Understanding the Basics of QuickBooks Sales Tax Management
Sales tax is a crucial component of a country’s revenue system, playing a pivotal role in funding various government initiatives and services. It is a consumption tax imposed on the sale of goods and, in some cases, services. Comprehending the basics of sales tax is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike.
Importance of Sales Tax Compliance:
Sales tax compliance is crucial for businesses to operate legally and efficiently. Failure to comply with sales tax regulations can result in penalties, fines, and legal consequences. Additionally, proper sales tax compliance ensures that businesses contribute their fair share to government revenues, supporting public services such as education, infrastructure, and healthcare. Compliance also fosters a level playing field among businesses, preventing unfair advantages for those who evade taxes.
Overview of Sales Tax Components:
Sales tax is not a uniform concept; rather, it comprises various components that differ across jurisdictions. The primary components include the tax rate, taxable goods and services, and the point of sale. The tax rate is a percentage of the sale price, and it varies from region to region. Taxable goods and services encompass the specific items or activities subject to taxation. The point of sale refers to the location where the sale occurs, influencing which jurisdiction’s tax laws apply.
Different Types of Sales Tax:

Sales tax can take different forms, each with its unique characteristics. One common type is the state sales tax, imposed by individual U.S. states on retail transactions. Another variation is the local sales tax, levied by cities, counties, or other local jurisdictions. Additionally, some countries implement a value-added tax (VAT) system, where taxes are applied at each stage of production and distribution. Understanding these various types of sales tax is essential for businesses to navigate the complex landscape of taxation and ensure compliance with applicable laws.
QuickBooks Sales Tax Setup:
QuickBooks Sales Tax Setup involves several essential steps to ensure accurate and efficient management of sales tax within the accounting system. These steps can be broadly categorized into configuring sales tax preferences, defining tax agencies and tax codes, and mapping taxable and non-taxable items.
Configuring Sales Tax Preferences:
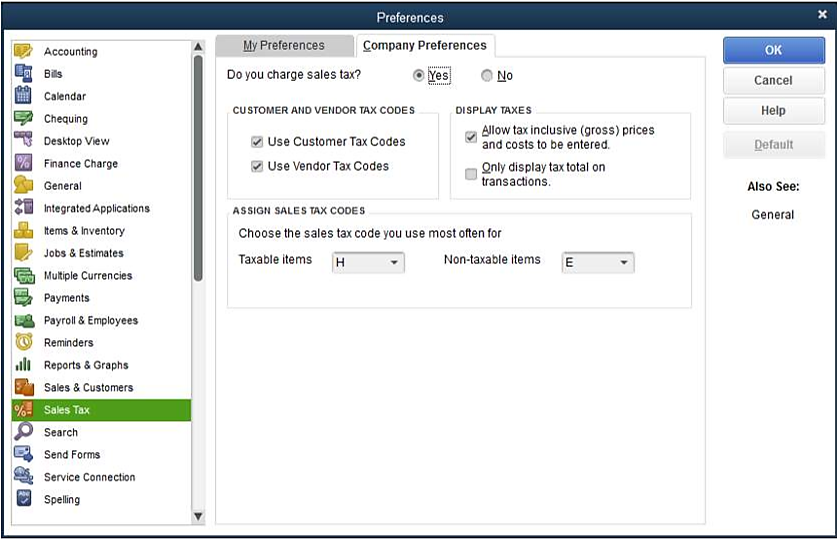
In this initial phase of the setup, users navigate through the Sales Tax Preferences within QuickBooks. This is where they customize settings related to sales tax calculations and reporting according to their business needs. Users can specify default tax rates, set up tax filing frequency, and define other preferences that align with the specific taxation requirements of their location.
Configuring sales tax preferences is crucial because it establishes the foundation for accurate sales tax calculations and ensures compliance with local tax regulations. Businesses may need to consider factors such as whether they operate in multiple tax jurisdictions or have exemptions that need to be accounted for in the system.
Defining Tax Agencies and Tax Codes:
Once the preferences are configured, the next step involves defining tax agencies and tax codes. Tax agencies represent the governmental entities responsible for collecting and managing taxes. Users input details such as the agency’s name, address, and tax identification number.
Tax codes, on the other hand, are used to categorize different types of sales tax. For instance, businesses might deal with state sales tax, county sales tax, and city sales tax. Each of these types requires a specific tax code to differentiate and track them accurately. Defining tax agencies and tax codes enables QuickBooks to organize and calculate sales tax amounts correctly based on the applicable rates.
Mapping Taxable and Non-taxable Items:
The final step involves mapping taxable and non-taxable items in the QuickBooks inventory. Each product or service offered by a business needs to be categorized as taxable or non-taxable. This information is crucial for the accurate calculation of sales tax on invoices and other financial transactions.
