Introduction:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a strategic approach that businesses use to manage and analyze customer interactions throughout the entire customer lifecycle, with the goal of improving customer satisfaction, retention, and overall business profitability. CRM software plays a crucial role in implementing and executing CRM strategies efficiently.
Brief Overview of CRM Software:
CRM software is a technology tool designed to help businesses manage and streamline their interactions with current and potential customers. It typically includes a range of features and functionalities that facilitate the tracking, analysis, and automation of various customer-related processes. Key components of CRM software often include contact management, sales automation, lead management, marketing automation, customer service, and analytics.
The primary objective of CRM software is to provide a centralized platform that allows businesses to gather, store, and systematically manage customer information. This helps organizations build stronger relationships with customers by understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors. CRM software can also automate routine tasks, allowing teams to focus on more value-added activities.
Importance of Salesforce CRM:
Salesforce is a leading CRM software provider and has gained widespread popularity due to its robust features and versatility. The importance of Salesforce CRM can be highlighted in several key areas:
- Comprehensive Customer View: Salesforce allows businesses to create a 360-degree view of their customers by consolidating information from various touchpoints. This comprehensive customer view helps in understanding customer needs, preferences, and history.
- Sales Process Optimization: Salesforce CRM streamlines the sales process by automating tasks such as lead management, opportunity tracking, and performance analytics. This results in increased sales efficiency and improved conversion rates.
- Marketing Automation: Salesforce offers tools for marketing automation, enabling businesses to create targeted campaigns, track customer engagement, and measure marketing ROI. This functionality is crucial for effective customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- Customer Service Enhancement: Salesforce’s CRM platform includes customer service functionalities that help organizations provide better support to their customers. It allows for case tracking, service analytics, and self-service options, contributing to improved customer satisfaction.
- Scalability and Customization: Salesforce CRM is highly scalable and can be customized to fit the specific needs of businesses across different industries and sizes. This flexibility makes it a preferred choice for companies experiencing growth and evolving business requirements.
Salesforce CRM is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to manage and nurture customer relationships effectively. Its versatile features contribute to enhanced sales, marketing, and customer service processes, making it a valuable asset for organizations striving to excel in today’s competitive business landscape.
Understanding Salesforce CRM:
Salesforce CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is a cloud-based platform that helps businesses manage their interactions and relationships with customers and potential customers. It provides a centralized hub for sales, marketing, customer service, and other essential functions. Here are some key aspects of understanding Salesforce CRM:
- Cloud-Based Solution: Salesforce is a cloud-based solution, meaning it is accessible from any device with an internet connection. This facilitates real-time collaboration and data accessibility.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Salesforce is designed to help organizations focus on their customers. It allows businesses to track customer interactions, manage leads, and streamline sales processes.
- Scalability: Salesforce is scalable and can accommodate the needs of both small businesses and large enterprises. It can grow with your business, providing flexibility and adaptability.
- Data Security: As a cloud-based platform, Salesforce places a strong emphasis on data security. It includes robust security features to protect sensitive customer information.
Core Features and Modules:
- Sales Cloud: Manages the sales process, from lead generation to deal closure. It includes tools for contact and opportunity management, as well as analytics to track sales performance.
- Service Cloud: Focuses on customer service and support. It includes features for case management, knowledge base, and customer communication tools.
- Marketing Cloud: Provides tools for marketing automation, email marketing, social media management, and analytics to help businesses execute and analyze their marketing campaigns.
- Commerce Cloud: Enables businesses to create personalized and seamless e-commerce experiences for their customers.
- Analytics Cloud: Allows organizations to visualize and analyze data for informed decision-making.
Customization Options:
- Salesforce is highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor the platform to their specific needs. Customization options include:
- Custom Objects and Fields: Users can create custom data objects and fields to capture unique information relevant to their business.
- Workflows and Automation: Businesses can automate processes using workflows to streamline repetitive tasks and ensure consistency.
- Custom Reports and Dashboards: Users can create custom reports and dashboards to gain insights into their data and monitor key performance indicators.
- Visualforce and Apex Code: For advanced customization, developers can use Visualforce to build custom user interfaces and Apex code for more complex business logic.
Integration Capabilities:
- Salesforce is designed to integrate seamlessly with other applications and systems. Integration capabilities include:
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Salesforce provides a robust set of APIs that allow for the integration of third-party applications and systems.
- AppExchange: Salesforce’s marketplace, AppExchange, offers a wide range of pre-built apps and integrations developed by third-party vendors.
- Middleware: Businesses can use middleware solutions to connect Salesforce with other enterprise applications.
