Understanding AWS Backup and Restore Services
What are AWS Backup and Restore Services?
AWS Backup and Restore Services are offerings provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enable users to efficiently back up and restore their data and applications within the AWS ecosystem. These services aim to simplify the process of data protection, ensuring that critical data remains secure, accessible, and recoverable in the event of data loss, corruption, or other disasters.
Key Components of AWS Backup and Restore Services:
- AWS Backup Console: A centralized management interface for configuring, monitoring, and managing backup and restore operations across various AWS services.
- AWS Backup Vault: A secure storage location where backup copies of data are stored. Vaults provide encryption, access control, and compliance features to safeguard the backed-up data.
- Backup Plans: Configurations that define the backup frequency, retention policies, and other parameters for different data sets or applications.
- Backup Jobs: Scheduled or manual tasks that initiate the backup process according to the defined backup plans.
- Recovery Points: Point-in-time snapshots of data that represent specific backup instances. These recovery points serve as the basis for restoring data to a previous state.
How AWS Backup Works:
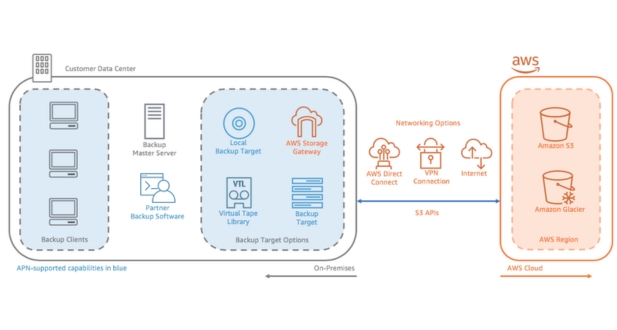
AWS Backup simplifies the backup process by automating the creation, scheduling, and retention of backups across various AWS services, such as Amazon EBS volumes, Amazon RDS databases, Amazon DynamoDB tables, Amazon EFS file systems, and more. Users can define backup plans to specify the backup frequency, retention period, and backup window for each data set or application. AWS Backup then orchestrates the backup process, creating recovery points according to the defined schedule.
How AWS Restore Works:
AWS Restore enables users to recover their data and applications from backup copies stored in AWS Backup Vaults. Users can initiate the restore process through the AWS Backup Console or programmatically using APIs. They can select specific recovery points corresponding to desired backup instances and initiate the restoration of data to the original or alternate locations within AWS. AWS Restore provides options for granular or full restores, depending on the user’s requirements.
AWS Backup vs. Traditional Backup Solutions:
- Scalability: AWS Backup scales automatically to accommodate growing data volumes and diverse workloads, eliminating the need for manual infrastructure provisioning.
- Automation: AWS Backup automates the backup process, reducing the administrative burden associated with managing backup operations manually.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AWS Backup follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing users to pay only for the storage and resources they consume, without upfront investments in hardware or software licenses.
- Integration: AWS Backup seamlessly integrates with various AWS services, enabling users to centrally manage backup and restore operations for their entire AWS environment.
- Security: AWS Backup employs encryption, access controls, and compliance features to protect backed-up data from unauthorized access or tampering, enhancing data security and regulatory compliance.
Features and Capabilities
Automated Backup Scheduling
This feature allows users to set up automatic backups on a predefined schedule. By automating the backup process, it ensures that critical data is consistently backed up without manual intervention, reducing the risk of data loss due to human error or oversight. Users can define backup frequency, retention policies, and other parameters to suit their specific requirements.
Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle management refers to the ability to manage data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to deletion or archival. This feature enables users to define policies for data retention, archival, and deletion based on predefined criteria such as age, usage, or regulatory requirements. By automating data lifecycle management, organizations can optimize storage resources, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with data retention policies.
