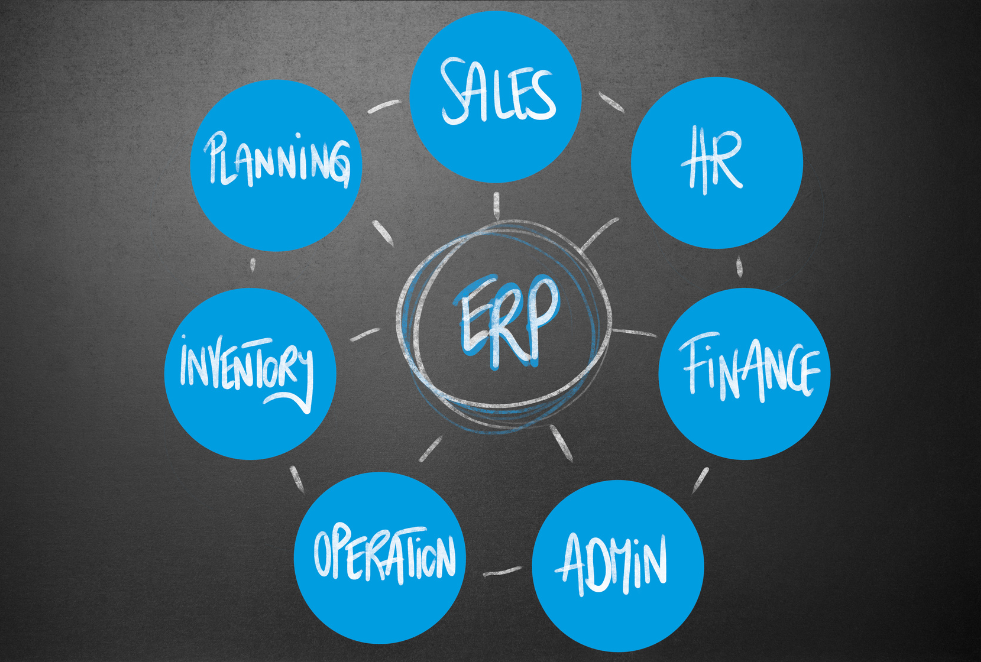
What is ERP
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a type of software used by businesses to handle day-to-day operations like compliance, project manager and supply chain operations. Enterprise performance management software, which helps plan, budget, forecast, and report on an organization’s financial results, is included in a complete ERP suite.
It is possible to easily exchange data across ERP systems, which connect diverse business processes. Common transactional data from a wide range of sources may be gathered by ERP systems, minimizing the need for redundant information and ensuring the integrity of data. ERP systems are currently required for the administration of tens of thousands of businesses of all sizes and in a variety of sectors. ERP is as necessary as power to these businesses. ERP systems will offer transparency to the whole company process by recording all aspects of production, shipping, and financials. As a company’s central center for point process and data, these integrated solutions are accessible to a wide variety of departments.
ERP software systems support a variety of functions in large, mid-sized, and small enterprises, as well as industry-specific adaptations. ERP software that is personalized to a company’s specific needs pays off handsomely, giving these systems a vital tool for businesses of all sizes and industries. ERP has been used by many of the world’s most well-known and successful companies over the last 25 years. This software may now be tailored and priced to meet the needs of businesses of any size.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) took a long time to develop, starting in the 1960s when manufacturers intended to use computer programmed to improve inventories management and control systems. In the 1970s, systems for scheduling manufacturing processes such as Material Requirements Planning (MRP) or Manufacturing Execution Systems (MRP-II) started to arise. Accounting and human capital systems were added to these systems in the 1990s. As a result, Gartner coined the term ERP to represent these new services in the beginning of the 1990s.
BI, SFA, e-commerce, and automated marketing may now all be found in ERP in addition to the previously mentioned elements. It doesn’t matter how large or little your company is; you can always get a used automobile.
What are the functions of ERP software?
An ERP system, sometimes known as an ERP suite, is a collection of interconnected modules or business applications that share a database. Each ERP module focuses on a different business sector, yet they all work together to satisfy the company’s needs through sharing data. Finance, accounting, human resources, sales, and chain are all popular entry points. Companies may pick and choose the modules they want, grow and add on as required.
Industry-specific requirements are also supported by ERP systems, either as part of the basic functionality or via application extensions that interact smoothly with the suite.
Accounting Administration
Accounting was the primary focus of the initial ERP programmes. Even as the number of choices and functionalities has risen, money management will always be a vital aspect of your erp systems. A good ERP system will let you connect your old and new accounting software, so you can keep an eye on and track your company’s numbers in real time and over time. It also arranges data in such a way that you may go deeper into it. You should look at the analytics that any system you’re thinking about has to offer to make sure you can use it to get the information you need.
Integration of ERP
Despite the fact that today’s ERP systems provide a broad variety of business operations, they still need integration and synchronisation with other applications and data sources.Companies can receive a single view of information from several systems, improve business process efficiency, customer experiences, and facilitate collaboration between teams and business partners with ERP integration.
Modern ERP systems are open, so they can easily connect to a wide range of software products through connectors or custom adaptors, such as application programming interfaces.

