definition: The home page is the first page users see when they log in to Salesforce. It serves as a central hub for accessing important information and tools.
Functionality: Users can customize their home pages to include components such as recent items, tasks, calendar events, and important reports. This customization helps individuals focus on the most relevant information for their roles.
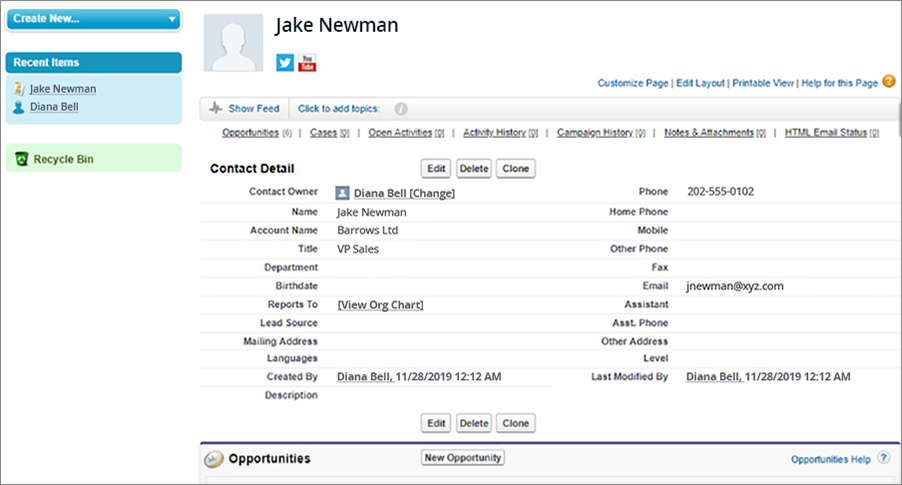
Record Pages:
Definition: Record pages in Salesforce display detailed information about specific records, such as leads, contacts, opportunities, or cases.
Functionality: Users can view, edit, and manage records from these pages. Record pages are customizable, allowing organizations to tailor the layout to their specific needs. They often include related lists, fields, and sections relevant to the record type.
Navigation Menu
Definition: The navigation menu is the set of menus and options that allow users to move through different sections and functionalities within Salesforce.
Functionality: It provides a hierarchical structure for easy navigation, enabling users to access modules like Sales, Service, Marketing, and more. The navigation menu ensures a user-friendly experience and helps individuals quickly find the tools and features they need.
Search Functionality:
Definition: The search functionality in Salesforce allows users to quickly locate records, documents, and information within the system.
Functionality: Users can perform global searches that span across multiple objects and fields. The search results are presented in a way that facilitates efficient information retrieval. The search functionality enhances productivity by enabling users to find relevant data without navigating through various menus.
Challenges in the Current UI
User feedback and pain points:
Understanding user feedback is crucial for improving the user interface (UI). Users may experience difficulties or find certain features confusing, leading to a less-than-optimal user experience.
Identifying pain points involves recognizing areas where users struggle or encounter frustration. This could include unclear navigation, confusing layouts, or inefficient workflows.
Solutions may involve conducting usability testing, collecting user surveys, and analyzing support tickets to gain insights into specific issues users face.
Performance issues:
Performance is a critical aspect of UI design, affecting how fast and smoothly the interface responds to user interactions.
Slow load times, delays in response to user actions, or unoptimized code can lead to a subpar user experience.
Addressing performance issues may involve optimizing code, minimizing server requests, and utilizing caching mechanisms. Regular performance testing is essential to identify and resolve bottlenecks.
Scalability concerns:
As user bases grow, the UI must be scalable to accommodate increased traffic and usage without sacrificing performance.
Scalability issues may arise from inadequately designed databases, inefficient algorithms, or insufficient server resources.
Solutions involve designing a scalable architecture, utilizing cloud services, and optimizing data retrieval and processing mechanisms to handle increased loads.