Centralized Management and Monitoring
Centralized management and monitoring provide a single interface or dashboard for managing and monitoring backup processes across multiple systems or environments. This feature streamlines administrative tasks, improves visibility into backup operations, and enables efficient troubleshooting and performance monitoring. Administrators can configure backup policies, track backup status, and receive alerts or notifications about backup issues or failures from a centralized location.
Cross-Region and Cross-Account Backups
Cross-region and cross-account backups allow users to replicate data backups across different geographic regions or AWS accounts. This feature enhances data resilience and disaster recovery capabilities by ensuring that backups are stored in multiple locations or accounts, reducing the risk of data loss due to regional outages or account-specific issues. It also facilitates compliance with data sovereignty requirements by enabling data to be stored in specific geographic regions.
Application Integration
Application integration enables seamless integration with existing applications or services, allowing data backups to be performed directly from the application environment. This feature simplifies backup workflows, minimizes disruption to business operations, and ensures consistency and accuracy in backup processes. Integration with popular applications and platforms allows organizations to leverage existing infrastructure and workflows for data protection.
Security and Compliance:
Security and compliance features ensure that backup data is protected against unauthorized access, tampering, or loss. This includes encryption of data both in transit and at rest, access controls, authentication mechanisms, and compliance with industry regulations and standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2. By implementing robust security and compliance measures, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, maintain data integrity, and mitigate the risk of data breaches or non-compliance penalties.
Benefits of AWS Backup and Restore Services
Data Protection and Redundancy:
AWS Backup and Restore Services offer robust data protection mechanisms by creating redundant copies of your data across multiple geographic locations. This ensures that even if one location fails, your data remains safe and accessible.
Features like versioning allow you to restore previous versions of your data, offering an additional layer of protection against accidental deletions or data corruption.
Cost Efficiency:
AWS Backup and Restore Services can help optimize costs by eliminating the need for expensive on-premises backup infrastructure.
With pay-as-you-go pricing models, you only pay for the storage and resources you use, reducing upfront costs and allowing for better budget management.
Additionally, automated backup policies and lifecycle management help optimize storage usage and minimize unnecessary expenses.
Scalability and Flexibility:
AWS Backup and Restore Services are highly scalable, allowing you to seamlessly scale your backup infrastructure as your data grows.
Flexible storage options enable you to choose the most suitable storage class for your backup needs, balancing performance, durability, and cost.
Integration with other AWS services allows for customization and automation of backup processes, adapting to changing business requirements.
Simplified Management:
The centralized management console provided by AWS Backup simplifies the management of backups across various AWS services, streamlining administrative tasks.
Unified backup policies and scheduling capabilities enable consistent backup practices across your entire AWS environment, reducing complexity and minimizing the risk of errors.
Monitoring and alerting features help ensure that backups are executed successfully and meet defined service level agreements (SLAs).
Compliance and Governance:
AWS Backup and Restore Services facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards by providing features like encryption, access controls, and audit logging.
Built-in data protection features help organizations meet data residency requirements by allowing them to specify the geographic regions where their data is stored.
Compliance-specific features such as Immutable Storage for Amazon S3 ensure that backup data remains tamper-proof and compliant with regulatory mandates.
Best Practices for Implementing AWS Backup and Restore Services
Define Backup Policies and Retention Periods
Establish clear backup policies outlining what data needs to be backed up, how frequently backups should occur, and how long backups should be retained. This involves determining the frequency of backups (e.g., hourly, daily, weekly), the types of data to be backed up (e.g., databases, files, configurations), and the retention periods (e.g., 7 days, 30 days, 90 days, 1 year). These policies should align with your organization’s data retention and compliance requirements.
Utilize Tagging for Resource Management
Implement tagging for your AWS resources to categorize and organize them effectively. Tags provide metadata that can be used for resource management, cost allocation, and automation. By tagging resources appropriately, you can easily identify which resources need to be backed up, track their ownership, and apply backup policies consistently across different resource types.
