Introduction: AWS Cost Optimization and Management
The advent of cloud storage has revolutionized how businesses manage, store, and access their data. In this era of digital transformation, embracing the cloud is not just an option but a strategic imperative. As businesses grapple with vast amounts of data, the need for scalable, secure, and flexible storage solutions has never been more critical. Enter the realm of cloud storage, where the prowess of platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) reshapes the storage landscape.
Embrace the Cloud: Unraveling the Benefits of Cloud Storage
- Unprecedented Scalability:
Cloud storage offers a paradigm shift from traditional on-premises solutions. The ability to scale storage dynamically based on demand is a game-changer. Whether your business experiences sudden growth or requires additional capacity for a specific project, cloud storage eliminates the constraints of physical infrastructure.
- Cost-Efficiency and Flexibility:
Cloud storage operates on a pay-as-you-go model, providing cost efficiencies through resource optimization. With AWS, businesses can choose from a variety of storage classes based on data access patterns, optimizing costs without compromising performance. This flexibility ensures that organizations pay only for the storage they consume, aligning expenses with actual usage.
- Enhanced Accessibility and Collaboration:
The cloud transcends geographical boundaries, fostering global collaboration. Cloud storage enables seamless access to data from anywhere, empowering teams to collaborate in real-time. With AWS, businesses can leverage features like Amazon S3’s cross-region replication for data redundancy, ensuring high availability and durability.
Navigating the AWS Ecosystem: A Guided Tour Through the Diverse Landscape of AWS Storage Solutions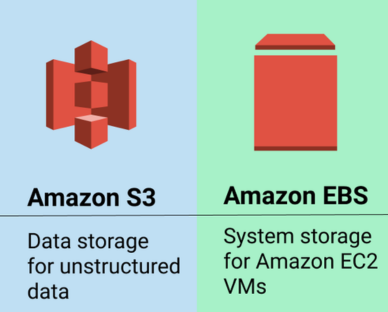
- Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service):
At the heart of AWS cloud storage lies Amazon S3, a scalable and secure object storage service. S3 serves as the cornerstone for storing and retrieving any amount of data at any time. Its simplicity, durability, and low-latency access make it a go-to solution for a myriad of use cases, from backup and restore to content distribution.
- Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store):
For workloads that demand high-performance block storage, Amazon EBS steps into the spotlight. Whether supporting database applications or providing persistent storage for Amazon EC2 instances, EBS delivers low-latency and consistent performance. With features like snapshotting, data integrity and recovery are paramount.
- Amazon Glacier:
When the archival of data for long-term retention is the goal, Amazon Glacier emerges as a cost-effective solution. Designed for infrequently accessed data, Glacier offers secure and durable storage with retrieval options that suit various latency requirements.
Choosing Your Weapon: Understanding the Key Types of Cloud Storage – Object, Block, and File
- Object Storage:
Object storage, exemplified by Amazon S3, is ideal for managing unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups. The simplicity of object storage lies in its ability to store data as discrete objects, each with a unique identifier, facilitating easy retrieval.
- Block Storage:
Amazon EBS provides block storage that serves as raw, unformatted volumes, akin to traditional hard drives. Ideal for use with EC2 instances, block storage enables organizations to attach additional storage volumes, ensuring the flexibility to meet diverse application requirements.
- File Storage:
For businesses with a focus on shared file systems, Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) delivers scalable and fully managed file storage. EFS seamlessly integrates with EC2 instances, enabling multiple instances to share file data concurrently.
In this exploration of the cloud storage frontier, businesses stand at the crossroads of innovation and efficiency. The journey into AWS’s diverse storage ecosystem holds the promise of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and unparalleled accessibility. As we delve deeper into the specific benefits of AWS cloud storage solutions, the power to choose the right weapon for your storage needs becomes a strategic advantage in conquering the cloud storage frontier.
Object Storage: The King of Scalability
In the realm of cloud storage, object storage reigns supreme, and Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) stands as the undisputed king. As the indispensable workhorse of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem, S3 embodies the essence of scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. In this exploration, we delve deep into the features, benefits, and diverse use cases of Amazon S3.