- Connectors: Salesforce supports various connectors that facilitate integration with popular tools and platforms, such as Microsoft Outlook, Google Apps, and more.
- Data Import/Export: Salesforce allows users to import and export data easily, making it compatible with various data formats and sources.
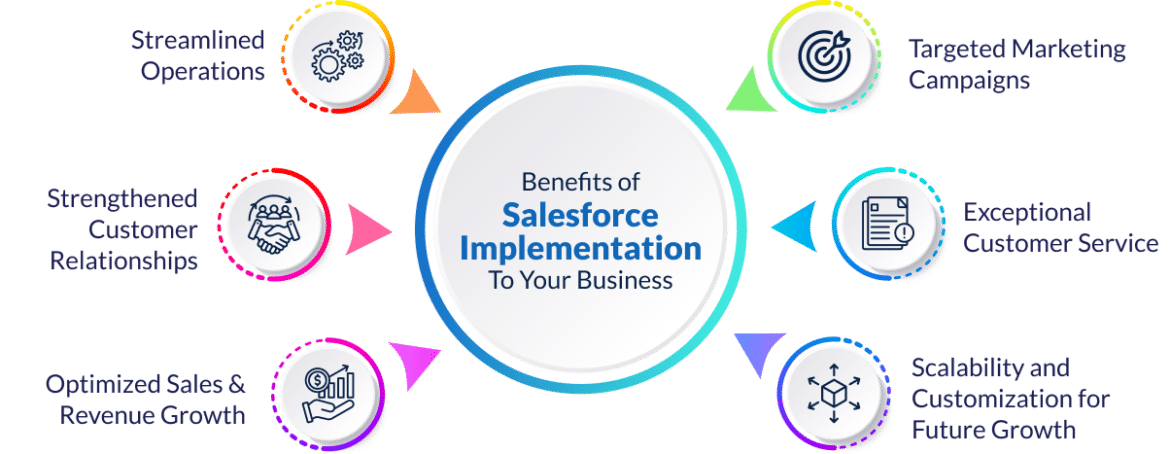
Benefits of Salesforce CRM Implementation
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- 360-Degree Customer View: Salesforce CRM allows businesses to consolidate customer data from various sources into a centralized platform. This provides a comprehensive and real-time view of each customer, including their preferences, purchase history, and interactions with the company.
- Personalized Customer Interactions: With a better understanding of customer behavior, businesses can personalize their interactions. This personalization can lead to more targeted marketing campaigns, tailored product recommendations, and improved customer satisfaction.
Streamlined Sales Processes:
- Lead Management: Salesforce helps in efficient lead tracking and management, ensuring that sales teams can prioritize and follow up on leads effectively.
- Opportunity Tracking: The CRM system assists in tracking sales opportunities through various stages of the sales pipeline, allowing for better forecasting and resource allocation.
- Automated Workflows: Salesforce enables the automation of repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. This leads to a more streamlined and efficient sales process.
Improved Collaboration and Communication:
- Centralized Communication: Salesforce provides a centralized platform for communication and collaboration among team members. This reduces the reliance on scattered communication channels and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
- Document Sharing: The CRM system facilitates document sharing and collaboration, making it easier for teams to access and work on shared documents related to sales, marketing, and customer support.
- Task and Event Management: Salesforce allows teams to schedule and track tasks and events, enhancing coordination and ensuring that important activities are not overlooked.
Data-driven Decision Making:
- Real-time Analytics: Salesforce offers robust analytics and reporting tools that provide real-time insights into various aspects of the business, including sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing effectiveness.
- Forecasting and Predictive Analytics: The CRM system supports forecasting, helping businesses anticipate future trends and plan accordingly. Predictive analytics can also identify potential opportunities or issues before they arise.
- Data Integration: Salesforce CRM can integrate with other data sources, allowing businesses to leverage a holistic view of their operations. This integration enhances the quality and depth of data available for decision-making processes.
Salesforce CRM implementation goes beyond just managing customer relationships. It optimizes sales processes, fosters collaboration, and empowers businesses with data-driven insights, ultimately contributing to improved overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Pre-Implementation Planning
Pre-implementation planning is a crucial phase in the development and execution of projects, initiatives, or strategies. This process involves several key components, including Needs Assessment, Defining Objectives and Goals, and Budgeting and Resource Allocation.
Needs Assessment:
- Purpose: The needs assessment is conducted to identify and analyze the requirements and challenges that the project or initiative aims to address.
- Process: This involves gathering data, conducting surveys, interviews, and analyzing existing systems or processes. The goal is to understand the current state and determine the gaps that need to be filled.