By mapping taxable and non-taxable items, businesses can ensure that the correct sales tax is applied to each transaction. This is particularly important in industries where certain products or services may be exempt from sales tax. Accurate mapping prevents errors and discrepancies in financial records, helping businesses maintain compliance with tax regulations and avoid penalties.
The QuickBooks Sales Tax Setup process is a comprehensive approach to configuring the system for effective sales tax management. From preferences to agencies and codes, and finally, mapping items, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and compliant accounting practices. Businesses that meticulously go through these steps can streamline their sales tax processes and focus on other aspects of financial management with confidence.
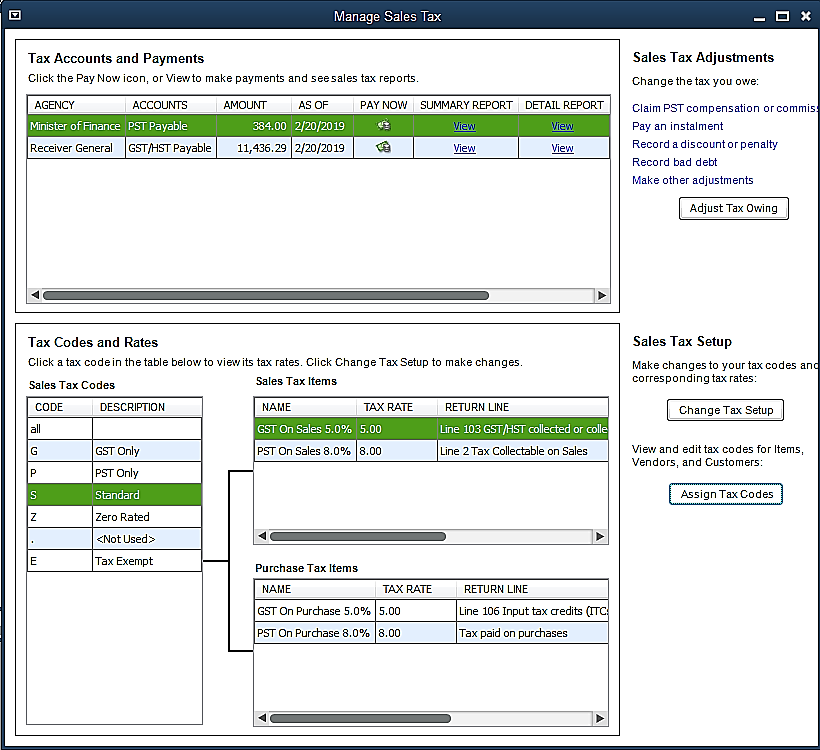
Sales Tax Reporting:

Sales Tax Reporting is a critical aspect of financial management for businesses, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and providing insights into financial health. One key component of this process is the generation of Sales Tax Liability Reports. These reports compile information on the sales tax collected by the business over a specific period, offering a comprehensive overview of tax obligations. This allows businesses to track their tax liabilities accurately and facilitates adherence to regulatory requirements.
Customizing Reports for Specific Time Periods is another vital aspect of Sales Tax Reporting. Businesses often operate on various timelines, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. Customization options enable organizations to tailor their reports to align with specific reporting periods, ensuring accurate and relevant insights. This flexibility is essential for businesses with diverse operational structures, allowing them to meet regulatory deadlines and make informed financial decisions based on the specific timeframes that matter most to them.
Analyzing Sales Tax Summary and Detail Reports is an integral step in leveraging the information gathered. Sales Tax Summary Reports provide a high-level overview of tax data, offering insights into total tax collected, exemptions, and liabilities. On the other hand, Detail Reports break down this information further, providing a granular view of individual transactions, tax rates, and customer details. By delving into both summary and detailed reports, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their sales tax data, identifying trends, anomalies, and areas for potential improvement or optimization.
Sales Tax Reporting encompasses the generation of Sales Tax Liability Reports, customization for specific periods, and the analysis of both summary and detailed reports. This multifaceted approach not only ensures regulatory compliance but also empowers businesses to make informed financial decisions based on a nuanced understanding of their sales tax obligations. The ability to generate, customize, and analyze these reports is instrumental in maintaining financial transparency, minimizing errors, and fostering a proactive approach to tax management.
Automated Sales Tax:
Introduction to Automated Sales Tax:
Automated Sales Tax is a cutting-edge feature designed to streamline and simplify the complex task of managing sales tax in financial systems. In the realm of accounting and business management, sales tax can be a burdensome and error-prone aspect that demands meticulous attention. Automated Sales Tax seeks to alleviate these challenges by leveraging technology to automate the calculation, tracking, and reporting of sales tax. This innovation is particularly relevant for businesses operating in regions with varying tax rates and regulations, as it ensures accuracy, reduces manual workload, and enhances overall compliance.