Amazon S3: The Indispensable Workhorse
Features that Define Excellence:
Amazon S3’s prominence is rooted in a rich feature set that caters to the most demanding storage needs. From industry-leading durability to virtually limitless scalability, S3 sets the gold standard for object storage.
- Durability and Redundancy:
- S3 boasts a remarkable durability rating, ensuring that stored objects are designed to withstand even multiple device failures.
- Redundancy mechanisms, such as data replication across multiple Availability Zones, reinforce the resilience of S3.
- Global Accessibility:
- With a vast network of edge locations, S3 ensures low-latency access to data for users around the globe.
- Integration with AWS CloudFront further accelerates content delivery through a robust content delivery network (CDN).
- Scalability Beyond Limits:
- S3 enables businesses to seamlessly scale their storage needs from gigabytes to petabytes and beyond, accommodating explosive data growth.
- The ability to handle virtually limitless concurrent connections makes S3 suitable for applications of any scale.
- Data Lifecycle Management:
- Automated lifecycle policies in S3 facilitate the transition of data between storage classes based on access patterns and age.
- This feature optimizes costs by moving data to more cost-effective storage classes as it ages, aligning expenses with data value.
Diverse Use Cases Across Industries:
- Backup and Restore:
- S3 serves as a robust solution for backup and restore, providing a secure and scalable repository for critical data.
- Versioning and cross-region replication options enhance data protection and availability.
- Content Distribution:
- With the integration of AWS CloudFront, S3 transforms into a powerful content distribution platform, delivering low-latency access to static and dynamic content.
- Streaming media, website assets, and software downloads benefit from the global reach of this combination.
- Big Data and Analytics:
- S3 plays a pivotal role in big data and analytics workflows, acting as a central data lake for storage and retrieval.
- Integration with services like Amazon Athena and Amazon Redshift facilitates seamless analysis of vast datasets.
- Application Hosting:
- Hosting static websites on S3 simplifies deployment and ensures high availability and scalability.
- S3’s integration with AWS Lambda allows for serverless computing, enabling dynamic content generation.
Unlimited Capacity, Unmatched Flexibility
Scalability on Demand:
- Bucket and Object Management:
- S3 provides the flexibility to organize data into “buckets,” each acting as a container for objects.
- Granular access controls at both the bucket and object levels ensure secure and controlled data access.
- Concurrency and Performance:
- High levels of concurrency and performance are inherent to S3, making it suitable for applications with varying workload demands.
- The ability to handle massive numbers of requests per second ensures optimal performance for dynamic applications.
- Multipart Uploads:
- Large object uploads are simplified with S3’s multipart upload capability, breaking files into smaller parts for efficient parallelization.
- This feature enhances resilience during uploads, minimizing the impact of network interruptions.
Data Lifecycle Management Strategies:
- Storage Classes:
- S3 offers a variety of storage classes, each designed to meet specific performance, durability, and cost requirements.
- Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier, and Deep Archive are among the storage classes catering to diverse use cases.
- Versioning and Cross-Region Replication:
- Versioning safeguards against accidental deletion or modification, providing a comprehensive history of changes to objects.
- Cross-region replication enhances data redundancy by replicating objects across multiple AWS regions.
- Expiration and Retention Policies:
- S3’s lifecycle policies allow organizations to define expiration rules, automatically deleting objects when they reach the end of their useful life.
- Retention policies add an extra layer of protection, preventing deletion or modification during a specified retention period.
Cost Optimization Strategies: Mastering Storage Classes and Pricing Tiers
Storage Classes Demystified:
- Standard Storage Class:
- Ideal for frequently accessed data with low-latency requirements.
- Suited for applications like big data analytics, mobile and gaming applications, and content distribution.
- Intelligent-Tiering:
- Automatically moves objects between two access tiers (frequent and infrequent access) based on changing access patterns.
- Optimizes costs for data with unknown or changing access patterns.
- Glacier and Glacier Deep Archive:
- Designed for archival storage with longer retrieval times.
- Ideal for data that is accessed infrequently and can tolerate retrieval times measured in hours.
Tiered Pricing Structure:
- Data Transfer Costs:
- Understanding the costs associated with data transfer out of S3 to the internet or other AWS regions is crucial for effective budgeting.
- Transfer acceleration options can optimize upload/download speeds at an additional cost.
