Introduction
Cloud storage has become an integral component of modern computing infrastructure, revolutionizing the way data is stored, accessed, and managed. One prominent player in the realm of cloud storage solutions is Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Cloud Storage. This service offers a robust and flexible platform for storing and retrieving data in the cloud, catering to the evolving needs of businesses and individuals in the digital age.
Definition and Overview
GCP Cloud Storage can be defined as a scalable and secure object storage service provided by Google Cloud Platform. It allows users to store and retrieve data through Google’s infrastructure, offering a reliable and cost-effective solution for managing vast amounts of information in a cloud environment. In essence, GCP Cloud Storage serves as a virtual repository that enables users to store and access their data seamlessly, without the constraints of physical hardware.
In the broader context of cloud computing, GCP Cloud Storage holds significant importance. It aligns with the core principles of cloud computing, offering on-demand storage resources, flexibility, and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, the role of robust and efficient cloud storage solutions like GCP Cloud Storage becomes pivotal in ensuring the integrity, availability, and scalability of data.
The significance of GCP Cloud Storage extends beyond mere data storage; it plays a crucial role in supporting diverse applications, from simple document storage to complex data analytics and machine learning processes. As organizations grapple with ever-growing datasets and the need for real-time access to information, GCP Cloud Storage emerges as a reliable solution to meet these demands.
Key Features
GCP Cloud Storage boasts several key features that set it apart in the competitive landscape of cloud storage solutions. One of its primary strengths lies in scalability, allowing users to effortlessly scale their storage resources up or down based on their evolving requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable as businesses experience fluctuations in data volume, ensuring they only pay for the storage they actually use.
Durability is another critical feature of GCP Cloud Storage. The service is designed to provide high durability by replicating data across multiple locations, thereby minimizing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or unforeseen events. This ensures that stored data remains highly available and resilient, meeting the reliability expectations of users and businesses.
Global accessibility is a key aspect that caters to the modern, geographically dispersed nature of businesses. GCP Cloud Storage allows users to access their data from anywhere in the world, promoting collaboration and data-driven decision-making on a global scale. This feature is particularly beneficial for enterprises with distributed teams or customers spanning different regions.
GCP Cloud Storage stands out as a powerful and versatile solution in the cloud storage landscape, addressing the evolving needs of businesses by providing scalable, durable, and globally accessible storage resources.
GCP Cloud Storage Architecture
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Cloud Storage provides a scalable and durable object storage solution. It is designed to handle massive amounts of unstructured data and offers various features to optimize performance, accessibility, and cost. One key aspect of GCP Cloud Storage architecture is its storage classes, which allow users to tailor their storage solutions to specific needs.
Storage Classes
GCP Cloud Storage offers different storage classes to cater to diverse requirements. The three main classes are:
- Standard Storage: This class is suitable for frequently accessed data. It provides low-latency and high-throughput access and is ideal for scenarios where data is regularly read or modified.
- Nearline Storage: Nearline is designed for data that is accessed less frequently but needs to be quickly retrievable when necessary. It strikes a balance between access time and cost, making it suitable for backup and archival use cases.
- Coldline Storage: Coldline is the most cost-effective storage class, intended for data that is rarely accessed but requires long-term retention. It is suitable for compliance or regulatory data that needs to be stored for an extended period.
Choosing the appropriate storage class depends on factors such as access frequency, performance requirements, and budget considerations.
Buckets and Objects
In GCP Cloud Storage, data is organized into containers called buckets. Buckets are like top-level folders, providing a way to group and manage related data. Each bucket has a globally unique name, and users can control access permissions at the bucket level.
Within these buckets, data is stored as objects. Objects are the fundamental units of storage, representing files and their metadata. Objects can range from small text files to large multimedia files. GCP Cloud Storage allows users to set fine-grained access controls at the object level, ensuring secure data management.
