Introduction to Microsoft 365 Migration
Definition of Microsoft 365 Migration
Microsoft 365 migration refers to the process of moving data, applications, and user accounts from an existing environment (on-premises servers or another cloud platform) to Microsoft 365, a cloud-based suite of productivity and collaboration tools. This involves migrating email, calendars, contacts, documents, SharePoint sites, and other data to Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure.
Importance of Seamless Transition
A successful Microsoft 365 migration is crucial for businesses to leverage the full benefits of the cloud platform. This includes:
- Increased productivity: Cloud-based applications offer anywhere, anytime access, enabling employees to work from any device and location.
- Improved collaboration: Microsoft 365 tools like Teams and SharePoint facilitate seamless collaboration between colleagues and teams.
- Enhanced security: Microsoft’s robust security infrastructure provides greater protection against data breaches and cyber threats.
- Reduced costs: Eliminating on-premises hardware and software maintenance lowers IT infrastructure costs.
- Scalability: Microsoft 365 is readily scalable to accommodate future growth and evolving business needs.
A seamless transition ensures minimal disruption to business operations and user productivity during the migration process. This involves careful planning, execution, and ongoing support to ensure a smooth transition to the new cloud environment.
Overview of the Migration Process
Microsoft 365 migration typically involves the following stages:
- Planning and Assessment:
- Define migration goals and objectives.
- Assess the current environment and data to be migrated.
- Develop a comprehensive migration plan outlining the scope, timeline, resources, and budget.
- Choose the appropriate migration method (e.g., cutover, staged, hybrid).
- Preparation and Configuration:
- Set up the Microsoft 365 tenant and configure services.
- Create user accounts and assign licenses.
- Establish data migration tools and processes.
- Conduct pilot migrations to test and refine the process.
- Data Migration:
- Execute the chosen migration method to transfer data from the source environment to Microsoft 365.
- Monitor the migration process and address any issues that may arise.
- Verify data integrity and perform post-migration validation.
- User Adoption and Change Management:
- Provide training users on the new Microsoft 365 tools and applications.
- Offer support and assistance to users during the transition.
- Monitor user adoption and address any concerns or challenges.
- Optimization and Continuous Improvement:
- Review the migration process and identify areas for improvement.
- Optimize the use of Microsoft 365 services and features to maximize benefits.
- Continuously monitor and adapt the cloud environment to meet evolving business needs.
By understanding the definition, importance, and process of Microsoft 365 migration, businesses can ensure a smooth and successful transition to the cloud, unlocking the full potential of Microsoft’s productivity and collaboration tools.
Assessment and Planning
Evaluating Current IT Infrastructure
A thorough assessment of your existing IT infrastructure is crucial before embarking on a Microsoft 365 migration. This involves:
- Hardware and software inventory: Analyze the hardware and software currently in use, including servers, operating systems, applications, and network components. Identify any compatibility issues with Microsoft 365.
- Network assessment: Evaluate the bandwidth, latency, and security of your network to ensure it can support cloud-based applications and data transfer.
- Data analysis: Assess the volume and types of data to be migrated, including email, documents, SharePoint sites, and other relevant information.
- Security assessment: Evaluate your existing security measures and identify any potential vulnerabilities that need to be addressed during the migration.
- User analysis: Assess the number of users who need to be migrated and their level of technical expertise to determine training requirements.
Identifying Migration Goals and Objectives
Clearly defined goals and objectives provide direction and focus for the migration process. This involves:
- Defining business needs: Identify the primary reasons for migrating to Microsoft 365, such as improved collaboration, increased mobility, or cost reduction.
- Setting achievable goals: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the migration. This may include user adoption targets, performance metrics, or cost savings goals.
- Identifying success criteria: Define clear criteria for evaluating the success of the migration. This could involve user satisfaction surveys, productivity metrics, or uptime statistics.
- Developing a migration roadmap: Create a detailed roadmap outlining the key milestones, phases, and activities involved in the migration process.
Conducting Risk Assessment
Proactively identifying and mitigating potential risks is essential for a successful migration. This involves:
- Technical risks: Identify potential technical challenges such as data loss, compatibility issues, or network outages.
- Security risks: Analyze potential security threats such as data breaches or unauthorized access.
- Change management risks: Evaluate potential challenges associated with user adoption, training, and resistance to change.