Management of Human Resources
The most successful CEOs and businesspersons recognise that a successful organisation functions for reasons other than accounting spreadsheets. By using your company’s data, today’s ERP software helps you to effectively manage your employees. Payroll can be processed, time can be logged, performance and efficiency can be assessed, and a variety of data can be analysed to help you find your best employees, reward achievement, and identify possible HR concerns.You may also evaluate the value of make some decisions and performance reviews by looking at changes in performance.
Management of Customer Relationships
Finally, corporate resource planning software aids in the analysis of client interactions. You’ll be able to place orders faster and keep track of how quickly they are filled. You may keep track of how much each client spends over time to assist your salespeople determine where they should focus their efforts.
Good customer relationships are essential for success, therefore leveraging your ERP system to measure and cultivate such ties gives you a significant competitive advantage.


Management of Orders
Tracking orders from receipt through delivery is the primary function of an order management system. There are several warehouses, distribution centers, and retail outlets where orders may be transferred from clients to be processed and completed before being sent back to the consumer.The order management solution prevents orders from going missing and increases on-time delivery rates, keeping customers satisfied and reducing expedited shipping costs.
Management of Supply Chain
From sub-suppliers to raw material suppliers to distributors to retailers or consumers, a supply chain management module maintains track of every stage in the distribution chain. It may also handle returned goods or materials that have been returned for a refund or replacement.


Service Automation for Professionals (Service Resource Management)
An organisation can plan and manage projects with a business services automation (PSA) modules, often known as a service resource management program. Service businesses use this module all the time. Managers can use the programme to approve expenses and timesheets. It also monitors project progress and manages both human and financial resources. It makes it simpler for teams to collaborate by centralising all important documents.
Management of the Workforce
A workforce management module is similar to a human resource management module, except it is geared for companies with more hourly workers than salaried workers. It may track employees’ hours and attendance, as well as their productivity and how often they call in sick.

Types of ERP

ERP for generalists
Many legacy and cloud ERP systems are specialists. They learn how things work in many different fields. These systems can be changed and put together in different ways to meet the needs of many different industries. It’s also not surprising, given that generalist ERP suppliers are among the largest in the market.

ERP that is vertical
These ERPs are industry-specific. Vertical ERP suppliers are typically startups or small firms that want to specialise in a specific area, such as construction, grocery delivery, or retail fashion. One of the most well-known instances of this platform is Microsoft Dynamics AX.
ERP for small businesses
There are off-the-shelf cloud ERP solutions and on-premise ERP solutions. The ERP is often broken up into parts, which means it has fewer functions. Instead of giving a fully integrated system, small business ERPs like PeopleSoft focus on one or two business processes and leave out the rest.
Open-source ERP
Anybody may utilise open source ERP software. Open-source ERP systems account for a modest percentage of the overall ERP market. On the other hand, companies with their own IT teams can use tools like Odoo ERP to build and connect their apps to the ERP.
Basic ERP System Modules
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning System, and it is a system or software that is used to manage all of a company’s resources. Everything, from employee salaries to a small screw entering the organization, can be managed and monitored using ERP Systems. ERP stands for enterprise resource planning, and it is a software program that supports all of an organization’s business processes.
ERP is a centralized tool that aids in the seamless running of enterprises across all departments and operations. ” ERP provides us with all of the data we need to make all of the critical choices that need to be made.