Data Lifecycle Management
GCP Cloud Storage facilitates efficient data lifecycle management through features like object versioning, access controls, and automated policies. Data lifecycle management involves defining how data evolves from creation to deletion, including storage class transitions and deletion policies.
- Storage Class Transitions: Users can set up rules to automatically transition data between storage classes based on its lifecycle. For example, data initially stored in the Standard class may be transitioned to Nearline or Coldline as it becomes less frequently accessed, optimizing costs over time.
- Automatic Deletion Policies: Defining policies for automatic deletion helps manage data retention efficiently. This is crucial for compliance and cost optimization, ensuring that data is deleted when it’s no longer needed or required by regulations.
GCP Cloud Storage offers a robust architecture with diverse storage classes, efficient organization through buckets and objects, and powerful data lifecycle management features. Understanding and leveraging these components enable users to build scalable, cost-effective, and reliable storage solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Security and Compliance in GCP Cloud Storage
Encryption:
In GCP Cloud Storage, encryption plays a pivotal role in safeguarding data integrity and confidentiality. The platform offers robust encryption options to ensure data security both at rest and in transit. Server-side encryption involves the encryption of data before it is written to disk, with GCP managing the encryption keys. On the other hand, client-side encryption allows users to manage their encryption keys, providing an additional layer of control and security. This dual approach ensures that even in the event of a security breach, sensitive data remains protected.
Access Control:
Access control is a critical aspect of securing data in GCP Cloud Storage. The platform employs Identity and Access Management (IAM) to manage access permissions effectively. IAM roles and permissions are used to control who can access, modify, or delete data within the storage environment. The principle of least privilege is emphasized, ensuring that users are granted only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks. This practice helps minimize the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Compliance:
GCP Cloud Storage prioritizes compliance with industry standards and regulations, aligning with the evolving landscape of data protection and privacy. The platform adheres to various certifications and attestations, demonstrating its commitment to meeting rigorous security standards. This includes compliance with standards such as ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA, showcasing GCP Cloud Storage’s ability to handle data securely across diverse industries. These certifications provide assurance to users that their data is stored and managed in a manner that complies with industry-specific regulatory requirements, reinforcing the platform’s commitment to robust data protection practices.
Integration with Other GCP Services
GCP Cloud Storage plays a pivotal role in facilitating seamless integration with various Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services, enhancing the overall efficiency and functionality of cloud-based solutions. One significant integration lies in its collaboration with BigQuery for data analytics. BigQuery, Google’s fully managed, serverless data warehouse, can directly query data stored in Cloud Storage. This integration streamlines the data analysis process, allowing businesses to derive valuable insights from their stored data. By connecting Cloud Storage and BigQuery, organizations can harness the power of scalable analytics, performing complex queries on vast datasets without the need for extensive infrastructure management.
BigQuery and Data Analysis
The integration between GCP Cloud Storage and BigQuery opens up a realm of possibilities for data analysis. Businesses can leverage the advantages of storing their data in Cloud Storage by seamlessly querying and analyzing it with the powerful capabilities of BigQuery. This integration promotes agility and scalability in data analytics, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time insights. The ability to perform advanced analytics on large datasets stored in Cloud Storage enhances the value of accumulated data, transforming it into a strategic asset for decision-makers.
Machine Learning with Cloud Storage
GCP Cloud Storage’s integration with machine learning services establishes a robust foundation for organizations aiming to implement machine learning models. By storing datasets in Cloud Storage, businesses can easily access and utilize this data for training machine learning algorithms. This integration simplifies the machine learning workflow, as training data stored in Cloud Storage becomes readily available for model development. The benefits extend to improved model accuracy and efficiency, as machine learning algorithms can leverage the vast and diverse datasets stored in GCP Cloud Storage for more comprehensive training.