- Business continuity risks: Develop a plan to minimize disruptions to business operations during the migration.
- Develop mitigation strategies: Create a plan to address each identified risk, including contingency plans for potential issues.
By conducting a comprehensive assessment and planning process, businesses can gain valuable insights into their current IT environment, establish clear goals for the migration, and proactively address potential risks. This creates a solid foundation for a successful and seamless transition to Microsoft 365.
Selecting the Right Microsoft 365 Plan
Once you have a clear understanding of your current IT infrastructure and migration goals, choosing the right Microsoft 365 plan becomes the next crucial step.
Overview of Microsoft 365 Subscription Plans
Microsoft offers a range of subscription plans to cater to the diverse needs of individual users, small businesses, and large enterprises.
For Individuals:
- Microsoft 365 Personal: $6.99/month or $69.99/year. Includes Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneNote, 1TB OneDrive storage, and Outlook.
- Microsoft 365 Family: $9.99/month or $99.99/year. Includes all the features of Personal plus the ability to share the subscription with up to 5 other users, adding a total of 6TB OneDrive storage.
For Businesses:
- Microsoft 365 Business Basic: $5/user/month. Includes web versions of Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and 1TB OneDrive storage per user.
- Microsoft 365 Business Standard: $12.50/user/month. Includes all the features of Business Basic plus desktop versions of Office apps, 5TB OneDrive storage per user, and advanced security features.
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium: $20/user/month. Includes all the features of Business Standard, plus additional features like Microsoft Teams, OneDrive premium features, and advanced security and compliance tools.
- Microsoft 365 Apps for Business: $8.25/user/month. Provides access to desktop versions of Office apps only.
For Enterprises:
- Microsoft 365 E3: $34/user/month. Includes all the features of Business Premium, plus additional features like eDiscovery, In-Place Archiving, and enhanced security and compliance controls.
- Microsoft 365 E5: $57/user/month. Provides all the features of E3, plus advanced features like Power BI Pro, Audio Conferencing, and advanced analytics and reporting.
Matching Plans with Organizational Needs
Choosing the right Microsoft 365 plan requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs, including:
- Number of users: Determine how many users will need access to Microsoft 365 and choose a plan that accommodates them.
- Software requirements: Identify the Office applications needed by your users and ensure the chosen plan includes them.
- Data storage needs: Consider the amount of data your users need to store and choose a plan that provides sufficient OneDrive storage.
- Security and compliance requirements: Evaluate your organization’s security and compliance needs and choose a plan that offers the necessary features and controls.
- Budget: Determine your budget for Microsoft 365 and choose a plan that fits within your financial constraints.
Licensing Considerations
Once you have selected a plan, you need to consider the different licensing options available. You can purchase licenses:
- Directly from Microsoft: Microsoft offers various online and offline purchasing options.
- Through Cloud Solution Providers (CSPs): CSPs are authorized partners who can offer additional services and support alongside Microsoft 365 licenses.
- Through volume licensing programs: For large organizations, volume licensing programs offer discounts and additional benefits.
- Choosing the right licensing option depends on your specific needs and preferences. It is important to compare pricing and features to find the best option for your organization.
By carefully assessing your organization’s needs and considering the features and pricing of each plan, you can select the right Microsoft 365 plan that provides the best value and functionality for your business.
Preparing Your Environment
Prior to embarking on your Microsoft 365 migration journey, meticulous preparation of your existing environment is crucial for ensuring a seamless transition. This involves crucial steps like software updates, compatibility checks, and data backups.
Updating Software and Systems
Updating your on-premises software and systems to the latest versions is essential for compatibility with Microsoft 365 and to avoid migration issues. This includes updating:
- Operating systems: Ensure your servers and workstations are running the latest supported versions of Windows or macOS.
- Office applications: Update all Office applications to the latest versions to ensure compatibility with Microsoft 365.
- Web browsers: Update your web browsers to the latest versions to access Microsoft 365 services and applications.
- Other software: Identify and update any other software that may be used with Microsoft 365, such as security software or email clients.
Ensuring Compatibility with Microsoft 365
Thorough compatibility checks are essential to prevent unforeseen challenges during the migration process. This involves:
- Hardware and software compatibility: Check the compatibility of your existing hardware and software with Microsoft 365 requirements.
