Google Workspace Security and Compliance
Introduction
In today’s digital era, businesses rely heavily on cloud-based productivity and collaboration tools to streamline operations, foster remote work, and enhance communication. Google Workspace, formerly known as G Suite, is a popular choice for organizations seeking a robust set of applications for productivity and collaboration. However, with the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and the importance of data privacy and compliance, ensuring the security and compliance of Google Workspace is paramount. This article delves into Google Workspace’s security and compliance features, addressing the challenges and best practices for protecting your business in the digital age.
The Importance of Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are non-negotiable in modern business environments. Companies, regardless of size, need to safeguard sensitive information, adhere to legal requirements, and maintain customer trust. Google Workspace plays a crucial role in these aspects, offering a secure and collaborative workspace while helping organizations meet compliance obligations.
Before we dive deeper into security and compliance, let’s start with an overview of what Google Workspace encompasses. Google Workspace is a suite of cloud-based productivity tools that include Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, Google Meet, and more. It’s designed to enable efficient communication, collaboration, and document sharing among teams, whether they are in the same office or spread across the globe.
Security in Google Workspace
Google Workspace provides a robust security framework that encompasses multiple layers of protection. These layers are designed to address various aspects of security, including data protection, access control, and threat detection. Here’s a closer look at some of the security features within Google Workspace.
-
Data Encryption
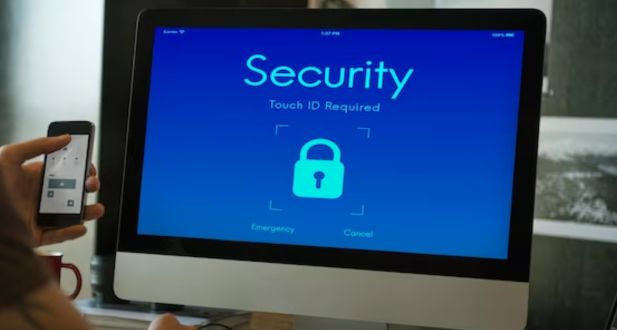
Data encryption is a fundamental component of data security. Google Workspace encrypts data both in transit and at rest. In transit, data is encrypted using industry-standard TLS (Transport Layer Security) to prevent eavesdropping during transmission. At rest, data stored in Google Drive and other services is encrypted using 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). This ensures that even if a breach were to occur, the data remains protected.
2. Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication is a widely recognized security practice that adds an extra layer of protection to user accounts. Google Workspace supports 2FA, which requires users to provide two forms of verification (typically, a password and a temporary code sent to a mobile device) before they can access their accounts. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
3. Access Control and Identity Management
Google Workspace allows organizations to set strict access controls. Administrators can define who has access to specific files, folders, or applications. Additionally, identity management tools help ensure that only authorized individuals can access the company’s resources.
4. Mobile Device Management (MDM)
As the use of mobile devices for work continues to grow, Google Workspace provides Mobile Device Management tools that allow organizations to secure and manage devices used to access company data. This includes the ability to remotely wipe a device if it’s lost or stolen, ensuring that sensitive information doesn’t fall into the wrong hands.
5. Security Key Enforcement
Organizations can further enhance security by enforcing the use of security keys for user authentication. Security keys are physical devices or smartphone apps that provide an extra layer of protection beyond traditional passwords.
6. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Google Workspace offers advanced DLP features that help prevent sensitive data from being shared or leaked inadvertently. These features allow administrators to create rules and policies to protect confidential information.
7. Email Security
Email is a common vector for cyberattacks. Google Workspace includes strong email security measures, such as spam and malware filtering, as well as phishing detection. These features help ensure that malicious emails are identified and quarantined, protecting users from potentially harmful content.
8. Advanced Threat Detection
Google Workspace employs advanced threat detection capabilities to identify and respond to suspicious activities. This includes machine learning algorithms that can detect anomalies and potential security threats, such as suspicious login attempts or data exfiltration.
Compliance in Google Workspace
In addition to security, compliance is a critical aspect of business operations, especially in highly regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and government. Google Workspace is designed to help organizations meet their compliance requirements, whether it’s HIPAA, GDPR, or industry-specific regulations. Here’s how Google Workspace addresses compliance concerns:
-
HIPAA Compliance
Healthcare organizations that handle patient data must adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Google Workspace offers a Business Associate Agreement (BAA), a legal contract that ensures Google’s commitment to maintaining HIPAA compliance. This allows healthcare providers to use Google Workspace while meeting their obligations under HIPAA.
2. GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs how organizations handle the personal data of European Union (EU) citizens. Google Workspace helps users comply with GDPR by providing tools for data protection, transparency, and user consent. It also includes a Data Processing Amendment (DPA) that outlines Google’s commitment to GDPR compliance.
