Introduction
Brief Overview of Cloud Storage
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital technology, the need for efficient data storage and accessibility has become paramount. Cloud storage, a revolutionary solution, has emerged as the cornerstone for businesses and individuals alike. Unlike traditional on-premise storage systems, cloud storage allows users to store and retrieve data over the internet from remote servers.
Cloud storage offers a scalable and flexible alternative to physical storage methods, enabling users to expand their storage capacity seamlessly. This flexibility is particularly crucial in a world where data volumes are growing exponentially. Whether it’s documents, images, or multimedia files, cloud storage provides a centralized and easily accessible repository for all types of data.
Importance of Cloud Storage Solutions
The importance of cloud storage solutions cannot be overstated in today’s digital era. One of the key advantages is the cost-effectiveness it brings to the table. Traditional storage systems often involve significant upfront costs for hardware and maintenance, whereas cloud storage operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to pay only for the resources they use.
Furthermore, cloud storage solutions offer unparalleled scalability. As businesses grow, their data storage needs evolve as well. Cloud storage allows for seamless scaling, ensuring that organizations can adapt to changing demands without the hassle of physical infrastructure expansion.
Security is another critical aspect. Cloud storage providers implement robust security measures to safeguard data against unauthorized access, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of stored information. Regular security updates and compliance certifications add an extra layer of confidence for businesses entrusting their sensitive data to the cloud.
Introduction to AWS Cloud Storage
Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out as a leader in the realm of cloud storage solutions. AWS Cloud Storage provides a comprehensive suite of services designed to address various storage requirements with efficiency and reliability. The platform boasts a global infrastructure, ensuring low-latency access to data from anywhere in the world.
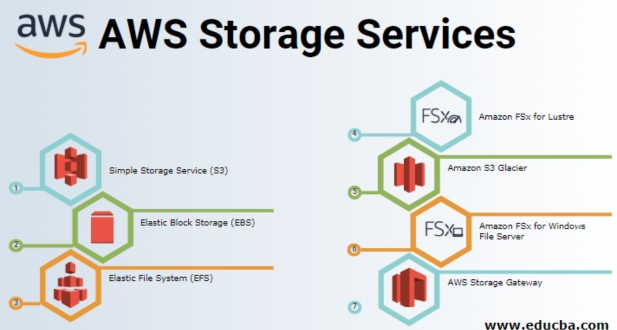
AWS offers a variety of storage options, each tailored to specific use cases. From the highly scalable and durable Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) to the high-performance Elastic Block Store (EBS) and the cost-effective Glacier, AWS provides a spectrum of choices catering to diverse storage needs.
As we delve deeper into this exploration of AWS Cloud Storage Solutions, we will unravel the features, benefits, and best practices associated with each service, empowering users to make informed decisions about their data storage strategy in the cloud. Join us on this journey as we navigate the vast landscape of AWS Cloud Storage, unlocking the full potential of modern data management.
Benefits of AWS Cloud Storage
Scalability and Flexibility
In the dynamic realm of modern business, the ability to scale and adapt quickly is a crucial factor for success. AWS Cloud Storage excels in this regard, offering unparalleled scalability and flexibility to meet the evolving needs of organizations.
- Scalability:
AWS provides elastic storage solutions that can scale up or down based on demand. With Amazon S3, for example, users can seamlessly expand their storage capacity as data grows, ensuring that they only pay for the resources they use. This scalability is particularly advantageous for businesses experiencing fluctuations in data volume, allowing them to stay agile and responsive to changing requirements.
- Flexibility:
AWS Cloud Storage supports a diverse range of storage classes, each optimized for specific use cases. From the standard storage class in Amazon S3 for frequently accessed data to the Glacier storage class for archival purposes, AWS allows users to choose the storage option that best aligns with their performance and cost requirements. This flexibility empowers organizations to tailor their storage strategy to the unique demands of their applications and workloads.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the standout features of AWS Cloud Storage is its cost-effectiveness, driven by a pay-as-you-go pricing model and various storage classes designed to optimize costs based on usage patterns.
- Pay-as-You-Go Model:
AWS follows a pay-as-you-go pricing structure, eliminating the need for upfront capital investments in hardware. Users are billed only for the storage and data transfer they consume, enabling cost optimization and efficient budget management. This model is particularly advantageous for businesses of all sizes, allowing them to align their expenses with actual usage.
- Storage Classes for Cost Optimization:
AWS offers multiple storage classes, each with its own pricing model. For instance, Amazon S3’s Standard storage class is suitable for frequently accessed data, while the Glacier storage class offers lower costs for infrequently accessed archival data. By intelligently selecting the appropriate storage class for each type of data, organizations can achieve significant cost savings without compromising on performance or durability.
High-Security Standards
Security is paramount in the digital landscape, and AWS Cloud Storage places a strong emphasis on implementing robust security measures to safeguard user data.