- Application compatibility: Test your critical applications to ensure they are compatible with Microsoft 365 and function properly in the new environment.
- Network compatibility: Verify that your network can handle the additional bandwidth and security requirements of Microsoft 365.
Backing Up Critical Data
Data backup ensures protection against potential data loss during the migration process. This involves:
- Identifying critical data: Determine which data is essential for your organization and needs to be backed up.
- Choosing a backup solution: Select a reliable backup solution that meets your needs and storage requirements.
- Creating a backup schedule: Develop a regular backup schedule to ensure your data is always protected.
- Validating backups: Regularly test your backups to ensure they are functioning correctly and can be restored in case of an emergency.
Additional Preparation Steps:
- Cleaning up data: Archive old or unnecessary data to reduce the amount of information that needs to be migrated.
- Creating user accounts: Create user accounts in Microsoft 365 for all users who will need access.
- Configuring single sign-on (SSO): Set up SSO to simplify user access and enhance security.
- Training users: Provide training to users on the new Microsoft 365 tools and applications to encourage adoption and smooth transition.
By diligently preparing your environment, you can mitigate potential risks, ensure data integrity, and pave the way for a successful and efficient Microsoft 365 migration. Remember, thorough preparation can save you time, resources, and frustration in the long run.
User Communication and Training
Effective user communication and training are critical elements of a successful Microsoft 365 migration. By keeping users informed and equipped with the necessary skills, you can ensure a smooth transition and maximize user adoption of the new platform.
Communicating the Migration Plan to Users
Transparency and timely communication are crucial for user buy-in and minimizing disruption during the migration process. This involves:
- Announcing the migration: Provide a clear and concise announcement about the upcoming migration, including the timeline, benefits, and potential impacts.
- Explaining the process: Explain the migration process in detail, outlining the steps involved and what users can expect.
- Highlighting the benefits: Clearly communicate the benefits of migrating to Microsoft 365, such as increased accessibility, improved collaboration, and enhanced security.
- Addressing potential concerns: Anticipate and address potential user concerns about the migration, such as data loss, compatibility issues, and change management.
- Creating communication channels: Establish clear and consistent communication channels, such as email, company intranet, or town hall meetings, to keep users informed throughout the process.
Providing Training Resources
Empowering users with the necessary knowledge and skills is essential for seamless adoption of Microsoft 365. This involves:
- Developing training materials: Create comprehensive training materials, such as user guides, online tutorials, and video demonstrations, that explain the new applications and features.
- Offering training sessions: Provide hands-on training sessions to help users learn how to use the new platform effectively.
- Creating FAQs and support resources: Develop FAQs and other support resources to answer common questions and address user concerns.
- Encouraging peer-to-peer learning: Facilitate peer-to-peer learning by encouraging experienced users to help and support others.
- Providing ongoing support: Offer ongoing support to users after the migration to ensure they are comfortable with the new environment and can access the help they need.
Addressing User Concerns
It’s natural for users to have questions and concerns about the migration process. Proactively addressing these concerns can build trust and minimize resistance. This involves:
- Identifying common concerns: Actively listen to user feedback and identify common concerns and anxieties about the migration.
- Providing clear and honest information: Address concerns directly and transparently, providing accurate and up-to-date information.
- Emphasizing the benefits: Reiterate the benefits of the migration and how it will improve their work experience.
- Offering personalized support: Provide individual support to users who have specific concerns or need additional assistance.
- Collecting feedback and iterating: Encourage users to provide feedback after the migration and use it to identify areas for improvement.
By implementing effective communication strategies, providing comprehensive training, and addressing user concerns proactively, you can create a positive and supportive environment for your workforce during the Microsoft 365 migration. This contributes to a smoother transition, higher user adoption, and ultimately, the success of your migration project.
Data Migration Strategies
Overview of Data Migration Methods
Data migration is a crucial stage of any Microsoft 365 project, involving the transfer of your data from your existing environment to the cloud. Several different methods can be employed, each with its own advantages and disadvantages: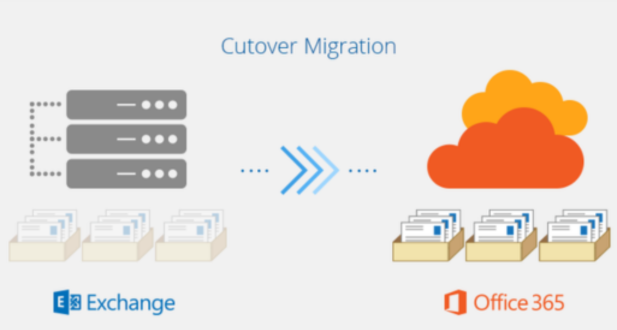
- Cutover Migration: This method involves migrating all data at once, typically used for smaller organizations or those with limited downtime tolerance. While fast, it carries higher risks of disruptions and requires careful planning and execution.