3. Other Regulatory Compliance
Google Workspace can assist organizations in meeting various other regulatory requirements, including the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the education sector and the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) for government agencies. Google’s commitment to compliance extends to many industries.
Challenges in Security and Compliance
The challenges in security and compliance faced by organizations using Google Workspace, or any similar cloud-based platform, are significant and require ongoing attention and effort to mitigate. Here’s a more detailed description of these challenges:
- User Awareness: Users can be a weak link in the security chain. No matter how secure the platform itself is, human error or lack of awareness can lead to security breaches. Phishing attacks and social engineering often exploit users’ lack of awareness. To address this challenge, organizations need to provide security training and raise awareness among their employees. Regular training sessions, simulated phishing tests, and clear security policies can help users understand best practices and potential risks.
- Data Governance: With the increasing reliance on cloud-based solutions like Google Workspace, maintaining data governance and compliance can become complex. Data governance involves managing data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to deletion. Organizations must create and enforce policies for data classification (categorizing data based on its sensitivity), access controls (who can access what data), and data retention (how long data should be stored). This is crucial to ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Third-Party Apps and Integrations: While Google Workspace itself provides robust security and compliance features, third-party apps and integrations can introduce vulnerabilities. These external applications may not be as secure as the core platform, and they can potentially access or expose sensitive data. To mitigate this challenge, organizations must carefully evaluate the security of any third-party applications they integrate into their environment. Regular monitoring and updates are necessary to ensure the continued security of these integrations.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Data loss can happen for various reasons, including accidental deletion, cyberattacks, or system failures. To maintain data integrity and ensure business continuity, organizations need robust data backup and recovery solutions. This involves creating and implementing regular data backup plans and testing the ability to recover data quickly and effectively in case of a disaster. Having a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy is essential to minimize data loss and downtime.
- Ongoing Compliance Monitoring: Compliance with regulatory obligations is not a one-time effort; it’s an ongoing process. Organizations must continuously monitor their practices and systems to ensure they meet the relevant compliance standards. This includes regular audits, reporting, and adapting to changes in regulations or industry standards. Compliance is a dynamic process, and organizations must be agile in responding to new requirements or emerging threats.
The challenges in security and compliance for organizations using Google Workspace are multifaceted. They require a combination of user education, policy development and enforcement, risk assessment of third-party integrations, robust backup and recovery strategies, and ongoing vigilance in maintaining compliance standards. Addressing these challenges is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the trust of customers, partners, and regulators.
Google Workspace security features
One of the fundamental security features of Google Workspace is encryption. All data is encrypted in transit and at rest. In transit, Google uses industry-standard Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt data as it travels between the user’s device and Google’s servers. This ensures that sensitive information cannot be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties during transmission. At rest, data is encrypted on Google’s servers, meaning that even if someone were to gain physical access to Google’s data centers, they would be unable to decipher the information without the encryption keys.
Google also provides robust access controls. Administrators can set user permissions and access levels, which restrict who can view, edit, and share specific documents or files. This feature ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to individuals with proper authorization. Additionally, Google Workspace supports multi-factor authentication (MFA), which adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before granting access. MFA helps safeguard against unauthorized account access, even if someone obtains a user’s password.
A critical component of security in Google Workspace is user identity management. The platform utilizes a unified identity and access management system to keep track of who has access to what resources. This centralized identity management simplifies user onboarding and offboarding processes, ensuring that access is granted or revoked promptly when personnel changes occur within an organization. Google Workspace also supports single sign-on (SSO), making it easier for users to access various applications without the need to remember multiple passwords. This not only improves user experience but also reduces the risk associated with weak or reused passwords.
Phishing and malware protection are crucial aspects of Google Workspace security. Google’s sophisticated algorithms scan incoming emails and attachments for signs of phishing attacks or malware. If a suspicious email is detected, it is automatically moved to the spam folder or flagged with a warning. This proactive approach helps protect users from falling victim to phishing scams or malware infections that can compromise data security.
Google Workspace also includes advanced threat protection features. It offers data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities that allow administrators to set policies for preventing the sharing or transmission of sensitive data, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers, outside the organization. Google scans content for matches against predefined DLP rules, providing an additional layer of protection against accidental or intentional data leaks.
For businesses subject to regulatory compliance requirements, Google Workspace offers auditing and reporting tools. These tools allow administrators to monitor user activity, track changes to documents, and generate detailed reports. This information can be invaluable for compliance audits and investigations, ensuring that organizations meet legal and industry-specific data protection requirements.
Another aspect of Google Workspace’s security features is mobile device management (MDM). With the increasing use of mobile devices for work, Google Workspace provides the ability to control and secure mobile devices that access company data. Administrators can enforce security policies, remotely wipe data from lost or stolen devices, and ensure that mobile devices adhere to organizational security standards.
