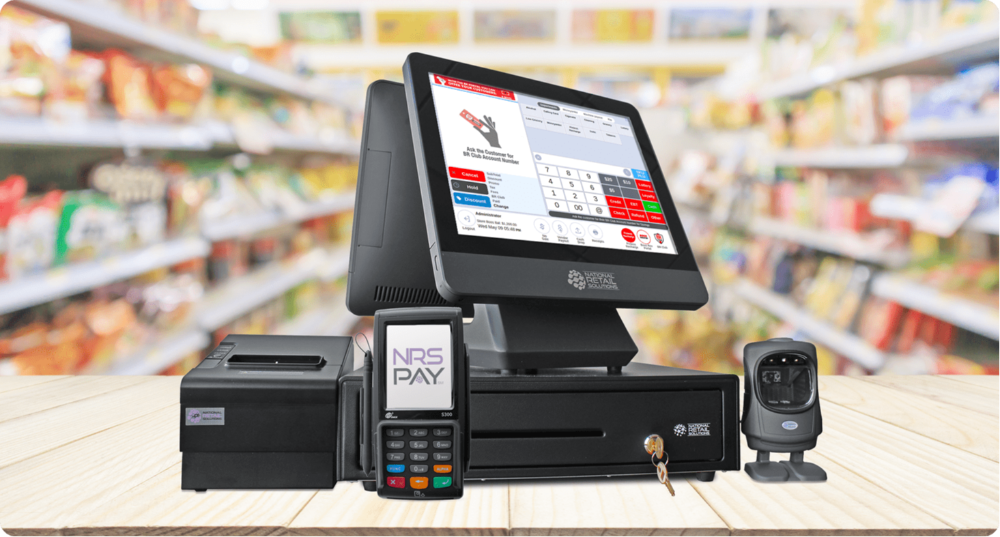
The Retail POS and Stock Software is a robust and all-encompassing solution that was developed with the purpose of streamlining the processes of retail organisations. It combines the capabilities of an advanced stock and inventory management system with those of a point of sale (POS) system. Retailers will have an easier time managing sales transactions, keeping track of inventory levels, monitoring stock movement, and generating reports to assist them in making decisions based on data when they use this program.
In addition to this, the system delivers real-time insights about customer behaviour, which enables companies to better cater their products and services to match the requirements of their clientele. By automating repetitive procedures and offering a centralised system to manage all elements of their business, retail POS and stock software assist merchants in optimising their operations, lowering their costs, and increasing their profitability. These goals can be accomplished with the software.
Features of Retail POS and Stock Software:
- Purchase- Putting together a buy order for the goods that a retailer intends to order from their respective vendors is the initial step in the process of making a purchase. This buy order provides specifics like the product’s name, quantity, price, information about the supplier, and the date it will be delivered. A database of suppliers is also maintained by the program, which enables the store to better manage its relationships with its suppliers, track delivery schedules, and negotiates better rates.
- Sale- A retail POS and stock software application’s sales process begins with the cashier adding the products that the customer wishes to purchase to the cart by scanning the barcode or manually entering the product details. This may be done in either case, depending on the application. The total amount that must be paid is then determined by the program based on the cost of the products as well as any taxes or reductions that are relevant.
- Customer Due Tracking- It is crucial to keep track of your consumers in order to promote your goods or services to them in a manner that is more effective. Customer tracking is a strategy that gives owners of businesses the ability to learn a great deal about their clients, including who they are, where they reside, what their buying patterns are, and a great deal more.
- Supplier Due Tracking- The practice of performing assessments of potential suppliers as part of the supplier due diligence process ensures that such suppliers comply with all applicable laws and regulations, that they meet accepted business standards, and that they are able to deliver the products and services that they have promised.
- Inventory- Inventory is a broad term that encompasses all of the commodities, goods, merchandise, and materials that are held by a company with the intention of selling them in the market in order to make a profit.
- Expense- In terms of accounting, an expense is an operational cost that is incurred in order to generate revenues for a company. It refers to the transfer of cash in exchange for the acquisition of products or services. Expenses can alternatively be written as the sum of all operations that typically bring in a profit. This is another way of expressing expenses.
- Multiple Register Support- Although there is only one service worker for each PWA, this does not always indicate that the code must be placed in just a single file.
- Daily Summary- The Daily Summary report provides an overview of the raw data values for a specific day. It is important to compile daily summaries of statistics for any data that has been gathered for a period of time that is shorter than 24 hours.
- Hold Sale- When a customer is being rung up, and the process is halted before it is finished, this is known as a sale hold. A cashier has the ability to resume the pending sale at a later time.
- User Access Control- Users are recognised by access control systems after having their various login credentials validated. These credentials can include usernames and passwords, personal identification numbers (PINs), biometric scans, and security tokens. Multifactor authentication (MFA) is a mechanism that requires multiple authentication methods to validate the identity of a user. Many access control systems feature MFA as an additional authentication method.