- Encryption at Rest and in Transit:
AWS provides encryption mechanisms to secure data both at rest and in transit. Amazon S3, for example, supports server-side encryption, ensuring that stored data remains confidential. Additionally, AWS utilizes industry-standard encryption protocols for data transmission, guaranteeing the security of data as it travels between the user’s devices and the AWS servers.
- Access Controls and Permissions:
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables organizations to define fine-grained access controls and permissions. This ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. By implementing strong access controls, AWS empowers users to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of their stored information.
Reliability and Durability
AWS Cloud Storage is renowned for its high reliability and durability, providing users with confidence that their data is available and secure at all times.
- Global Infrastructure:
AWS operates a global network of data centers, allowing users to deploy their storage resources in multiple geographic regions. This distributed infrastructure enhances reliability by minimizing the impact of regional outages or disruptions. Organizations can architect their storage solutions across multiple AWS regions for added redundancy and resilience.
- Durability of Storage Services:
Storage services like Amazon S3 boast exceptional durability. Amazon S3’s Standard storage class, for example, is designed to provide 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability, meaning that data is highly resistant to loss. This level of durability, coupled with automatic data replication across multiple devices and facilities, ensures that organizations can rely on AWS Cloud Storage for the long-term preservation of their critical data.
In conclusion, the benefits of AWS Cloud Storage, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, high-security standards, and reliability, collectively contribute to a robust and flexible storage solution. By leveraging these advantages, organizations can optimize their data management strategies, reduce operational costs, and elevate the overall efficiency and security of their digital infrastructure.
Types of AWS Cloud Storage
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Overview
Amazon S3, or Simple Storage Service, is a cornerstone of AWS Cloud Storage, offering scalable object storage designed to store and retrieve any amount of data. Launched in 2006, S3 has become a ubiquitous and reliable storage solution for a wide range of applications.
Features:
- Bucket Structure: S3 uses a bucket system for organizing data, where each object (file) is stored within a unique bucket.
- Scalability: S3 is highly scalable, allowing users to store and retrieve any amount of data with low latency and high throughput.
- Durability: With 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability, S3 ensures that data remains intact and available even in the face of hardware failures.
- Use Cases
- Web Hosting: S3 serves as an excellent platform for hosting static websites, providing cost-effective and scalable web hosting solutions.
- Backup and Archiving: Organizations use S3 for backup and archival purposes due to its durability and cost-effective storage classes.
- Data Lakes: S3 is a fundamental component of building data lakes, enabling efficient storage and management of large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
- Key Features
- Storage Classes: S3 offers multiple storage classes, including Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier, and more, each tailored for different use cases.
- Versioning: S3 supports versioning, allowing users to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object stored in a bucket.
- Access Control: Fine-grained access controls through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) enable secure sharing of data with specific users or applications.
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store)
Overview
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) provides block-level storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. It offers high-performance and low-latency storage solutions that can be attached to EC2 instances to meet a variety of application requirements.
Features:
- Block Storage: EBS volumes provide raw block-level storage, allowing users to format them with their preferred file system.
- Snapshot Backup: EBS supports snapshot backups, enabling users to create point-in-time copies of their volumes for data protection and disaster recovery.
- Elasticity: EBS volumes can be easily attached to and detached from EC2 instances, providing flexibility in adjusting storage capacity.
- Use Cases
- Database Storage: EBS is commonly used to store database files, providing scalable and high-performance storage for applications with demanding I/O requirements.
- Enterprise Applications: Applications requiring persistent and low-latency storage, such as CRM systems and ERP solutions, benefit from EBS.
- Development and Testing: EBS volumes can be quickly provisioned for development and testing environments, enhancing agility in software development processes.
- Key Features
- Provisioned IOPS: Users can provision EBS volumes with the desired level of I/O performance, ensuring predictable and consistent storage performance.
- Encryption: EBS supports encryption at rest, providing an additional layer of security for sensitive data.
- Snapshots and Lifecycle Management: Snapshots can be used for backup and can also be used to create new volumes, facilitating efficient data management.
Amazon Glacier
Overview
Amazon Glacier is a cost-effective storage service designed for data archiving and long-term backup. It is optimized for infrequently accessed data, providing durable and secure storage with low retrieval latency.
Features:
- Low-Cost Archiving: Glacier offers significantly lower storage costs compared to other AWS storage options, making it suitable for archiving large volumes of data.
- Tiered Storage: Glacier provides different storage classes, including Glacier Standard and Glacier Deep Archive, each optimized for specific access requirements and costs.
- Vaults and Archives: Data in Glacier is organized into vaults, and each vault contains archives that represent the stored data.
- Use Cases
- Data Archiving: Glacier is ideal for organizations looking to archive data for compliance, regulatory, or long-term storage purposes.