Lastly, Google Workspace benefits from Google’s extensive experience in cloud security. Google invests heavily in the security of its cloud infrastructure, including data centers, networks, and hardware. This includes features like automatic updates, strong physical security, and continuous monitoring for security threats.
Google Workspace offers a comprehensive array of security features to protect user data and ensure the privacy and confidentiality of information. From encryption to access controls, identity management to advanced threat protection, auditing, and mobile device management, Google Workspace provides the tools and capabilities necessary to safeguard data in the modern digital workplace. These robust security measures help organizations mitigate risks and meet compliance requirements, making Google Workspace a trusted and reliable solution for businesses of all sizes.
Security Measures in Google Workspace
- Data Encryption:
- Google Workspace employs robust data encryption techniques to ensure the security of your data. This includes both data at rest and data in transit.
- Data at rest is encrypted using industry-standard encryption algorithms. This means that any data stored on Google’s servers is scrambled in a way that makes it unreadable without the proper encryption key.
- Data in transit is secured using protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security). TLS ensures that data being transmitted between your devices and Google’s servers is encrypted, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept and access this data during transmission.
2. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Two-Factor Authentication is a key security feature in Google Workspace. It adds an extra layer of protection to user accounts.
- With 2FA enabled, users are required to provide two forms of authentication to access their accounts. Typically, this involves a password and a verification code sent to their mobile device.
- Even if someone gains access to a user’s password, they would still need the second factor (verification code) to log in, significantly enhancing the security of the account.
3. Identity and Access Management:
- Google Workspace provides administrators with the tools for effective Identity and Access Management.
- This feature allows organizations to control user access based on roles, responsibilities, and permissions.
- Role-based access controls and permissions can be set, ensuring that employees only have access to the data and resources they need for their specific job responsibilities.
- This helps prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive information within the organization.
4. Security Center:
- Google Workspace offers a Security Center that serves as an advanced threat detection and response hub.
- The Security Center provides insights into security threats, suspicious activities, and potential data breaches within your organization.
- Administrators can take immediate actions to mitigate risks and safeguard their data by responding to the information provided by the Security Center.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
- Data Loss Prevention is a critical aspect of security and compliance in Google Workspace.
- The DLP solution within Google Workspace allows administrators to create rules and policies to prevent the unauthorized sharing of sensitive information.
- These rules can be configured to automatically block or warn users when they attempt to share specific types of data, reducing the risk of data leaks and ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
Google Workspace incorporates a comprehensive set of security measures, including data encryption, two-factor authentication, identity and access management, a security center for threat detection and response, and data loss prevention. These measures are designed to protect your organization’s data and ensure that unauthorized access and data breaches are minimized.
Best Practices for Google Workspace Security and Compliance
To overcome the challenges associated with Google Workspace security and compliance, organizations should adopt best practices to fortify their digital environment. Here are some recommendations:
1. User Training and Awareness
Invest in user training and awareness programs to educate employees about the importance of security and compliance. Regularly update them on emerging threats and best practices to stay safe.
2. Data Classification and Access Controls
Implement a robust data classification system that categorizes data based on its sensitivity. Apply access controls to restrict data access to authorized personnel only.
3. Third-Party App Vetting
Before integrating third-party applications, thoroughly vet their security measures and data handling practices. Only use apps from trusted sources.
4. Data Backup and Recovery
Set up automated data backup and recovery solutions to ensure that critical data is regularly backed up and can be restored in case of data loss.
5. Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Implement tools and processes for continuous compliance monitoring. Regularly review and update compliance policies to reflect changing regulations and business needs.
6. Incident Response Plan
Create a comprehensive incident response plan to address security breaches or compliance violations promptly. Test the plan through simulated exercises to ensure preparedness.
7. Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Address any security gaps proactively.
8. Collaboration with Experts
Consider partnering with cybersecurity and compliance experts who can provide guidance, assess your environment, and offer tailored solutions to meet your specific needs.
Google Workspace security training
Google Workspace security training is an essential component of an organization’s efforts to protect its digital assets, sensitive data, and overall cybersecurity posture. With the increasing reliance on cloud-based services, email communication, and collaborative tools, Google Workspace has become a common choice for businesses and institutions. However, this digital ecosystem also presents various security challenges. Security training for Google Workspace equips employees with the knowledge and skills to navigate this environment safely and securely.
One of the primary objectives of Google Workspace security training is to educate users about the potential threats and vulnerabilities they may encounter while using Google’s suite of cloud-based applications. This includes Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, and many other tools that are integrated into the platform. Cyber threats such as phishing attacks, malware distribution, and data breaches are real and growing concerns. Through training, users become more adept at recognizing suspicious emails, links, and file attachments, reducing the risk of falling victim to malicious actors.