- Request Pricing:
- Tailoring storage class choices based on data access patterns is key to optimizing request-related costs.
- Frequent access data might benefit from the Standard Storage Class, while infrequently accessed data can be stored in Glacier for cost savings.
- Data Retrieval Costs in Glacier:
- Glacier retrieval times vary, with Standard offering expedited retrieval and Glacier Deep Archive having the longest retrieval time.
- Understanding the implications of retrieval times is vital for budget-conscious organizations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of S3 for Unmatched Scalability
In the grand tapestry of AWS cloud storage, Amazon S3 stands tall as the linchpin of object storage, providing a bedrock of scalability, durability, and versatility. By navigating its diverse features, harnessing its limitless scalability, and mastering cost optimization through strategic storage class choices
Block Storage: Powering Your Applications
In the intricate landscape of cloud storage, the role of block storage is paramount, providing the bedrock for persistent and scalable data solutions. Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) stands as a cornerstone within the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem, offering reliable block storage with high availability. This exploration delves into the fundamentals of EBS, explores its advanced features, and compares it with Amazon S3 to guide users in making informed storage decisions.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS): Building the Bedrock
Reliable and Persistent Block Storage:
- Foundation of AWS Storage:
Amazon EBS serves as the foundational block storage service in AWS, offering scalable and high-performance storage volumes.
These volumes provide persistent data storage that persists independently of the lifespan of an Amazon EC2 instance.
- High Availability and Redundancy:
EBS is designed for high availability, with automatic replication of volumes within an Availability Zone (AZ) to protect against hardware failures.
Snapshots, which capture point-in-time images of EBS volumes, enhance data durability and recovery options.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Features
- Snapshots for Data Protection:
- EBS snapshots play a pivotal role in data protection and disaster recovery.
- Users can create snapshots manually or set up automated snapshot schedules to ensure consistent backups.
- Volume Types for Varied Workloads:
- EBS offers multiple volume types, each optimized for different use cases.
- Standard (SSD), Provisioned IOPS (SSD), and Magnetic volumes cater to diverse performance and cost requirements.
- Elastic Volumes for Dynamic Scaling:
- Elastic Volumes allow users to dynamically adjust volume size, performance, and type without disrupting operations.
- This feature ensures that storage resources align with evolving application demands.
- Performance Tiers:
- EBS introduces different performance tiers to meet varying I/O requirements.
- Choosing between General Purpose (gp3), Provisioned IOPS (io2), and Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) depends on the application’s specific performance needs.
EBS vs. S3: Deciding the Champion for Your Needs
Matching the Right Storage Solution to Your Application’s Demands
- Use Cases for EBS:
- EBS is ideal for use cases where low-latency and high-performance block storage are crucial.
- Applications that require direct and persistent access to storage, such as databases and transactional workloads, benefit from EBS.
- Use Cases for S3:
- Amazon S3, as an object storage service, excels in use cases where scalable and durable storage for large amounts of unstructured data is paramount.
- S3 is well-suited for data lakes, backup and restore scenarios, content distribution, and static website hosting.
- Latency and Performance:
- EBS offers lower latency and is optimized for applications that demand consistent and low-latency I/O operations.
- S3, while highly scalable, may exhibit higher latency due to its distributed nature and focus on durability and availability.
- Scalability and Cost:
- S3 shines in scalability, catering to applications dealing with vast amounts of data and requiring seamless access across regions.
- EBS, with its focus on performance, offers a more cost-effective solution for applications with stringent I/O requirements.
- Durability and Redundancy:
- Both EBS and S3 ensure data durability through redundant storage mechanisms.
- EBS achieves redundancy within an Availability Zone, while S3 distributes data across multiple regions for enhanced global availability.
- Integration with Other AWS Services:
- EBS integrates seamlessly with Amazon EC2 instances, providing persistent block storage for applications running on EC2.
- S3, with its integration capabilities, serves as a versatile storage backend for various AWS services, including Lambda, Redshift, and Athena.
Making the Right Choice: Considerations and Best Practices
- Hybrid Solutions:
- For some applications, a hybrid approach utilizing both EBS and S3 may be optimal.
- Frequently accessed data requiring low-latency storage can reside in EBS, while archival or less frequently accessed data can be stored in S3.