- Staged Migration: This method involves migrating data in batches, enabling a more controlled and gradual transition. It minimizes downtime and allows for testing and adjustments throughout the process, making it suitable for larger organizations.
- Hybrid Migration: This method involves creating a hybrid environment where some data remains on-premises while others are migrated to the cloud. This allows organizations to gradually transition to the cloud while maintaining access to their existing infrastructure.
- IMAP Migration: This method involves migrating email data using the IMAP protocol, suitable for migrating email from other cloud or on-premises email servers. It’s a simple and efficient method but may not be suitable for migrating other types of data.
- Third-party tools: Various third-party tools can automate and simplify the migration process, offering additional features and functionalities. While convenient, these tools may incur additional costs and require technical expertise for configuration and usage.
Selecting the Appropriate Migration Strategy
Choosing the right data migration strategy depends on several factors, including:
- Organization size: Smaller organizations may find cutover migration suitable, while larger organizations may benefit from staged or hybrid approaches.
- Data volume: The size and complexity of your data can dictate the most efficient method. Larger datasets may require staged or hybrid approaches, while smaller datasets may be manageable with cutover migration.
- Downtime tolerance: Organizations with limited downtime tolerance may prefer cutover migration, while those with more flexibility can opt for staged or hybrid approaches.
- Technical expertise: The available technical expertise within your organization may influence the chosen method. Complex strategies may require specialized skills, while simpler methods may be manageable with basic technical knowledge.
- Budget: The cost of different migration methods can vary. Cutover migration is typically the most cost-effective, while third-party tools may incur additional expenses.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Security
Data security and integrity are paramount throughout the migration process. Here are key steps to ensure data protection:
- Planning and preparation: Thoroughly assess and address potential security risks before initiating the migration.
- Secure connections: Use secure protocols like TLS/SSL for data transfer between environments.
- Data encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access controls: Implement strong access controls and user permissions to limit access to sensitive data.
- Monitoring and logging: Continuously monitor the migration process and log all activities for audit purposes.
- Testing and validation: Thoroughly test the migrated data to ensure accuracy and completeness.
By carefully selecting the appropriate data migration strategy and prioritizing security measures, you can guarantee a successful and secure transfer of your data to Microsoft 365.
Migration Execution
Phased Migration vs. Big Bang Approach
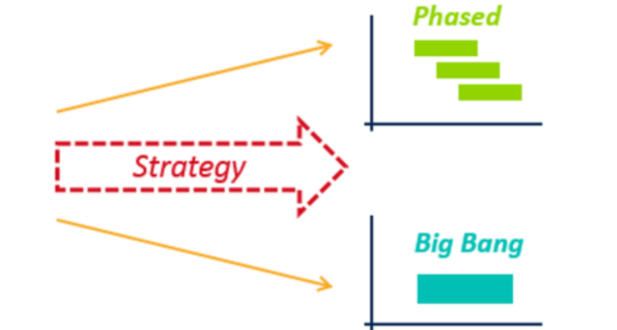 Executing the migration involves choosing between two main approaches:
Executing the migration involves choosing between two main approaches:
- Phased Migration:
Advantages:
- Minimizes downtime and disruption.
- Allows for testing and adjustments during each phase.
- Provides a more controlled transition.
Disadvantages:
- Requires more time and planning.
- Can be more complex to manage.
- Big Bang Migration:
Advantages:
- Faster implementation.
- Less complex to manage.
Disadvantages:
- Higher risk of downtime and disruption.
- Less room for error correction.
The most suitable approach depends on various factors, including:
- Organization size: Larger organizations may benefit from a phased approach to manage complexity and minimize disruption.
- Data volume: Migrating large datasets may be more manageable with a phased approach to avoid overloading systems.