Regularly Test Backup and Restore Procedures
Conduct regular testing of backup and restore procedures to ensure they are functioning as expected. Testing should include both backup processes to confirm data integrity and restore processes to verify data recoverability. Regular testing helps identify any issues or gaps in your backup and restore capabilities proactively, allowing you to address them before they impact critical data.
Implement Multi-Region and Multi-Account Strategies
Distribute backups across multiple AWS regions and accounts to enhance data durability and availability. Storing backups in multiple regions protects against regional failures or disasters, ensuring data resilience. Additionally, using multiple AWS accounts for backup storage can provide isolation and security controls, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or accidental deletion.
Monitor Backup Metrics and Alerts
Establish monitoring mechanisms to track backup metrics and receive alerts for any backup failures or anomalies. Monitoring backup metrics such as completion status, duration, and storage usage helps ensure backups are running smoothly and meeting defined SLAs. Setting up alerts enables timely detection and resolution of backup issues, minimizing potential data loss or downtime.
Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Implement encryption mechanisms to protect data both at rest and in transit during backup and restore operations. AWS Backup supports encryption of backup data using AWS Key Management Service (KMS), allowing you to manage encryption keys securely. Encrypting data at rest helps safeguard against unauthorized access or data breaches, while encrypting data in transit ensures data confidentiality during transmission over the network.
Use Cases and Real-world Scenarios
Disaster Recovery:
Disaster recovery refers to the process of restoring and recovering IT infrastructure and data after a catastrophic event such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or hardware failures. In this scenario, cloud storage offers an off-site backup solution that ensures data availability and business continuity. By replicating critical data and systems to the cloud, organizations can quickly recover their operations and minimize downtime.
Data Archiving and Compliance:
Data archiving involves storing inactive or historical data in a cost-effective and accessible manner for long-term retention. Cloud storage provides scalable and secure archival solutions, allowing organizations to store large volumes of data without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. Additionally, cloud storage services often include features for data governance and compliance, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Application Migration:
Application migration involves transferring software applications and workloads from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud or between cloud environments. Cloud storage facilitates seamless application migration by providing scalable storage resources and integration with migration tools. Organizations can leverage cloud storage to move data and application components efficiently, enabling agility, scalability, and cost savings.
Database Backups:
Database backups are essential for data protection and disaster recovery, ensuring that critical business data is securely backed up and recoverable in case of data loss or corruption. Cloud storage offers scalable and reliable solutions for storing database backups, with features such as automated backup scheduling, versioning, and encryption. By leveraging cloud storage for database backups, organizations can improve data resilience and reduce the risk of data loss.
File System Backups:
File system backups involve backing up files, folders, and directories from servers, workstations, or storage systems to protect against data loss and facilitate recovery. Cloud storage provides scalable and cost-effective solutions for file system backups, enabling organizations to securely store backup data off-site. With features such as deduplication, compression, and encryption, cloud storage enhances backup efficiency and security.
DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
DevOps practices focus on collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery to streamline software development and deployment processes. Cloud storage plays a crucial role in DevOps and CI/CD pipelines by providing reliable storage for artifacts, code repositories, and deployment packages. By integrating cloud storage into CI/CD workflows, organizations can achieve faster release cycles, improved scalability, and better resource utilization.
Implementation Guidelines and Deployment Strategies
Setting Up AWS Backup:
Setting up AWS Backup involves creating a centralized backup repository and configuring it to store backups of your AWS resources. This typically includes setting up the necessary permissions, roles, and policies to ensure that AWS Backup has the required access to your resources. Additionally, you may need to configure settings such as encryption and access controls to secure your backups.
Configuring Backup Plans and Vaults:
Once AWS Backup is set up, you’ll need to configure backup plans and vaults. Backup plans define the backup schedule, retention policies, and other parameters for backing up your resources. Vaults are storage containers where the actual backups are stored. Configuring backup plans involves specifying which resources to back up, how often to back them up, and how long to retain the backups.