Discussing the Benefits of Using Stored Data for Training Machine Learning Models
The benefits of using GCP Cloud Storage for training machine learning models are manifold. Firstly, the centralized storage of diverse datasets facilitates better model training by providing a comprehensive view of the data landscape. This, in turn, enhances the model’s ability to generalize and make accurate predictions. Additionally, the scalability of Cloud Storage ensures that machine learning processes can handle increasingly large datasets without compromising performance. As a result, organizations can achieve more accurate and sophisticated machine learning models, driving innovation and competitive advantage.
Cloud Storage and Compute Engine
The synergy between GCP Cloud Storage and Compute Engine is a cornerstone in the cloud computing landscape. Compute Engine, Google’s Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offering, seamlessly integrates with Cloud Storage to provide a powerful computational platform. Storing data in Cloud Storage enhances computational processes by ensuring that the data is readily available for analysis and computation. This collaboration is particularly beneficial in scenarios where extensive computational power is required, such as data processing, transformation, or running complex algorithms. The flexibility and scalability of GCP Cloud Storage contribute significantly to optimizing computational processes, allowing organizations to achieve more efficient and cost-effective solutions.
Industry Use Cases of GCP Cloud Storage:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Cloud Storage has emerged as a pivotal tool across diverse industries, offering scalable and reliable storage solutions. In the healthcare sector, GCP Cloud Storage is instrumental in managing vast amounts of patient data, facilitating seamless collaboration among medical professionals, and enabling advanced analytics for research. For instance, medical imaging files, such as MRIs and CT scans, can be stored securely in the cloud, allowing healthcare providers to access and analyze them swiftly, leading to quicker diagnoses and improved patient care.
In the finance industry, where data security and compliance are paramount, GCP Cloud Storage provides a robust solution for storing and managing sensitive financial information. Banking institutions leverage the platform for archival purposes, ensuring compliance with data retention policies. Additionally, the scalability of GCP Cloud Storage proves advantageous during peak transaction times, allowing financial organizations to dynamically adjust storage capacity based on demand, thereby optimizing costs and enhancing performance.
E-commerce is another sector where GCP Cloud Storage plays a pivotal role. Online retailers deal with a massive volume of product images, videos, and customer data. GCP Cloud Storage provides a reliable and scalable solution for storing and serving these media assets. This not only enhances the overall user experience by ensuring fast and efficient content delivery but also allows for the seamless expansion of storage resources to accommodate the ever-growing data generated by e-commerce platforms.
Best Practices for Optimizing Performance and Cost in GCP Cloud Storage:
1. Data Organization:
Efficient data organization is crucial for optimizing performance in GCP Cloud Storage. Implementing a logical and well-structured hierarchy for bucket and object naming helps improve data accessibility and reduces latency. Utilizing appropriate prefixes, metadata, and object lifecycle policies ensures that data is organized in a manner that aligns with the specific needs of the business.
2. Access Control:
Robust access control mechanisms are vital for safeguarding data stored in GCP Cloud Storage. Implementing the principle of least privilege ensures that users have only the minimum levels of access required to perform their tasks. Utilizing Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and policies allows organizations to define and manage permissions effectively. Regular audits of access controls help identify and rectify any potential security loopholes.
3. Security:
Ensuring the security of stored data is a top priority. GCP Cloud Storage provides encryption at rest and in transit, offering a comprehensive security solution. Best practices include enabling bucket-level and object-level access controls, implementing versioning to track changes, and regularly reviewing and updating security configurations. Additionally, utilizing tools such as Cloud Audit Logs and Cloud Monitoring enhances the ability to monitor and respond to security incidents promptly.
4. Performance Optimization:
To optimize performance in GCP Cloud Storage, consider utilizing features such as regional and multi-regional storage classes based on the access patterns of your data. Implementing cache control headers for frequently accessed objects and leveraging Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) can significantly reduce latency and enhance the overall user experience. Regularly monitoring storage usage and performance metrics allows for proactive identification and resolution of potential bottlenecks.