- Outcome: The outcome of the needs assessment helps in defining the scope of the project, understanding stakeholder expectations, and ensuring that the proposed solution aligns with the identified needs.
Defining Objectives and Goals:
- Purpose: This step involves clearly outlining the objectives and goals that the project intends to achieve. It provides a roadmap for the project team and stakeholders, guiding them throughout the implementation process.
- Process: Stakeholders collaborate to establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. These objectives should be aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and the findings from the needs assessment.
- Outcome: A well-defined set of objectives and goals serve as benchmarks for success, helping to measure the project’s effectiveness and ensuring that efforts are focused on achieving tangible outcomes.
Budgeting and Resource Allocation:
- Purpose: Budgeting and resource allocation involve estimating the financial requirements and determining the necessary resources for successful implementation.
- Process: The project team, in collaboration with financial experts, creates a budget that includes costs associated with technology, personnel, training, and any other relevant expenses. Resource allocation involves assigning the right people to the right tasks and ensuring that sufficient resources are available throughout the project lifecycle.
- Outcome: A well-prepared budget and resource allocation plan provide financial clarity, preventing overspending and ensuring that the necessary resources are available when needed. It also helps in making informed decisions about priorities and trade-offs during the implementation phase.
Selecting the Right Salesforce Edition
Salesforce Essentials:
- Target Audience: Small businesses and startups.
- Features: Essentials is designed to provide basic CRM functionalities, such as lead and opportunity management, email integration, and collaboration tools. It’s a simplified version suitable for organizations with straightforward sales processes.
- Limitations: Limited customization options and may not include some advanced features found in higher editions.
- Pricing: Generally more affordable for smaller businesses.
Salesforce Professional:
- Target Audience: Small to medium-sized businesses.
- Features: Professional edition includes more advanced features compared to Essentials. It offers increased customization options, workflow automation, and access to a broader range of Salesforce’s CRM capabilities.
- Limitations: Some limitations on the number of custom objects and workflow rules. It may not be suitable for large enterprises with complex requirements.
- Pricing: Higher than Essentials but still relatively affordable for businesses with moderate needs.
Salesforce Enterprise:
- Target Audience: Medium to large enterprises with more complex requirements.
- Features: Enterprise edition is feature-rich, providing a wide array of customization options, advanced analytics, and enhanced security features. It is suitable for businesses with more intricate sales processes and larger user bases.
- Limitations: While it offers more features than Professional, there are still certain limitations in terms of data storage and API usage.
- Pricing: Higher than Professional, reflecting the additional features and capabilities.
Salesforce Unlimited:
- Target Audience: Large enterprises with extensive customization and scalability needs.
- Features: Unlimited edition provides the highest level of customization, scalability, and support. It’s designed for organizations with complex processes, a large number of users, and the need for unlimited access to Salesforce features.
- Limitations: While it offers extensive capabilities, there may still be considerations related to data storage and API usage.
- Pricing: The highest among the editions, reflecting the comprehensive set of features and the scalability it offers.
When selecting a Salesforce edition, businesses should consider factors such as their size, budget, complexity of processes, and the level of customization required. It’s also important to anticipate future growth and choose an edition that can scale with the evolving needs of the organization. Additionally, businesses may consult with Salesforce representatives or partners to ensure they choose the edition that best aligns with their specific requirements.
Customization and Configuration:
Salesforce allows users to customize the platform to meet the specific needs and requirements of their business. This includes modifying existing features, creating new functionalities, and adjusting the interface to align with unique workflows. Customization can involve changes to fields, page layouts, and record types, among other elements.
Configuration refers to the setup and arrangement of Salesforce features without changing the platform’s underlying code. Users can configure various settings, permissions, and rules to ensure Salesforce aligns with the business processes. Configuration is often done through the Salesforce setup menu, where administrators can adjust system settings to match the organization’s needs.
Tailoring Salesforce to Your Business:
Salesforce is designed to be highly flexible and adaptable to different business models and industries. Tailoring Salesforce to your business involves aligning the platform with your unique processes, data models, and terminology. This can include modifying standard objects (like Accounts, Contacts, and Opportunities) or creating entirely new custom objects to store specific types of data relevant to your business.
Designing Custom Objects:
In Salesforce, objects are database tables that store data specific to your business. While standard objects come pre-built (e.g., Account, Contact, Opportunity), custom objects can be designed to store information that is unique to your organization. This could be anything from a custom entity related to a specific business process to an object designed to track specialized information like project details or customer feedback.