- Cost Optimization:
- Cost considerations should include the type of data, access patterns, and performance requirements.
- Evaluating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) based on storage and data transfer costs is essential for optimizing expenses.
- Security and Compliance:
- Both EBS and S3 offer robust security features, including encryption and access controls.
- Organizations must align their choice with specific security and compliance requirements.
Conclusion: Navigating the Block Storage Landscape
As organizations navigate the intricacies of the block storage landscape, understanding the strengths and use cases of Amazon EBS and Amazon S3 is crucial. EBS, with its focus on high-performance block storage, serves as the backbone for applications demanding low-latency access to data. Meanwhile, S3, as an object storage solution, excels in scalability, durability, and accessibility, making it the go-to choice for storing large volumes of unstructured data.
By carefully evaluating application requirements, latency considerations, and scalability needs, businesses can make informed decisions about whether Amazon EBS or S3 is the champion for their storage demands. Whether building a robust database infrastructure with EBS or creating a versatile data lake with S3, AWS provides the tools and flexibility needed to power diverse applications in the cloud. As we continue our exploration of AWS storage solutions, the interplay between block and object storage becomes increasingly evident, shaping the foundation for resilient and scalable cloud architectures.
File Storage: The Familiar Face in the Cloud
In the diverse landscape of cloud storage, file storage emerges as the familiar face, providing a seamless and accessible solution for sharing files across cloud applications. Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) takes center stage in this arena, offering easy integration of file storage into your cloud infrastructure.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS): Sharing Files with Ease
- Seamless Integration:
Amazon EFS simplifies the process of integrating file storage into your cloud environment. It serves as a scalable and fully managed file storage service, designed to support multiple Amazon EC2 instances concurrently.
Leveraging NFS for Familiarity
- NFS Protocol:
EFS leverages the Network File System (NFS) protocol, a widely adopted standard for file sharing. This familiarity allows users to effortlessly share files across diverse applications and systems, promoting interoperability within their cloud architecture.
Amazon FSx: When Performance Reigns Supreme
- Unleashing High-Performance File Systems:
For scenarios where performance is paramount, Amazon FSx steps into the spotlight. It provides high-performance file systems such as Lustre and Windows File Server, catering to specific application demands.
- Lustre File System:
Amazon FSx for Lustre delivers a high-performance file system optimized for compute-intensive workloads. It is ideal for scenarios where rapid data processing and analysis are critical, such as in scientific simulations and machine learning.
- Windows File Server:
Amazon FSx for Windows File Server offers fully managed, Windows-compatible file storage with support for the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. This makes it an excellent choice for Windows-based applications that require high-performance file storage.
In the realm of cloud-based file storage, Amazon EFS and Amazon FSx provide organizations with flexible options to meet their specific requirements. Whether seeking ease of integration and NFS familiarity with EFS or demanding high-performance file systems like Lustre and Windows File Server with FSx, AWS offers the tools needed to seamlessly incorporate file storage into diverse cloud architectures. As we delve deeper into the AWS storage ecosystem, the versatility and accessibility of file storage become integral components in crafting robust and efficient cloud solutions.
Data Archiving & Backup: Preserving Your Digital Legacy
In the realm of data management, preserving digital legacies and safeguarding critical information is paramount. Amazon Glacier, known as the deep freeze of data storage, emerges as a secure and cost-effective solution for long-term archiving of rarely accessed data.
Amazon Glacier: The Deep Freeze of Data Storage
- Secure and Cost-Effective Archiving:
Amazon Glacier provides a secure and economical avenue for archiving data that is rarely accessed but requires long-term preservation. Organizations benefit from a scalable and durable solution, ensuring the integrity of their digital legacy.
Protecting the Present, Securing the Future
- Robust Backup Strategies:
AWS storage solutions empower businesses to implement robust backup strategies, ensuring the protection of vital data in the present and fortifying their ability to recover in the future. These strategies leverage services like Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS to create resilient and scalable backup systems.
Disaster Recovery Made Easy
- Efficient Recovery from Unforeseen Events:
Cloud backup with AWS storage solutions facilitates efficient disaster recovery, enabling organizations to swiftly recover from unforeseen events. By leveraging the cloud for backup and archiving, businesses enhance their resilience and minimize downtime in the face of disasters.