Benefits of Automated Sales Tax:
The implementation of Automated Sales Tax brings forth a myriad of advantages for businesses. One primary benefit is the reduction of human errors associated with manual tax calculations. Automation ensures that tax rates are consistently and accurately applied, minimizing the risk of miscalculations that can lead to financial discrepancies and compliance issues. Additionally, Automated Sales Tax enables businesses to adapt seamlessly to changes in tax laws and rates, ensuring ongoing compliance without the need for constant manual adjustments.
Another significant advantage is the time and resource savings. By automating the sales tax process, businesses can redirect valuable human resources to more strategic and value-added tasks, enhancing overall productivity. Moreover, the risk of penalties and fines due to non-compliance is significantly reduced, as the system inherently follows the latest tax regulations, helping businesses stay on the right side of the law.
Configuring and Activating Automated Sales Tax in QuickBooks:
Configuring and activating Automated Sales Tax in QuickBooks is a straightforward yet pivotal process for businesses seeking to harness the benefits of automation. QuickBooks, a widely used accounting software, provides a user-friendly interface for setting up and activating Automated Sales Tax.
To configure, businesses typically need to input essential information such as their location, tax agency details, and product or service categories. QuickBooks then utilizes this information to automatically calculate and apply the appropriate sales tax rates for each transaction. This not only ensures accuracy but also simplifies the often complex task of managing tax compliance.
Activation involves enabling the Automated Sales Tax feature within the QuickBooks settings. This step-by-step process is usually guided by the software itself, making it accessible even for users with limited technical expertise. Once activated, businesses can enjoy the seamless integration of Automated Sales Tax into their financial workflows, allowing for a more efficient and error-free sales tax management experience. Overall, configuring and activating Automated Sales Tax in QuickBooks represents a proactive step towards modernizing financial processes and ensuring compliance in an ever-evolving regulatory landscape.
Sales Tax Center:
Sales Tax Center serves as a centralized hub for businesses to manage and monitor their sales tax-related activities efficiently. The dashboard of the Sales Tax Center is designed to provide users with a comprehensive overview of their sales tax obligations and activities. It acts as a control panel where businesses can access key information and tools to streamline their sales tax processes.
The dashboard is the primary interface through which users can explore and navigate various features within the Sales Tax Center. It offers visual representations and summary data that allow businesses to quickly assess their sales tax status. Key metrics such as sales tax liabilities, recent transactions, and compliance status are prominently displayed, enabling users to make informed decisions and take timely actions.
One crucial aspect of the Sales Tax Center is its functionality in tracking sales tax due dates. Businesses often have multiple tax jurisdictions and varying filing frequencies, making it challenging to stay on top of deadlines. The Sales Tax Center simplifies this by providing a centralized calendar or alert system that highlights upcoming due dates for sales tax filings. This feature ensures that businesses can meet their obligations punctually, avoiding penalties and maintaining compliance with tax regulations.
Managing sales tax payments and filings is another essential capability offered by the Sales Tax Center. Businesses can use the platform to initiate and track payments, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring accurate and timely remittance of sales tax to the appropriate tax authorities. Additionally, the center facilitates the filing process, guiding users through the necessary steps and documentation required for compliance. This streamlined approach not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the potential for mistakes in the complex landscape of sales tax regulations.
The Sales Tax Center serves as a valuable tool for businesses to navigate the intricacies of sales tax management. Its intuitive dashboard, coupled with features for tracking due dates and managing payments and filings, empowers businesses to maintain compliance, minimize risks, and allocate resources more effectively. Whether for small enterprises or large corporations, the Sales Tax Center provides a centralized solution to address the challenges associated with sales tax obligations.
Sales Tax on Invoices and Sales Receipts:
Sales Tax on Invoices and Sales Receipts is a critical aspect of financial transactions for businesses, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and providing transparency in financial dealings. This process involves adding sales tax to invoices, managing tax-exempt sales, and including sales tax information on sales receipts.
When it comes to adding sales tax to invoices, businesses must accurately calculate and apply the appropriate sales tax rate to the total amount of the transaction. This ensures that the customer is charged the correct amount of tax based on the products or services purchased and the applicable tax jurisdiction. In many cases, businesses may need to consider different tax rates for different items or services, making it essential to have a robust invoicing system that can handle complex tax scenarios.
Handling tax-exempt sales is another facet of the sales tax process. Certain transactions, such as those involving nonprofit organizations or specific types of goods and services, may be exempt from sales tax. Businesses need to have mechanisms in place to identify and appropriately mark these tax-exempt sales to avoid overcharging customers and to comply with tax regulations. This requires a thorough understanding of the tax laws relevant to the business’s operations and the ability to apply exemptions accurately.