Integrating AWS Backup with Other AWS Services:
AWS Backup can integrate with other AWS services to provide additional functionality and flexibility. This may include integrating with services like Amazon S3 for storing backups, AWS Lambda for executing custom backup tasks, or AWS CloudFormation for managing backup resources using infrastructure as code.
Monitoring and Managing Backups:
Monitoring and managing backups is essential to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of your backup solution. This involves monitoring backup jobs, verifying that backups are completed successfully, and managing backup storage usage. AWS Backup provides tools and features for monitoring backup status, viewing backup logs, and managing backup resources.
Optimizing Costs and Performance:
Optimizing costs and performance involves fine-tuning your backup solution to achieve the right balance between cost-effectiveness and performance. This may include optimizing backup schedules to minimize costs, using storage lifecycle policies to automatically transition backups to lower-cost storage tiers, or implementing data deduplication and compression techniques to reduce storage usage. Additionally, monitoring performance metrics and adjusting configuration settings as needed can help ensure that backups are performed efficiently without impacting the performance of your AWS resources.
Future Trends and Innovations
Machine Learning and AI-driven Backup Solutions
Machine learning and AI technologies are increasingly being integrated into backup solutions to enhance their efficiency and effectiveness.
These AI-driven systems can analyze patterns in data usage, predict potential failures, optimize storage allocation, and automate backup processes.
By learning from historical data and user behavior, these solutions can adapt and improve over time, providing more reliable and intelligent backup capabilities.
Enhanced Security and Compliance Features
With the growing concerns around data security and privacy, backup solutions are incorporating advanced security features to protect sensitive information.
This includes encryption of data both in transit and at rest, access controls, identity management, and compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others.
Additionally, features like ransomware detection and recovery are becoming essential to safeguard against cyber threats.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Backup solutions are exploring integration with emerging technologies like blockchain to enhance data integrity and security.
Blockchain technology can provide tamper-proof, decentralized ledgers for recording backup operations, ensuring the authenticity and immutability of data.
This integration can also enable innovative approaches to data sharing and collaboration while maintaining trust and transparency.
Expansion of Backup-as-a-Service Offerings
Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS) models are gaining popularity due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Providers are expanding their BaaS offerings to cater to diverse needs, including support for hybrid and multi-cloud environments, endpoint devices, and mission-critical applications.
These services may include features such as automated backups, instant recovery, and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Advancements in Data Governance and Policy Management
Data governance and policy management are crucial for ensuring compliance, optimizing data usage, and minimizing risks.
Backup solutions are incorporating advanced tools for defining and enforcing data governance policies, including retention periods, access controls, and data lifecycle management.
This enables organizations to efficiently manage their data assets, adhere to regulatory requirements, and mitigate potential legal and operational risks.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, AWS Backup and Restore Services offer a robust suite of tools and capabilities to protect and manage data in the cloud effectively. By leveraging automated backup scheduling, centralized management, and scalable infrastructure, businesses can ensure the resilience and availability of their critical data assets.
AWS Backup is a fully managed backup service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that centralizes and automates data protection across various AWS services. It allows you to create backup policies, manage backup schedules, and restore data from a single console.
AWS Backup supports a wide range of AWS services including Amazon EBS, Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon EFS, Amazon EC2, and AWS Storage Gateway, among others.
AWS Backup works by creating backup plans, which define backup policies such as frequency, retention periods, and backup vaults. These plans are then applied to AWS resources to automate the backup process. Backups are stored in backup vaults, providing centralized management and easy access for restores.
AWS Backup pricing is based on the storage used for backups and the amount of data restored. There are no upfront fees or commitments, and you only pay for what you use. Pricing varies depending on the AWS region and the specific services being backed up.
AWS Backup employs various security measures to protect your data, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications such as SOC, PCI DSS, and HIPAA. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest to ensure its confidentiality and integrity.