Workflow Automation:
Salesforce provides powerful workflow automation tools that enable businesses to automate their processes. Workflows define a series of automated steps and rules to trigger actions based on certain conditions. For example, you can set up a workflow to automatically send an email when a new lead is created, or update a record’s status when specific criteria are met. This helps streamline and optimize business processes, reducing manual effort and ensuring consistency.
Common Challenges in Salesforce CRM Implementation
Resistance to Change:
- Explanation: Resistance to change is a common challenge in any organizational shift, including the implementation of a new CRM system like Salesforce. Employees might be accustomed to existing processes and tools, making it difficult for them to embrace a new system.
- Impact: Resistance can hinder the adoption of Salesforce, leading to decreased productivity, inefficiencies, and potential errors in data entry or usage.
Insufficient User Training:
- Explanation: Inadequate training is a significant obstacle during CRM implementation. Users may not be familiar with Salesforce’s features and functionalities, leading to underutilization or misuse of the system.
- Impact: Without proper training, users might struggle to navigate Salesforce, resulting in data inaccuracies, slower workflows, and frustration among the workforce.
Data Quality Issues:
- Explanation: Poor data quality can arise from inaccurate or incomplete data during migration or ongoing usage. Inconsistent data formats, duplicate records, and outdated information are common issues that impact the reliability of the CRM.
- Impact: Low data quality undermines the value of Salesforce, affecting decision-making, analytics, and overall business insights.
Integration Challenges:
- Explanation: Integration challenges occur when Salesforce needs to interact with other systems and applications within the organization. Poorly planned integrations can lead to data silos, synchronization issues, and a lack of real-time information flow.
- Impact: Incomplete or problematic integrations can hinder the seamless flow of data between Salesforce and other systems, diminishing the effectiveness of the CRM.
Customization Overload:
- Explanation: While Salesforce offers extensive customization capabilities, it’s possible to go overboard with unnecessary customizations. Excessive customization can lead to a complex system that is challenging to maintain and upgrade.
- Impact: Customization overload can result in increased implementation and maintenance costs, longer deployment times, and a system that is difficult for users to navigate and understand.
Future Trends in Salesforce CRM
Artificial Intelligence Integration:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration involves incorporating machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and other AI capabilities into Salesforce CRM systems. This empowers organizations to automate routine tasks, gain valuable insights from data, and enhance the overall user experience.
Salesforce is likely to leverage AI to provide smarter and more predictive functionalities. This could include AI-driven chatbots for customer support, predictive lead scoring, and intelligent automation of repetitive tasks. AI integration aims to streamline business processes, improve decision-making, and offer personalized experiences for users.
Enhanced Mobile Capabilities:
With the increasing reliance on mobile devices, future trends in Salesforce CRM will likely focus on enhancing mobile capabilities. This involves optimizing the CRM platform for seamless and efficient use on various mobile devices, ensuring that users can access critical information and perform tasks while on the go.
Mobile CRM capabilities may include responsive design, intuitive mobile apps, and features that facilitate remote collaboration. Users should be able to view and update customer information, manage sales opportunities, and perform other CRM functions from their smartphones and tablets, providing flexibility and accessibility.
Blockchain in CRM:
Blockchain technology is known for its secure and transparent ledger system. In the context of CRM, blockchain can be used to enhance data security, integrity, and transparency in customer interactions and transactions.
Salesforce CRM with blockchain integration could offer benefits such as secure and tamper-proof record-keeping, improved trust in customer relationships, and streamlined processes for contracts and transactions. Blockchain in CRM can ensure that data remains unaltered, enhancing trust among stakeholders and reducing the risk of data manipulation.
Predictive Analytics:
Predictive analytics involves using statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and predict future outcomes. In the context of Salesforce CRM, this means leveraging advanced analytics to make informed predictions about customer behavior, sales trends, and other key business metrics.
Predictive analytics in Salesforce CRM can help organizations forecast sales, identify potential opportunities, and optimize marketing strategies. By analyzing patterns and trends in historical data, businesses can make data-driven decisions, allocate resources more effectively, and personalize their approach to customers, ultimately improving overall CRM performance.
The future trends in Salesforce CRM are characterized by the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, enhanced mobile capabilities, blockchain, and predictive analytics. These advancements aim to make CRM systems more intelligent, user-friendly, secure, and capable of providing valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the implementation of Salesforce CRM is a transformative journey that requires careful planning, customization, and ongoing support. By understanding the core features, planning effectively, and learning from successful case studies, organizations can unlock the full potential of Salesforce CRM. As the business landscape continues to evolve, embracing a robust CRM solution becomes not just a choice but a necessity for those aiming to thrive in a customer-centric world.