As we explore the intricacies of data archiving and backup within the AWS storage ecosystem, the combination of Amazon Glacier and backup strategies becomes instrumental in preserving digital legacies and fortifying organizations against the uncertainties of the future.
Securing Your Cloud Storage Fortress
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud storage, fortifying your digital fortress against potential threats is paramount. This segment delves into the foundational elements of building a robust defense for your AWS storage environment.
Building a Wall of Defense
- Understanding Security Best Practices:
Navigating the intricate terrain of AWS storage security involves comprehending and implementing industry-leading security best practices. This proactive approach is essential for safeguarding your data against evolving threats.
Encryption, Access Control, and Auditing
- Robust Security Measures:
Implementing a multi-faceted security strategy involves leveraging encryption, precise access controls, and comprehensive auditing. These measures collectively contribute to the resilience and integrity of your stored data.
Compliance at Your Fingertips
- Ensuring Adherence to Regulations:
In the complex regulatory landscape, adherence to industry regulations and data privacy laws is non-negotiable. This segment elucidates how AWS storage solutions provide the tools and features necessary for maintaining compliance effortlessly.
As we explore the strategies for securing your cloud storage fortress, the emphasis on proactive defense, encryption, and compliance measures underscores the commitment to data integrity and confidentiality within the AWS storage ecosystem.
Cost Optimization: Mastering the Financial Cloudscape
In the dynamic realm of cloud storage, mastering the financial landscape is essential for achieving optimal efficiency. This section illuminates key strategies for cost optimization within the AWS storage environment.
Rightsizing Your Storage Footprint
- Choosing Optimal Storage Solutions:
Efficiently managing costs involves rightsizing your storage footprint—selecting storage solutions that align with both your budget and usage patterns. This strategic approach ensures that you pay for the storage you need, optimizing financial resources.
Leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
- Securing Significant Cost Savings:
Embracing Reserved Instances and Savings Plans unlocks substantial cost savings through long-term commitments. This financial strategy allows organizations to benefit from discounted rates while ensuring predictable budgeting.
Automating Storage Management
- Utilizing Tools for Optimization:
Automation becomes a key ally in the pursuit of cost optimization. By leveraging AWS tools and services, organizations can automate storage management, ensuring efficient resource utilization and continual alignment with budgetary constraints.
As we navigate the financial cloudscape of AWS storage, the principles of rightsizing, commitment, and automation emerge as pillars for achieving fiscal efficiency in the cloud.
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of AWS storage, mastering cost optimization and management emerges as a linchpin for sustainable and efficient cloud operations. As organizations navigate the ever-expanding digital terrain, the strategic orchestration of resources becomes imperative to balance functionality with fiscal responsibility.
The journey through AWS cost optimization involves a nuanced interplay of rightsizing storage footprints, leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans for economic advantages, and embracing automation for streamlined management. By choosing optimal storage solutions tailored to budgetary constraints, organizations ensure that they pay for precisely what they need, avoiding unnecessary financial overhead.
Reserved Instances and Savings Plans provide a financial compass, allowing businesses to secure significant cost savings through strategic, long-term commitments. The artful use of automation further cements the path to fiscal prudence, optimizing resource utilization while maintaining alignment with budgetary parameters.
In conclusion, mastering AWS cost optimization and management encapsulates a holistic approach, harmonizing technological prowess with financial acumen. By implementing these strategies, organizations not only navigate the financial cloudscape effectively but also fortify their foundation for sustained innovation and success in the cloud.
Rightsizing involves choosing the optimal size and type of AWS resources, such as instances and storage, to match your actual usage patterns and budget.
Reserved Instances allow organizations to commit to a one- or three-year term, securing significantly discounted rates compared to on-demand pricing.
Savings Plans offer flexible pricing with significant savings compared to on-demand pricing, providing cost predictability for a wide range of instance usage.
Automation in AWS enables organizations to streamline resource management, automatically adjusting capacity based on demand, thus optimizing costs.
Rightsizing storage involves selecting storage solutions that align with usage patterns, preventing overprovisioning and ensuring cost-efficient resource utilization.