- Backup Storage: It serves as a cost-effective solution for storing backup data that is accessed infrequently but needs to be retained for extended periods.
- Digital Preservation: Glacier’s durability and low costs make it suitable for preserving digital assets and historical records.
- Key Features
- Retrieval Options: Glacier offers multiple retrieval options, allowing users to choose between expedited, standard, or bulk retrievals based on their latency requirements.
- Vault Lock: Glacier provides a Vault Lock feature that enforces compliance controls by allowing users to lock down their vaults, preventing the deletion of archives for a specified retention period.
- Data Transfer Acceleration: Glacier accelerates data transfers using the AWS Snowball device for large-scale data ingestion.
In summary, Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon Glacier are integral components of AWS Cloud Storage, each serving specific use cases with their unique features and capabilities. Understanding these services empowers users to architect storage solutions that align with their application requirements and business objectives.
Best Practices for AWS Cloud Storage
Data Encryption
Data security is paramount in the cloud environment, and AWS Cloud Storage provides robust encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive information.
- Server-Side Encryption (SSE):
AWS offers Server-Side Encryption for data at rest, ensuring that stored data remains confidential. Amazon S3, for instance, supports SSE with AWS Key Management Service (KMS) or SSE with Amazon S3 Managed Keys (SSE-S3). SSE with KMS allows users to manage their encryption keys, providing an additional layer of control over data security.
- Client-Side Encryption:
For an extra layer of security, users can implement client-side encryption before uploading data to AWS Cloud Storage. By encrypting data on the client side before transmission, organizations can maintain full control over the encryption process and the keys used.
- Transit Encryption:
To secure data during transit, AWS utilizes industry-standard encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS. This ensures that data transmitted between clients and AWS storage services remains protected against interception and tampering.
Versioning and Backup Strategies
- Versioning:
Enabling versioning on Amazon S3 buckets is a recommended practice to safeguard against accidental data deletions or overwrites. With versioning, each modification to an object results in the creation of a new version, allowing users to roll back to previous versions if needed. This provides a comprehensive history of changes and enhances data integrity.
- Regular Backups:
Implementing regular backup strategies is essential for disaster recovery and data resilience. Utilize features like Amazon S3’s cross-region replication to create redundant copies of critical data in different geographic locations. Additionally, leverage Amazon S3’s lifecycle policies to automatically transition older data to lower-cost storage classes, optimizing costs without compromising data availability.
Access Control and Permissions
Fine-grained access controls are crucial to ensure that only authorized entities can access and modify data stored in AWS Cloud Storage.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM):
IAM allows organizations to define granular access policies, specifying which users or systems have permissions to perform specific actions on storage resources. Regularly review and update IAM policies to align with changing organizational structures and data access requirements.
- Bucket Policies:
Leverage bucket policies in Amazon S3 to control access at the bucket level. This allows administrators to define rules for both resource-based and user-based access control, offering flexibility in configuring access permissions.
- Access Logging:
Enable access logging to monitor and audit access to storage resources. By logging requests made to an S3 bucket, organizations gain insights into who accessed the data, when, and from where. This aids in security investigations and compliance adherence.
Monitoring and Logging
Effective monitoring and logging are vital components of a proactive cloud storage management strategy.
- AWS CloudWatch:
Integrate AWS CloudWatch with storage services to gain real-time insights into performance metrics, error rates, and operational trends. Set up custom CloudWatch alarms to receive notifications when predefined thresholds are breached, enabling prompt response to potential issues.
- Logging and Auditing:
Enable comprehensive logging and auditing for storage services. This includes configuring logging options in Amazon S3 to track requests, setting up AWS CloudTrail to monitor API calls, and utilizing AWS Config for tracking configuration changes. Centralized logging helps in troubleshooting, compliance auditing, and maintaining a secure storage environment.
- Regular Performance Optimization:
Regularly analyze storage performance metrics to identify bottlenecks or areas for optimization. Consider using AWS Trusted Advisor, a service that provides recommendations for cost optimization, security, and performance improvements based on best practices.
In conclusion, implementing best practices for AWS Cloud Storage, including robust data encryption, versioning and backup strategies, access control and permissions, as well as proactive monitoring and logging, ensures a secure, resilient, and well-managed storage environment. Adhering to these practices not only enhances data protection but also contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of cloud storage solutions on the AWS platform.
Integrating AWS Cloud Storage with Applications
AWS SDKs (Software Development Kits)
AWS Software Development Kits (SDKs) provide developers with pre-built libraries and tools to seamlessly integrate AWS Cloud Storage services into their applications. Supporting multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, and .NET, AWS SDKs simplify the process of interacting with storage services like Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS. Developers can leverage SDKs to perform operations such as uploading, downloading, and managing objects in storage, streamlining application development and ensuring compatibility with AWS services.