Mobile responsiveness:
With the prevalence of mobile devices, ensuring that the UI is responsive and provides a seamless experience across different screen sizes and resolutions is vital.
Mobile responsiveness challenges include issues like text readability, touch-friendly navigation, and adapting complex layouts to smaller screens.
Solutions involve implementing responsive design principles, using flexible layouts and images, and testing the UI on various devices to ensure a consistent and user-friendly experience.
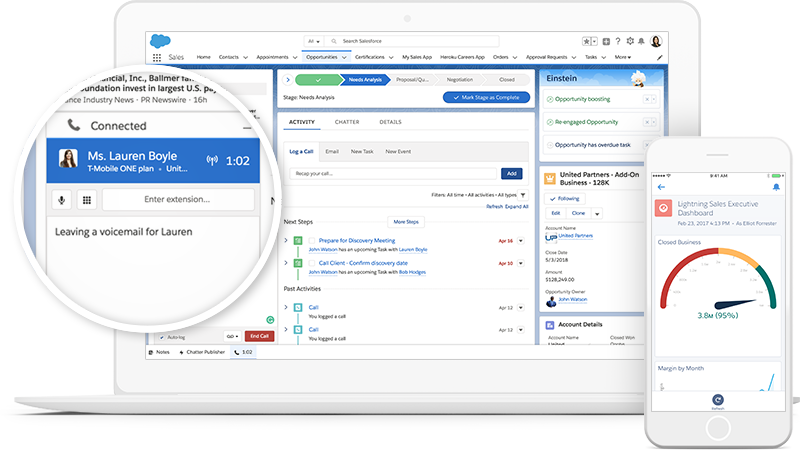
Salesforce Lightning Experience
Introduction to Salesforce Lightning:
User Interface Redesign: Salesforce Lightning introduces a revamped user interface (UI) that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also more dynamic and interactive compared to the classic version. The interface is designed to be responsive, making it accessible across various devices and screen sizes.
Enhanced Productivity: Lightning Experience is built with a focus on improving user productivity. It includes features that streamline and automate processes, reducing the time spent on repetitive tasks and allowing users to be more efficient in their daily activities.
Customization: Lightning allows for greater customization of the user interface, making it easier for organizations to tailor Salesforce to their specific needs. Users can create dynamic dashboards, customize record pages, and leverage the App Builder to design custom applications.
Features and Benefits:
Lightning App Builder: Users can design custom applications and pages with the Lightning App Builder, a drag-and-drop tool that doesn’t require coding skills. This empowers organizations to create tailored user interfaces to suit their unique business processes.
Lightning Components: Lightning Experience is built on a component-based framework, allowing for the development and integration of Lightning components. These reusable building blocks enable developers to create modular and scalable applications.
Sales Cloud and Service Cloud Enhancements: Lightning Experience offers improvements to both Sales Cloud and Service Cloud, providing more efficient workflows and better integration between sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
Einstein Analytics: Lightning includes integration with Einstein Analytics, Salesforce’s AI-driven analytics platform. This allows users to gain insights from their data, make data-driven decisions, and identify trends within their Salesforce environment.
How Lightning Improves User Experience:
Intuitive Navigation: Lightning Experience provides a more intuitive and streamlined navigation experience. Users can easily find the information they need with a more organized and visually appealing interface.
Dynamic Pages: Lightning pages are dynamic and responsive, adapting to the user’s preferences and workflow. This flexibility enhances the overall user experience, allowing for a more personalized and efficient interaction with Salesforce.
Collaboration and Communication: Lightning includes features that promote collaboration and communication within the platform. Chatter, Salesforce’s enterprise social network, is integrated to facilitate real-time communication and information sharing among users.
Migration from Classic to Lightning:
Planning and Assessment: Before migrating from Salesforce Classic to Lightning, organizations need to conduct a thorough assessment of their existing Salesforce implementation. This involves identifying customizations, integrations, and potential challenges that may arise during the migration process.