Including sales tax information on sales receipts is crucial for providing customers with a clear breakdown of the total amount paid, including the applicable taxes. Sales receipts serve as a record of the transaction and may be requested by customers for reimbursement or tax purposes. Businesses need to ensure that sales tax details are clearly stated on receipts, including the tax rate, amount, and any relevant exemption information. This transparency not only builds trust with customers but also helps in maintaining accurate financial records for tax reporting and auditing purposes.
Managing sales tax on invoices and sales receipts is a multifaceted process that requires attention to detail and compliance with tax regulations. Businesses must implement systems and procedures to accurately calculate and apply sales tax, handle tax-exempt sales, and provide transparent information on sales receipts. This not only facilitates smooth financial transactions but also ensures that the business remains in good standing with tax authorities and builds trust with customers.
Best Practices in QuickBooks Sales Tax Management:
Effective management of sales tax in QuickBooks is crucial for ensuring accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. Here are some best practices to enhance your sales tax management within the QuickBooks platform.
Regularly Reviewing Sales Tax Settings:
To maintain accurate financial records and comply with tax regulations, it is essential to regularly review and update your sales tax settings in QuickBooks. Ensure that the tax rates, agencies, and items are correctly configured based on your business operations and the jurisdictions where you conduct business. This practice helps prevent errors in tax calculations and ensures that your financial reports accurately reflect your tax liabilities.
Regular reviews also enable you to identify and rectify any discrepancies promptly. Auditing your sales tax settings on a periodic basis helps in maintaining the integrity of your financial data and minimizes the risk of miscalculations or inaccuracies in sales tax reporting.
Training Team Members on Sales Tax Procedures:
A well-informed and trained team is instrumental in maintaining compliance with sales tax regulations. Provide comprehensive training to your team members, especially those involved in financial transactions and record-keeping, about the proper procedures for handling sales tax in QuickBooks.
Training should cover topics such as entering sales tax codes, creating invoices with accurate tax calculations, and recording tax payments. Educate your team on the importance of consistent and accurate data entry to avoid potential issues during audits. This ensures that everyone in your organization is aligned with the correct sales tax procedures, reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing overall compliance.
Staying Informed About Sales Tax Regulation Changes:
Sales tax regulations are subject to change, and staying informed about these changes is vital for compliance. Regularly monitor updates from tax authorities and other relevant sources to stay abreast of any modifications to sales tax rates, thresholds, or reporting requirements.
QuickBooks may release updates to address changes in tax regulations, so keeping your software up to date is equally important. Failure to adapt to new regulations could result in miscalculations, underpayment, or overpayment of sales tax. Establish a system for continuous learning and communication within your organization to disseminate information about any changes promptly and ensure that your business remains in compliance with the latest sales tax regulations.
Effective sales tax management in QuickBooks involves a combination of regular reviews, comprehensive training, and staying informed about regulatory changes. By implementing these best practices, your business can streamline its sales tax processes, reduce the risk of errors, and maintain compliance with evolving tax regulations.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting:
Identifying and Resolving Sales Tax Errors:
Sales tax errors can pose significant challenges for businesses, impacting financial accuracy and compliance. Identifying these errors requires a meticulous review of transactions, invoices, and applicable tax rates. Common issues may include misclassification of products or services, inaccurate tax calculations, or outdated tax rates. Regular audits and reconciliation processes can help pinpoint discrepancies.
Once identified, resolving sales tax errors involves a step-by-step approach. This may include updating tax codes, revising invoices, and ensuring that the accounting system is configured with the latest tax regulations. Communication with relevant stakeholders, such as customers or tax authorities, may be necessary to rectify any errors that have impacted financial transactions.
Addressing Syncing Issues with Automated Sales Tax:
Automated sales tax systems are designed to streamline processes and reduce manual efforts, but syncing issues can undermine their effectiveness. Troubleshooting syncing problems involves assessing integration points between different software platforms, ensuring seamless data flow. Common challenges include API conflicts, data format discrepancies, and system downtime.
To address syncing issues, businesses should conduct a comprehensive review of integration settings, update software versions, and collaborate with software providers for technical support. Regular system testing and monitoring can help preemptively identify potential syncing problems, allowing for proactive resolution before they disrupt operations.
Handling Discrepancies in Sales Tax Reporting:
Discrepancies in sales tax reporting can arise due to various factors, including human error, software glitches, or changes in tax regulations. Addressing these discrepancies requires a thorough examination of financial records, sales reports, and tax filings. Businesses must identify the root causes of discrepancies to prevent recurring issues.
Resolving reporting discrepancies involves updating records, amending tax returns if necessary, and implementing corrective measures in the reporting process. Businesses may need to collaborate with tax professionals to ensure compliance with changing regulations and to establish robust internal controls. Training staff on accurate reporting procedures and leveraging technology for real-time monitoring can contribute to long-term accuracy in sales tax reporting.