Module for Inventory
With an inventory module, you can also keep track of what’s in stock. A serial number can be used to find an item. The inventory system can keep track of items and find out where they are in the organisation right now by using their unique numbers.
If you purchased 100 hard discs, for example, you might use the inventory system to keep track of how many are where. how many are left, and so forth.
Module on Human Resources (HR)
The Human Resource module aids the HR staff in efficiently managing human resources. Employee data such as performance assessments, designations, job titles, skill matrices, and time and attendance monitoring are all recorded in the HR module. Payroll System is a key submodule of the HR module that helps with salary management, payment reports, and so on. It can also keep track of travel costs and payments. ERP can also keep track of how employees are being trained.


Module for Business Development
Sales questions and inquiries are analysed and handled, quotations are written, sales orders are accepted, sales invoices are written with proper taxation, material or service is dispatched or shipped, and pending sales orders are tracked. All of these transactions are taken care of by the ERP’s sales module. The CRM module can work with the Sales module to find new business opportunities and leads.
Module of Purchase
Purchase modules, as the name implies, handle all aspects of the organization’s procurement of commodities or raw materials. The purchase module has features like listing suppliers and vendors, linking suppliers and products, sending quotation requests to vendors, receiving and recording quotations, analyzing quotations, making purchase requisitions, keeping track of items bought, making Good Receipt Notes, and running different reports. The Inventory module and the Engineering/Production module are linked to the Purchase module so that stock levels can be kept up to date.


Module for Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
By providing better customer service and developing a healthy relations with clients, the CRM department is assisting in improving sales performance. The CRM module has access to all of the customer’s information.
CRM module assists in managing and tracking detailed customer information such as contact history, calls, conferences, details of client purchases, contract term, and so on. To improve sales opportunities, the CRM module can be linked to the Sales module.
Module on Finance and Accountancy
The finance module oversees the whole inflow and outflow of money/capital. This module records all account-related transactions such as expenses, balance sheets, account account balances, planning, bank statements, pay stubs, tax management, and so on. This ERP module makes financial reporting a simple task. With a single click on the Finance module, you may access any financial data needed to run your firm.


Modules for Engineering and Manufacturing
The manufacturing business benefits greatly from the production module when it comes to product delivery. Planning process, machine planning, raw material utilization, (Bill of Material) preparation, daily production progress tracking, production forecasting, and actual production reporting are all features of this module.
Advantages of ERP
Improved Business Reporting
More real-time reporting tools. One database for all business processes. a single source of truth
Improved Inventory Costs
Carry only as much inventory as is required to prevent these concerns. Inventory overstocking and greater overhead expenses Longer client fulfilment periods due to a lack of inventory.
Better customer service
More information about customers. Response times that are shorter. Timely delivery has improved. Order precision has improved.
Cost savings
When you plan your inventory better, you save money. Getting things done has become easier. Service to customers got better The way that vendor relationships are managed has gotten better.
Improvements to Business Processes
Automate repetitive or laborious chores. Implement more intelligent workflows. Boost your productivity
Better Data & Cloud Security
Dedicated security resources for better data and cloud security. Installing harmful software should be avoided. Data is distributed across multiple servers.
Disadvantages of ERP
ERP Software Costs
Third-party software add-ons Costs of implementation Maintenance. Initial and ongoing education.
Training
To get the most out of ERP software, you need to be trained on how to use it. The training should be based on how the business works and cover all of the ERP system’s features. IT workers should also be in charge of the system’s technological parts.
Customization
A system must be fine-tuned to a company’s needs to properly reap ERP benefits. Whether it’s a ready-to-use system or a custom-built solution, tailoring it to your company’s goals and procedures is important to its success.
Data Conversion
It can be hard to come up with a good plan for converting data. Data sources need to be defined, checked, and analysed. If you don’t convert data well, it will take longer and cost more
Requires extensive training
During training, each of the ERP system’s functions must be covered in depth. During ERP training, business processes must be kept in mind. IT users need to be taught how to use the technical parts of the ERP System.
Why is ERP so important for your company?
Even though there isn’t one software solution that works for all corporate functions, ERP technology is getting better at linking processes together. Once your processes, technologies, and data are all connected, you’ll have the intelligence, speed, and flexibility you need to start improving how your business works.
Here are 3 ways ERP can help your company:
- Assist in achieving peak performance.
AI solutions give you access to information that helps you make better decisions and find ways to improve operational performance in the future.
- Speed up how quickly your operational decisions are felt.
By combining information and processes, you may be able to give employees more visibility and freedom, letting them act faster and create more value for the whole organisation.
- Ensure that your company is flexible.
Many ERP solutions are made to change with your business and adapt to your needs. This lets you plan ahead for any operational problems or changes in the market and react quickly.