User Training: As Lightning Experience introduces a new interface, it’s crucial to provide adequate training to users to ensure a smooth transition. Training programs can help users familiarize themselves with the new features and functionalities of Lightning.
Pilot Testing: Before rolling out Lightning Experience to the entire organization, it’s advisable to conduct a pilot test with a smaller group of users. This allows organizations to identify and address any issues or concerns before a full-scale migration.
Data Migration: Migrating from Classic to Lightning involves transitioning not only the user interface but also ensuring that data is seamlessly transferred. Organizations need to plan and execute a data migration strategy to maintain data integrity during the transition.
Salesforce Lightning Experience is a comprehensive upgrade to the classic interface, offering improved features, customization options, and a more intuitive user experience. The migration process requires careful planning, user training, and testing to ensure a successful transition for organizations using Salesforce.
Customization Options
Personalization of Home Page:
- This feature enables users to customize the main landing page or home screen of the application or platform to suit their needs.
- Users can often choose which modules, widgets, or information they want to see prominently when they log in.
- This personalization may involve rearranging elements, adding shortcuts to frequently used features, or selecting specific data to be displayed.
Dashboard Customization:
- Dashboards are often used to present summarized and visually appealing data.
- Users can customize their dashboards by choosing the type of charts, graphs, or data visualizations they prefer.
- It may involve rearranging widgets, resizing elements, and selecting key performance indicators (KPIs) that are relevant to the user’s role or responsibilities.
Record Page Layouts:
- In many applications, data is organized in records, such as customer profiles, project details, or sales opportunities.
- Record page layouts customization allows users to modify the arrangement and display of fields, making it more tailored to their workflow.
- Users can choose which information is visible, set the order of fields, and determine the format in which data is presented.
Theming and Branding Options:
- Theming refers to the ability to change the overall look and feel of the application.
- Users can customize the color scheme, fonts, and other visual elements to align with their personal or corporate branding.
- This customization option is beneficial for creating a consistent and branded user experience across different platforms and applications.
Integration of AI and Automation
Efficiency Improvement: Combining AI with automation can lead to improved efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual efforts, and allowing systems to adapt and learn from data over time.
Decision-Making Support: AI can assist in decision-making by analyzing complex data sets, identifying patterns, and providing insights, allowing businesses to make informed decisions quickly.
Introduction to Einstein AI:
Salesforce’s Einstein AI: If you are referring to Einstein AI, it is Salesforce’s artificial intelligence technology. It is designed to bring AI capabilities to the Salesforce platform, enabling businesses to leverage predictive analytics, natural language processing, and machine learning to enhance customer relationship management (CRM) and other business processes.
Predictive Analytics: Einstein AI can analyze historical data to make predictions about future outcomes, helping organizations anticipate customer needs, optimize workflows, and make data-driven decisions.
Automation Features in UI:
User Interface (UI) Integration: This suggests that automation features are seamlessly incorporated into the user interface of a system or application, making it user-friendly and accessible.
Task Automation: Automation features in the UI can automate routine tasks, making processes more efficient and allowing users to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their work.
User-Friendly Design: Integration of automation features in the UI should prioritize a user-friendly design, ensuring that users can easily navigate and utilize the automation functionalities without a steep learning curve.
AI-Driven Insights for Users:
Data Analysis: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to extract meaningful insights. Users can benefit from these insights to understand trends, patterns, and anomalies in their data.
Personalized Recommendations: AI-driven insights can be used to provide users with personalized recommendations, whether in the context of e-commerce, content consumption, or any other domain.
Continuous Learning: AI systems, such as machine learning models, can continuously learn and adapt to new data, ensuring that the insights provided remain relevant and up-to-date.
The integration of AI and automation, especially in the context of Einstein AI, brings about enhanced efficiency, decision-making support, and user-friendly automation features. The provision of AI-driven insights further empowers users with valuable information, contributing to more informed and strategic decision-making.