5. Cost Optimization:
Cost optimization is a critical aspect of managing GCP Cloud Storage resources effectively. Implementing lifecycle policies to transition data to cheaper storage classes as it ages can result in substantial cost savings. Regularly reviewing and right-sizing storage resources based on actual usage patterns helps prevent over-provisioning and unnecessary costs. Additionally, taking advantage of features such as Nearline and Coldline storage classes for infrequently accessed data can further optimize storage costs.
GCP Cloud Storage offers a versatile and scalable solution for diverse industries, providing a foundation for secure and efficient data management. By implementing best practices in data organization, access control, security, performance optimization, and cost management, organizations can harness the full potential of GCP Cloud Storage to meet their specific industry requirements and achieve operational excellence.
Best Practices for GCP Cloud Storage
Performance Optimization
Performance optimization is a critical aspect of managing data in GCP Cloud Storage. To enhance performance, it is essential to adopt best practices that take advantage of the platform’s distributed infrastructure. Considerations such as data layout, parallelism, and caching play pivotal roles in achieving optimal speed and efficiency. By strategically organizing data and leveraging parallel processing capabilities, users can unlock the full potential of GCP Cloud Storage’s architecture. This section provides insights into these best practices, empowering users to make informed decisions that positively impact the performance of their storage solutions.
Cost Management
Effectively managing costs is a key concern when utilizing GCP Cloud Storage. This section delves into strategies for cost management, guiding users on selecting the most appropriate storage class based on their specific needs. Additionally, it explores the implementation of lifecycle policies to automate data management tasks and optimize costs over time. Monitoring usage is another crucial aspect covered, allowing users to gain insights into their storage consumption patterns. The goal is to strike a balance between cost-effectiveness and ensuring that performance and reliability are not compromised, enabling users to make financially prudent decisions in their storage solutions.
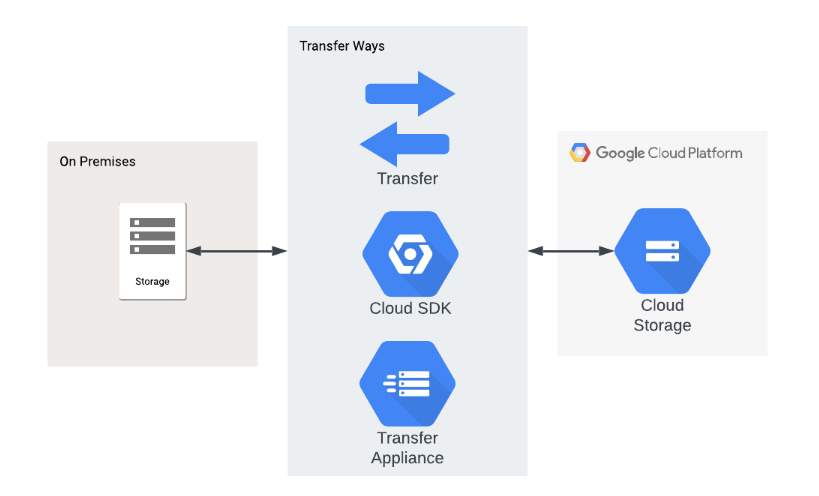
Data Migration and Transfer
This section focuses on the tools and techniques available for seamless data migration to and from GCP Cloud Storage. Understanding the nuances of data transfer, including speed, security, and minimizing downtime, is essential for successful migration processes. Users will gain insights into choosing the most suitable migration methods, ensuring a smooth transition of data while maintaining the integrity and security of the information. By addressing considerations related to data transfer, this section equips users with the knowledge needed to execute efficient and secure migration processes, facilitating the seamless integration of data into GCP Cloud Storage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GCP Cloud Storage stands out as a versatile and powerful solution for storing and managing data in the cloud. From its robust storage classes to advanced features and seamless integrations, GCP Cloud Storage offers a comprehensive suite for enterprises seeking scalable, reliable, and cost-effective storage solutions. By understanding its features, best practices, and real-world use cases, businesses can harness the full potential of GCP Cloud Storage to drive innovation and success in the digital era.