List of the top five ERP software’s
ERP software is a collection of Enterprise Resource Management solutions. With the assistance of an integrated software system, the process entails the collection and organization of corporate data.

DEAR Systems
It is a company that develops and sells. It’s a cloud-based ERP system aimed for small to mid-sized retailers, manufacturers, distributors, and e-commerce businesses. Dear Systems is a comprehensive system that includes modules such as purchasing, e-commerce, production, accounting, inventory control, and sales, among others. Businesses can use DEAR inventories to develop, plan, and track every stage of the purchase process using this solution.
In addition, the solutions encourage all of their customers to reorder product before it runs out. With reports for outstanding purchase orders and buy cost analysis, businesses can keep track of all purchase orders.
SAP
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Information Processing) provides firms with strong tools to help them organise their logistics, human resources, finances, and other business functions. SAP is a company in Europe that is based in Waldorf. It makes business software to help businesses make their management tasks easier. SAP was started 40 years ago in the world.
SAP’s ERP software has a number of baseline capabilities, as well as optional modules for enhanced functionality, numerous integrations, and additional industry-specific add-ons. Clients can use SAP’s ERP software to manage overall inventory, make supplier orders, monitor security, manage warehouses, and ship, among other things. All of these things will aid in the efficiency and organisation of your company.


Microsoft Dynamics AX
It is a business management software.
Microsoft, a global leader in computer software and technology, was founded in 1975 in New Mexico and now offers a variety of Windows PC and offline services to businesses and people throughout the world. MS Dynamics develops CRM and other software solutions for corporate activities such as ERP, finance, and supply chain management, as well as for sales and marketing.
Microsoft is building a number of data centres to serve the Dynamics 365 suite’s cloud capabilities. Microsoft Dynamics AX provides all of your company’s operational and administrative responsibilities, as well as a variety of management solutions for various divisions.
Netsuite
Netsuite was founded in 2007 with the goal of providing clients with solutions that combined relationships with customers, tion, ERP, and inventory control into a single platform. It’s about the ERP software industry’s contributor to software-as-a-service. Netsuite ERP adds to the typical accounting software’s capability.

FAQs
An ERP is a business application that uses a central database to gather information from different parts of a company. Accounting, keeping track of inventory, and keeping in touch with customers are all linked in the ERP.
ERP implementation approach varies significantly, with numerous options for rollout manner and employees involved.
The majority of providers offer some kind of training solution to help end users learn how to utilise the ERP. Oracle University, for example, offers a complete training and certification programme that breaks down parts and capabilities of Oracle’s ERP into discrete courses.
From start to completion, the implementation life cycle defines the stages of ERP implementation. It’s vital to remember, however, that the ERP life cycle encourages continuous improvement through fine-tuning technology to better serve business processes that support specified goals.
From start to completion, the implementation life cycle defines the stages of ERP implementation. It’s crucial to note.
LIST OF ECOMMERCE WEBSITE DESIGN MENUS