Best Practices for UI Enhancement
Regular Updates and Patches:
Purpose: Regular updates and patches are crucial for maintaining and enhancing the UI of an application. They help address bugs, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues, ensuring a smoother and more secure user experience.
Implementation: Developers should release updates periodically, incorporating improvements to the UI based on user feedback and technological advancements. Patches should be promptly deployed to fix any issues that arise post-release.
User Testing and Feedback Loops:
Purpose: User testing involves gathering feedback from real users to identify usability issues, understand user preferences, and refine the UI design. Establishing feedback loops ensures a continuous improvement cycle based on user experiences.
Implementation: Conduct usability testing with representative users to observe how they interact with the UI. Collect feedback through surveys, interviews, and analytics tools. Use this information to iterate on the UI design, addressing pain points and enhancing user satisfaction.
Collaboration with User Community:
Purpose: Engaging with the user community fosters a sense of collaboration, making users feel heard and valued. It also allows developers to gain insights into user needs and expectations, guiding UI enhancements in a user-centric manner.
Implementation: Create channels for communication such as forums, social media, or user groups. Actively participate in discussions, address user queries, and involve the community in beta testing or early access programs. Consider implementing features or improvements suggested by the community, demonstrating responsiveness to user input.
Best practices for UI enhancement involve a combination of technical measures, user-centric methodologies, and community engagement. Regular updates and patches maintain the health of the application, user testing and feedback loops ensure continuous improvement, and collaboration with the user community helps align the UI with user expectations and preferences. Adopting these practices contributes to the creation of a more robust and user-friendly UI.
Future Trends in Salesforce UI
Emerging Technologies Influencing Salesforce UI:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Integration of AI and ML can enhance the user experience by providing predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and personalized recommendations. This could optimize workflows, making the Salesforce UI more intuitive and efficient.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies can be employed to create immersive user interfaces. In the context of Salesforce, this might mean visualizing data in 3D, conducting virtual meetings, or interacting with Salesforce elements in a more spatial manner.
Voice User Interface (VUI): The use of voice commands and interactions could become more prevalent, making it easier for users to navigate Salesforce and perform tasks through natural language commands.
Chatbots and Natural Language Processing (NLP): Integration of intelligent chatbots using NLP can provide users with a conversational interface, allowing them to interact with Salesforce in a more natural and user-friendly way.
Mobile-First Design: With the increasing reliance on mobile devices, Salesforce UI might focus more on mobile-first design principles, ensuring a seamless and responsive experience across various screen sizes.
Predictions for the Future of Salesforce UI:
Enhanced Personalization: The future Salesforce UI might leverage user data and AI to provide highly personalized experiences, tailoring the interface to individual user preferences and roles.
Simplified Workflows: Continued efforts to simplify and streamline workflows are likely, making it easier for users to perform complex tasks with minimal effort. This could involve further automation and intelligent suggestions.
Integration with Collaboration Tools: Salesforce may deepen its integration with collaboration tools, enabling users to seamlessly work on projects, share information, and communicate within the Salesforce environment.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: A strong focus on accessibility and inclusivity might be expected, ensuring that the Salesforce UI is usable by individuals with diverse abilities and needs.
Data Visualization Advances: Improved data visualization tools could be integrated, offering more sophisticated ways to analyze and interpret data directly within the Salesforce UI.
Security and Compliance: Given the increasing importance of data security and compliance, the future Salesforce UI may incorporate enhanced security features and compliance measures to meet evolving industry standards.
Conclusion
Salesforce CRM UI enhancement is an ongoing process that requires a combination of best practices, advanced techniques, and a commitment to user satisfaction. By prioritizing customization, responsiveness, and innovation, organizations can create a user interface that not only meets current needs but also adapts to future trends in technology and user expectations. Continuous improvement, feedback loops, and a user-centric approach are key elements in ensuring that Salesforce remains a valuable asset for businesses seeking to optimize their customer relationships and drive success in the digital era.