- Downtime tolerance: Organizations with strict uptime requirements may prefer a phased approach to minimize downtime risk.
- Technical resources: A phased approach may require more technical resources to manage multiple migration phases.
Step-by-Step Execution Plan
Regardless of the chosen approach, a carefully planned and executed step-by-step plan is crucial. Here’s a general outline: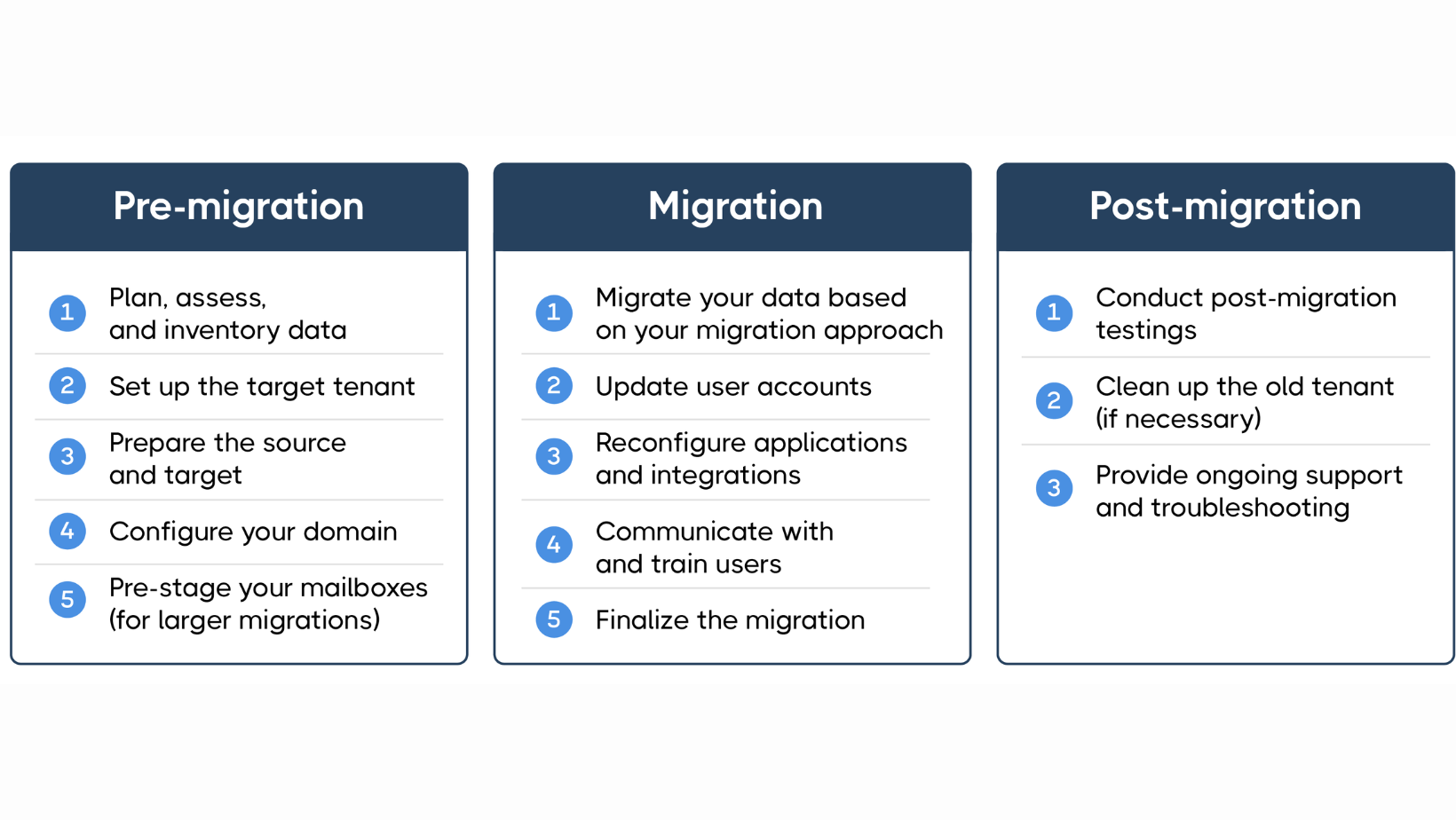
- Pre-migration activities:
- Review the migration plan and timeline.
- Prepare user accounts and licenses.