Moreover, Google Workspace security training provides an opportunity to introduce users to best practices for password management. Weak or easily guessable passwords are a significant security risk, as they can lead to unauthorized access. Training programs typically emphasize the importance of strong, unique passwords and the benefits of using multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. MFA requires users to provide two or more forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a mobile device, before accessing their Google Workspace accounts.
Data security is another crucial aspect covered in these training programs. Employees need to understand how to handle sensitive information properly. Google Workspace allows for data sharing and collaboration, but it’s crucial to educate users about the importance of setting appropriate access permissions and sharing settings to avoid accidental data exposure. In addition, users should be aware of the encryption mechanisms in place to protect their data during transit and storage within the Google Workspace environment.
Google Workspace security training also addresses the risks associated with third-party applications and extensions. Users should be cautious about granting permissions to external apps and extensions, as they can potentially access their Google Workspace data. Training helps users make informed decisions about which apps to trust and provides guidelines for reviewing and revoking permissions to maintain a secure ecosystem.
To ensure the success of any security training program, it’s important to create engaging and interactive content. Training materials should be regularly updated to reflect the latest threats and security features within Google Workspace. Interactive elements like quizzes and simulations can help reinforce the knowledge gained during training. Moreover, organizations can consider conducting simulated phishing exercises to assess how well employees can identify and respond to phishing attempts.
In addition to the technical aspects of security, training should also address the importance of maintaining a security-conscious culture within the organization. This means fostering a sense of collective responsibility among employees and encouraging them to report security incidents or suspicious activities promptly. Employees should understand that cybersecurity is not solely the responsibility of the IT department; every individual plays a part in maintaining a secure environment.
A vital component of Google Workspace security training is staying updated on emerging threats and security features. Google regularly releases updates and enhancements to its platform, many of which are related to security. Training programs should include information about these updates, educating users on new security tools and features they can leverage to protect their accounts and data.
Google Workspace security training is an ongoing process that should be ingrained into an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. It empowers employees to become the first line of defense against cyber threats and helps create a culture of vigilance and awareness. By investing in comprehensive training programs, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, improve overall cybersecurity, and protect their digital assets in the Google Workspace environment.
Conclusion
In the digital age, the security and compliance of cloud-based tools like Google Workspace are paramount to the success and trust of any organization. Google Workspace offers a robust set of security and compliance features, including data encryption, access controls, and tools to meet industry-specific regulations. However, organizations must address common challenges, including user awareness, data governance, and the risks associated with third-party apps.
By following best practices such as user training, data classification, and ongoing compliance monitoring, organizations can maximize the benefits of Google Workspace while maintaining a secure and compliant environment. With the right approach and commitment to security and compliance, businesses can harness the full potential of Google Workspace in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
Google Workspace complies with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA and provides data ownership and control features to the organization.
Yes, you can control user access through administrative controls, role-based permissions, and sharing settings.
DLP in Google Workspace helps prevent the accidental sharing of sensitive data by identifying and blocking potential breaches.
Yes, Google Workspace offers mobile device management (MDM) features to secure and manage mobile devices accessing company data.
Google Workspace uses advanced phishing detection algorithms and AI to identify and block phishing attempts.
Google Drive data is redundantly stored, and Google provides tools for data recovery and backup.
Yes, Google Workspace provides audit logs and reporting capabilities to track user activities.
Google Workspace complies with various standards, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and more.
Google Vault, a part of Google Workspace, allows for eDiscovery and legal holds to manage and retain data for legal purposes.
Yes, Google Workspace offers APIs and integrations to connect with third-party security tools and services.
Zero Trust is a security model that Google Workspace supports, ensuring continuous verification and least privilege access.
Yes, Google Workspace can be configured to meet the requirements of HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
Google Workspace offers tools to de-provision users, ensuring data security during employee offboarding.
Yes, Google Workspace uses encryption to protect data both during transmission (SSL/TLS) and at rest.
Google Meet includes encryption, access controls, and anti-abuse mechanisms to ensure secure video conferences.
Yes, Google Workspace can be used in regulated industries and can be configured to meet specific compliance requirements.
- Digital Marketing Services
- Brand Consultancy
- Website Design Services
- Web Hosting & Domain Registration in India
- Dynamic Website Development
- Website Redesign Service
- Website Maintenance Service
- AMC & IT Support
- Ecommerce Website Design Services
- SSL Certificate (HTTPS)
- Content Writing
- Complete Email Service
- G Suite Services
- Microsoft Office 365 Email Services
- Zoho Email Services
- ERP Bangalore
- Custom Web Application Development
- Mobile App Development and Services
- Android Application Development
- iOS Application Development
- Windows Application Development