API Integration
AWS Cloud Storage offers robust Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that enable direct integration with storage services. Developers can interact with these APIs to programmatically perform tasks like data uploads, retrievals, and metadata operations. API integration provides flexibility and control, allowing applications to seamlessly leverage AWS Cloud Storage capabilities. With comprehensive documentation and support, AWS APIs empower developers to build scalable and efficient storage solutions tailored to their application requirements.
Case Studies of Successful Integrations
Explore real-world case studies showcasing successful integrations of AWS Cloud Storage with diverse applications. Highlight instances where organizations achieved improved scalability, cost-efficiency, and data management by seamlessly incorporating AWS storage services. These case studies provide insights into the practical benefits of integrating AWS Cloud Storage, demonstrating how businesses across various industries have leveraged these solutions to enhance their application performance and overall operational efficiency.
Comparing AWS Cloud Storage Solutions
Performance Comparison
Evaluate the performance of AWS Cloud Storage solutions, comparing factors such as data retrieval speed, latency, and throughput. Amazon S3, with its high scalability, may excel in handling frequent data access, while Amazon EBS, designed for low-latency block storage, might be more suitable for applications requiring consistent performance. Assessing the performance characteristics of each solution ensures alignment with specific application requirements.
Cost Comparison
Conduct a thorough cost analysis of AWS Cloud Storage solutions to determine the most economical option for different use cases. Consider factors such as storage class pricing, data transfer costs, and retrieval fees. Amazon Glacier, designed for infrequently accessed data, may offer significant cost savings for archival purposes, while Amazon S3’s Standard storage class might be preferred for frequently accessed data. Balancing performance needs with cost considerations helps organizations optimize their storage expenditure.
Use Case Scenarios
Examine various use case scenarios to identify the most suitable AWS Cloud Storage solution for specific application requirements. For example, Amazon S3’s versatility makes it an ideal choice for dynamic web hosting, while Amazon EBS may be preferred for persistent block storage in database applications. Understanding the use case scenarios allows organizations to tailor their storage strategy, ensuring optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and data management across different applications and workloads.
Future Trends in AWS Cloud Storage
Emerging Technologies
As AWS continues to innovate, emerging technologies are expected to shape the future of cloud storage. Keep an eye on advancements such as edge computing, serverless architectures, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning within storage services. These technologies aim to enhance the speed, efficiency, and intelligence of data storage and retrieval processes, providing users with more sophisticated and automated solutions.
Anticipated Developments in Cloud Storage
Anticipate developments in areas such as data tiering, where intelligent algorithms dynamically move data between storage classes based on usage patterns, optimizing costs. Look out for advancements in security protocols and encryption methods to address evolving threats. Additionally, as the demand for real-time analytics grows, expect AWS Cloud Storage to evolve with enhanced capabilities for processing and analyzing data directly within the storage environment. Staying informed about these anticipated developments ensures organizations can proactively leverage new features and functionalities for a future-proof cloud storage strategy.
Conclusion
AWS Cloud Storage Solutions stand at the forefront of the digital revolution, providing a comprehensive suite of services that empower organizations to efficiently manage and leverage their data assets. The versatility of Amazon S3, with its scalability and durability, makes it a cornerstone for various applications, from web hosting to data lakes. Amazon EBS complements this with high-performance block storage tailored for specific application needs. Meanwhile, Amazon Glacier offers a cost-effective solution for archival and infrequently accessed data.
The benefits of AWS Cloud Storage, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, high-security standards, and reliability, underscore its significance in modern data management. Best practices such as data encryption, versioning, access control, and monitoring further enhance the security and resilience of storage solutions.
As we look to the future, emerging technologies like edge computing and the integration of AI and ML signal an era of intelligent and automated storage. Anticipated developments in data tiering, security, and real-time analytics underscore AWS’s commitment to staying at the forefront of technological advancements.
Ultimately, AWS Cloud Storage Solutions empower organizations to not only meet their current storage needs but also to adapt and thrive in an ever-evolving digital landscape, ensuring that their data remains secure, accessible, and strategically leveraged for continued success.
AWS Cloud Storage refers to a suite of scalable and secure storage services provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It includes services like Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon Glacier, offering various storage options for different use cases.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a scalable object storage service designed for storing and retrieving any amount of data. It is commonly used for web hosting, backup and archiving, and as a data lake for large datasets.
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) provides block-level storage volumes that can be attached to EC2 instances, offering low-latency performance. In contrast, Amazon S3 is object storage designed for scalable and durable storage of large amounts of data.
AWS Cloud Storage follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model. Users are billed based on the amount of storage they use, data transfer, and additional features like data retrieval in the case of services like Amazon Glacier.
AWS employs robust security measures, including encryption at rest and in transit, access controls through IAM, and compliance certifications. Users can also implement additional security features like server-side encryption and access policies.