- Configure the Microsoft 365 environment.
- Backup critical data.
- Conduct migration pilot tests.
- Data migration phase:
- Execute the chosen migration strategy (staged, cutover, etc.).
- Monitor the progress and address any issues that arise.
- Verify data integrity and completeness.
- Post-migration activities:
- Cutover to the new environment (if applicable).
- Provide user training and support.
- Monitor user adoption and address any concerns.
- Decommission the old environment.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Closely monitoring the migration process and being prepared to troubleshoot potential issues are crucial for success. This involves:
- Proactive monitoring: Utilize tools and logs to monitor data transfer, performance, and potential errors.
- Issue identification and resolution: Quickly identify and address any issues that arise to prevent further disruptions.
- Communication and updates: Keep stakeholders informed of the migration progress and any challenges encountered.
- Contingency plans: Implement contingency plans to address unforeseen issues and minimize downtime.
By meticulously planning and executing the migration phase, diligently monitoring the process, and swiftly addressing any challenges, you can ensure a smooth and successful transition to Microsoft 365.
Optimizing Microsoft 365 Usage
Once successfully migrated to Microsoft 365, the focus shifts to optimizing its usage for maximum benefit and productivity. Here are key strategies to achieve this:
Leveraging Advanced Features:
- Explore and utilize advanced features like Power Automate and PowerApps to automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows.
- Encourage collaboration through features like Microsoft Teams and SharePoint, fostering real-time communication and document sharing.
- Take advantage of AI-powered tools like Microsoft Editor and PowerPoint Designer for enhanced content creation and presentation delivery.
Regular Updates and Feature Exploration:
- Maintain updated versions of Microsoft 365 applications to benefit from new features and bug fixes.
- Regularly explore new features and functionalities added to Microsoft 365 through updates and releases.
- Participate in Microsoft training and webinars to learn about advanced features and best practices.
Seeking User Feedback for Improvement:
- Actively collect user feedback on their experience with Microsoft 365 tools and identify areas for improvement.
- Address user concerns and provide necessary training to enhance adoption and usage of specific features.
- Encourage users to share their tips and best practices for leveraging Microsoft 365 effectively.
By continuously exploring advanced features, staying updated, and incorporating user feedback, organizations can maximize the value of their Microsoft 365 investment and unlock its full potential for productivity and collaboration.
Additional Tips:
- Encourage the use of Microsoft Teams templates to simplify project management and team communication.
- Integrate Microsoft 365 with other business applications to streamline workflows and eliminate data silos.
- Encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration within the organization through Yammer and other Microsoft 365 communities.
- By implementing these optimization strategies, organizations can ensure they are reaping the full benefits of their Microsoft 365 investment and fostering a culture of collaboration and productivity.
Continuous Improvement
Migrating to Microsoft 365 is a strategic decision that can revolutionize an organization’s workflow and collaboration. By following the outlined steps, comprehensive planning, meticulous execution, and continuous monitoring, organizations can ensure a smooth and successful transition.
However, the journey doesn’t end with migration. To maximize the value of Microsoft 365 and drive ongoing improvement, organizations must:
- Continuously refine and optimize their environment: Explore advanced features, stay updated on the latest releases, and incorporate user feedback to unlock the full potential of the platform.
- Promote user adoption and training: Provide ongoing training and support to ensure users are comfortable with the new environment and can leverage its features effectively.
- Monitor usage and performance: Regularly track key metrics to identify areas for improvement and measure the impact of the migration on productivity and collaboration.
- Adapt and evolve: Be prepared to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements to continuously improve the use of Microsoft 365 within the organization.
By embracing a continuous improvement mindset and actively seeking ways to optimize their Microsoft 365 environment, organizations can unlock its full potential and drive sustainable success.
Conclusion
Migrating to Microsoft 365 unlocks opportunities for enhanced productivity, improved collaboration, and increased security. By meticulously planning, executing, and optimizing each step of the journey, organizations can ensure a smooth transition and reap the full benefits of this powerful platform.
However, it is crucial to remember that the journey doesn’t end with migration. Continuous improvement through feature exploration, user feedback, training, and performance monitoring is essential to maximize value and drive long-term success. By embracing this continuous learning approach, organizations can unlock the full potential of Microsoft 365 and empower their workforce to thrive in the digital age.